|
Tibialis Anterior
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin. It is situated on the lateral side of the tibia; it is thick and fleshy above, tendinous below. The tibialis anterior overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve in the upper part of the leg. Structure The tibialis anterior muscle is the most medial muscle of the anterior compartment of the leg. The muscle ends in a tendon which is apparent on the anteriomedial dorsal aspect of the foot close to the ankle. Its tendon is ensheathed in a synovial sheath. The tendon passes through the medial compartment superior and inferior extensor retinacula of the foot. Origin The tibialis anterior muscle arises from the upper 2/3 of the lateral surface of the tibia and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects the knee with the ankle bones, ankle. The tibia is found on the anatomical terms of location#Medial, medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute ''aulos, tibia''. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body. Structure In human anatomy, the tibia is the second largest bone next to the femur. As in other vertebrates the tibia is one of two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula, and is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
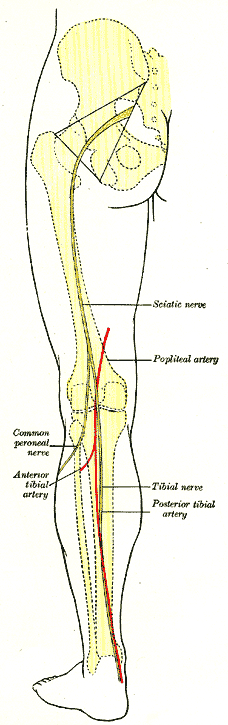
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: * posterior tibial recurrent artery * anterior tibial recurrent artery * muscular branches * anterior medial malleolar ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Fascia
Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments. This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the muscles, bones, nerves, and blood vessels of the body. It provides connection and communication in the form of aponeuroses, ligaments, tendons, retinaculum, retinacula, joint capsules, and septum, septa. The deep fasciae envelop all bone (periosteum and endosteum); cartilage (perichondrium), and blood vessels (tunica externa) and become specialized in muscles (epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium) and nerves (epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium). The high density of collagen fibers gives the deep fascia its strength and integrity. The amount of elastin fiber determines how much extensibility and resilience it will have. Examples Examples include: * Fascia lata * Deep fascia of leg * Brachial fascia * Buck's fascia Fascial dynamics D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Extensor Retinaculum Of Foot
The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot (cruciate crural ligament, lower part of anterior annular ligament) is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament The interosseous talocalcaneal ligament forms the chief bond of union between the talus and calcaneus. It is a portion of the united capsules of the talocalcaneonavicular and the talocalcaneal joints, and consists of two partially united layer ...; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus. At the medial border of the latter tendon, these two layers join, forming a compartment in which the tendons are enclosed. From the medial extremity of this sheath, the two limbs of the Y diverge: one is directed upward and medialward, to be attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallux
Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plantigrade''; '' unguligrade'' animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes. Structure There are normally five toes present on each human foot. Each toe consists of three phalanx bones, the proximal, middle, and distal, with the exception of the big toe (). For a minority of people, the little toe also is missing a middle bone. The hallux only contains two phalanx bones, the proximal and distal. The joints between each phalanx are the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanx bone of each toe articulates with the metatarsal bone of the foot at the metatarsophalangeal joint. Each toe is surrounded by skin, and present on all five toes is a toenail. The toes are, from medial to lateral: * the first toe, also known as the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of Foot#Structure, foot bones known as the tarsus (skeleton), tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the Lateral malleolus, lateral and Medial malleolus, medial malleoli) that articulation (anatomy), articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the Ball-and-socket joint, ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Fibular Nerve
The deep fibular nerve (also known as deep peroneal nerve) begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane, and comes into relation with the anterior tibial artery above the middle of the leg; it then descends with the artery to the front of the ankle-joint, where it divides into a ''lateral'' and a '' medial terminal branch''. Structure Lateral side of the leg The deep fibular nerve is the nerve of the anterior compartment of the leg and the dorsum of the foot. It is one of the terminal branches of the common fibular nerve. It corresponds to the posterior interosseus nerve of the forearm. It begins at the lateral side of the fibula bone, and then enters the anterior compartment by piercing the anterior intermuscular septum. It then pierces the extensor digitorum longus and lies next to the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg. Structure It arises from the lateral condyle of the tibia The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...; from the upper three-quarters of the anterior surface of the body of the fibula; from the upper part of the interosseous membrane; from the deep surface of the fascia; and from the intermuscular septa between it and the tibialis anterior on the medial, and the peroneal muscles on the lateral side. Between it and the tibialis anterior are the upper portions of the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve. The muscle passes under the superior and inferior extensor retinaculum of foot in company with the fibularis tertius, and divides into four slips, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Intermuscular Septum Of Thigh
The lateral intermuscular septum of thigh is a fold of deep fascia Deep fascia (or investing fascia) is a fascia, a layer of dense connective tissue that can surround individual muscles and groups of muscles to separate into fascial compartments. This fibrous connective tissue interpenetrates and surrounds the m ... in the thigh. It is between the vastus lateralis and biceps femoris. It separates the anterior compartment of the thigh from the posterior compartment of the thigh. See also * Medial intermuscular septum of thigh * Anterior compartment of thigh * Posterior compartment of thigh References External links Topographical Anatomy of the Lower Limb - Listed Alphabeticallyfrom UAMS Department of Neurobiology and Developmental Sciences from anatomy.med.umich.edu Lower limb anatomy {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interosseous Membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint. Interosseous membranes in the human body: * Interosseous membrane of forearm * Interosseous membrane of leg Gallery File:5 ligaments of interosseous membrane of forearm.png, Five ligaments of interosseous membrane of forearm:* Central band (key portion to be reconstructed in case of injury)* Accessory band * Distal oblique bundle * Proximal oblique cord* Dorsal oblique accessory cord Notes External links * * {{Authority control Skeletal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Extensor Retinaculum Of Foot
The inferior extensor retinaculum of the foot (cruciate crural ligament, lower part of anterior annular ligament) is a Y-shaped band placed in front of the ankle-joint, the stem of the Y being attached laterally to the upper surface of the calcaneus, in front of the depression for the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament The interosseous talocalcaneal ligament forms the chief bond of union between the talus and calcaneus. It is a portion of the united capsules of the talocalcaneonavicular and the talocalcaneal joints, and consists of two partially united layer ...; it is directed medialward as a double layer, one lamina passing in front of, and the other behind, the tendons of the peroneus tertius and extensor digitorum longus. At the medial border of the latter tendon, these two layers join, forming a compartment in which the tendons are enclosed. From the medial extremity of this sheath, the two limbs of the Y diverge: one is directed upward and medialward, to be attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Extensor Retinaculum Of Foot
The superior extensor retinaculum of the foot (transverse crural ligament) is the upper part of the extensor retinaculum of foot which extends from the ankle to the heelbone. The superior extensor retinaculum binds down the tendons of extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, peroneus tertius, and tibialis anterior as they descend on the front of the tibia and fibula; under it are found also the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve. It is found on the lateral side of the lower leg, attached laterally to the lower end of the fibula, and medially to the tibia; above it is continuous with the fascia A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. ... of the leg. Additional images File:Gray437.png, Muscles of the front of the leg. See also * Peroneal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |