|
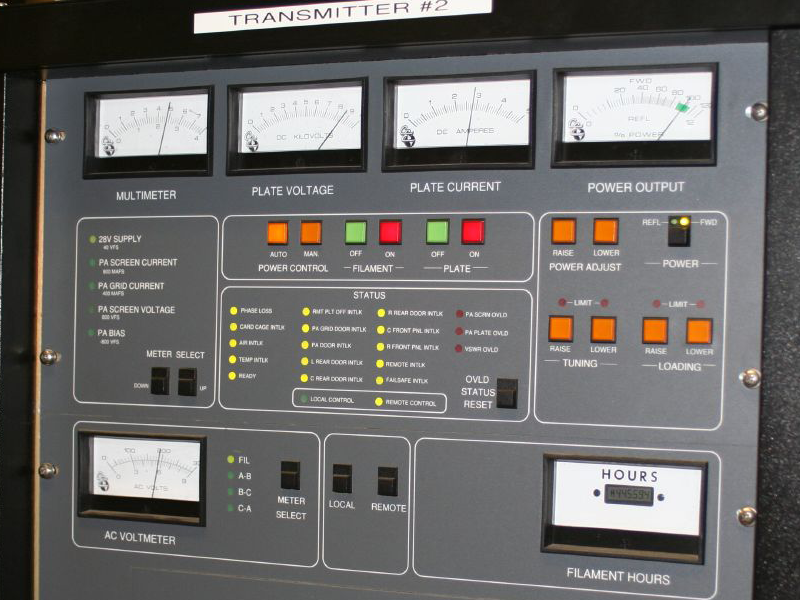
Transmitters
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio, such as radio (audio) and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves for communication purposes; or radiolocation, such as radar and navigational transmitters. Generators of radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcast Transmitter
A broadcast transmitter is an electronic device that radiates radio waves modulated with information content intended to be received by the general public. Examples are a transmitter, radio broadcasting transmitter which transmits Sound, audio (sound) to radio receiver#broadcast radio receiver, broadcast radio receivers (radios) owned by the public, or a television transmitter, which transmits moving images (video) to television receivers (televisions). The term often includes the Antenna (radio), antenna which radiates the radio waves, and the building and facilities associated with the transmitter. A broadcasting station (radio station or television station) consists of a broadcast transmitter along with the production studio which originates the broadcasts. Broadcast transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to specific frequencies and power levels. Each transmitter is assigned a unique identifier consisting of a string of letters and numbers called a call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Communication
Radio is the technology of telecommunication, communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna (radio), antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, radio control, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by Modulation, modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television Transmitter
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial television, terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio signal, audio channel, which is received by television receivers ('televisions' or 'TVs') belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the Television studio, broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency television channel frequencies, channels in the very high frequency, VHF and ultrahigh frequency, UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line-of-sight propagation, line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent Session (computer science), communication sessions. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the electrical telegraph, telegraph, telephone, television, and radio. Early telecommunication networks used metal wires as the medium for transmitting signals. These networks were used for telegraphy and telephony for many decades. In the first decade of the 20th century, a revolution in wireless communication began with breakthroughs including those made in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Broadcasting
Radio broadcasting is the broadcasting of audio signal, audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio station, while in ''satellite radio'' the radio waves are broadcast by a satellite in Earth orbit. To receive the content the listener must have a Radio receiver, broadcast radio receiver (''radio''). Stations are often affiliated with a radio network that provides content in a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast, or both. The code, encoding of a radio broadcast depends on whether it uses an analog signal, analog or digital signal. Analog radio broadcasts use one of two types of radio wave modulation: amplitude modulation for AM radio, or frequency modulation for FM radio. Newer, digital radio stations transmit in several different digital audio standards, such as DAB (Digital Audio Broadcas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
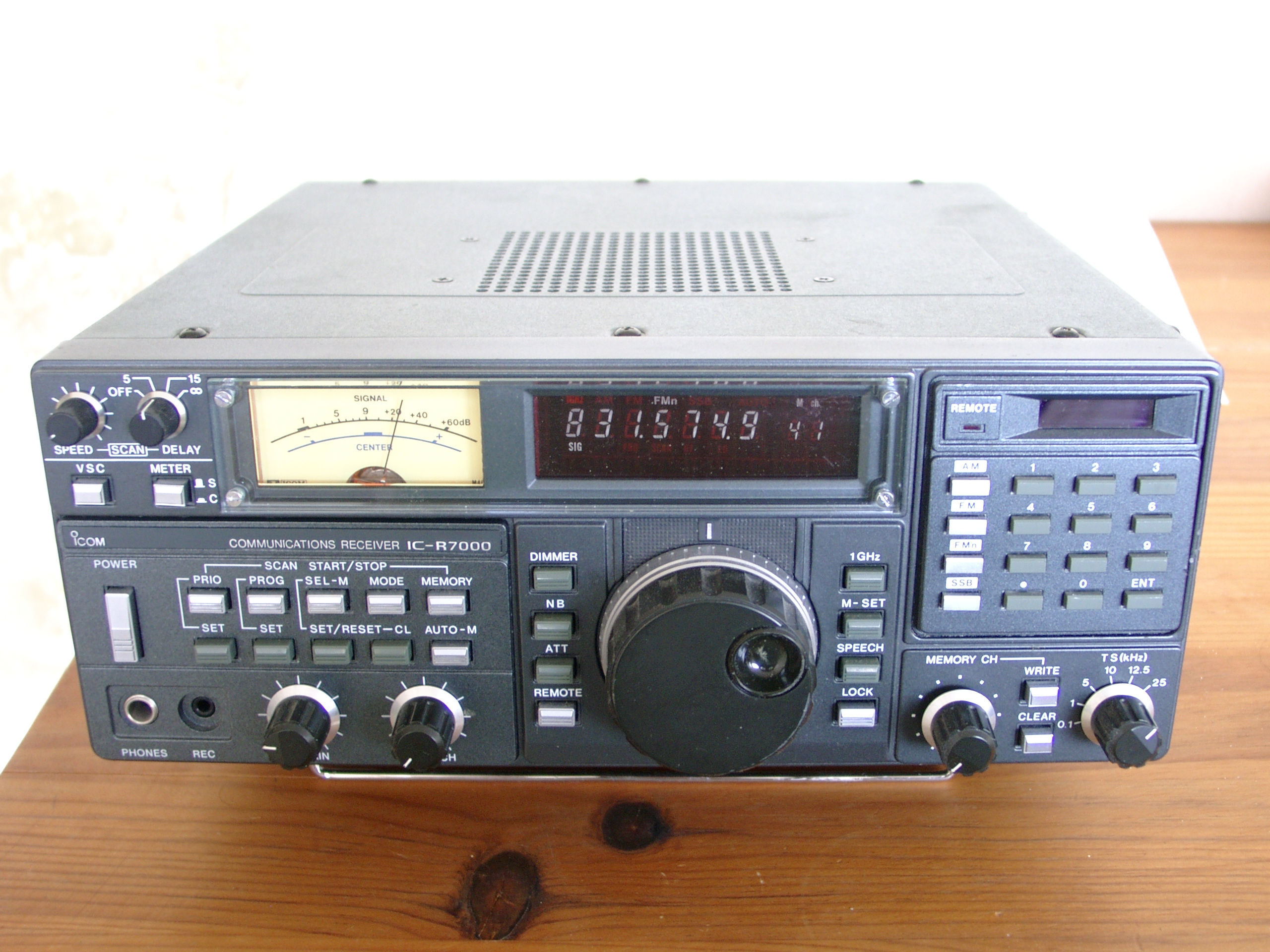
Radio Receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves (electromagnetic waves of radio frequency) and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation. Radio receivers are essential components of all systems based on radio technology. The information produced by the receiver may be in the form of sound, video (television), or digital data. A radio receiver may be a separate piece of electronic equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Engineering
Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments. A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching system, and other plain old telephone service facilities, optical fiber cabling, IP networks, and microwave transmission systems. Telecommunications engineering also overlaps with broadcast engineering. Telecommunication is a diverse field of engineering connected to electronic, civil and systems engineering. Ultimately, telecom engineers are responsible for providing high-speed data transmission services. They use a variety of equipment and transport media to design the telecom network infrastructure; the most common media used by wired telecommunications today are twisted pair, coax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves (electromagnetic waves of radio frequency) and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation. Radio receivers are essential components of all systems based on radio technology. The information produced by the receiver may be in the form of sound, video (television), or digital data. A radio receiver may be a separate piece of electronic equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Wave
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths greater than , about the diameter of a grain of rice. Radio waves with frequencies above about 1 GHz and wavelengths shorter than 30 centimeters are called microwaves. Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical radio source, astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna (radio), antenna, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies that humans can hear (though these are not electromagnetic) and the lower limit of infrared frequencies, and also encompasses the microwave range. These are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves, so they are used in radio technology, among other uses. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Device
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signals to digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in response to global demand. The semiconductor industry is one of the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |