|
Tax Benefits Of Debt
In the context of corporate finance, the tax benefits of debt or tax advantage of debt refers to the fact that from a tax perspective it is cheaper for firms and investors to finance with debt than with equity. Under a majority of taxation systems around the world, and until recently under the United States tax system, firms are taxed on their profits and individuals are taxed on their personal income. For example, a firm that earns $100 in profits in the United States would have to pay around $30 in taxes. If it then distributes these profits to its owners as dividends, then the owners in turn pay taxes on this income, say $20 on the $70 of dividends. The $100 of profits turned into $50 of investor income. If, instead the firm finances with debt, then, assuming the firm owes $100 of interest to investors, its profits are now 0. Investors now pay taxes on their interest income, say $30. This implies for $100 of profits before taxes, investors got $70. This tax-related encoura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is an area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of businesses, the actions that managers take to increase the Value investing, value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. The primary goal of corporate finance is to Shareholder value, maximize or increase valuation (finance), shareholder value.SeCorporate Finance: First Principles Aswath Damodaran, New York University's Stern School of Business Correspondingly, corporate finance comprises two main sub-disciplines. Capital budgeting is concerned with the setting of criteria about which value-adding Project#Corporate finance, projects should receive investment funding, and whether to finance that investment with ownership equity, equity or debt capital. Working capital management is the management of the company's monetary funds that deal with the short-term operating balance of current assets and Current liability, cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of #Principal, principal and interest. Loans, bond (finance), bonds, notes, and Mortgage loan, mortgages are all types of debt. In financial accounting, debt is a type of financial transaction, as distinct from equity (finance), equity. The term can also be used metaphorically to cover morality, moral obligations and other interactions not based on a monetary value. For example, in Western cultures, a person who has been helped by a second person is sometimes said to owe a "debt of gratitude" to the second person. Etymology The English term "debt" was first used in the late 13th century and comes by way of Old French from the Latin verb ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ownership Equity
In finance, equity is an ownership interest in property that may be subject to debts or other liabilities. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business. A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity in order to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. When liabilities attached to an asset exceed its value, the difference is called a deficit and the asset is informally said to be "underwater" or "upside-down". In government finance or other non-profit settings, equity is known as "net position" or "net assets". Origins The term "equity" describes this type of ownership in English because it was regulated through the system of equity law that develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
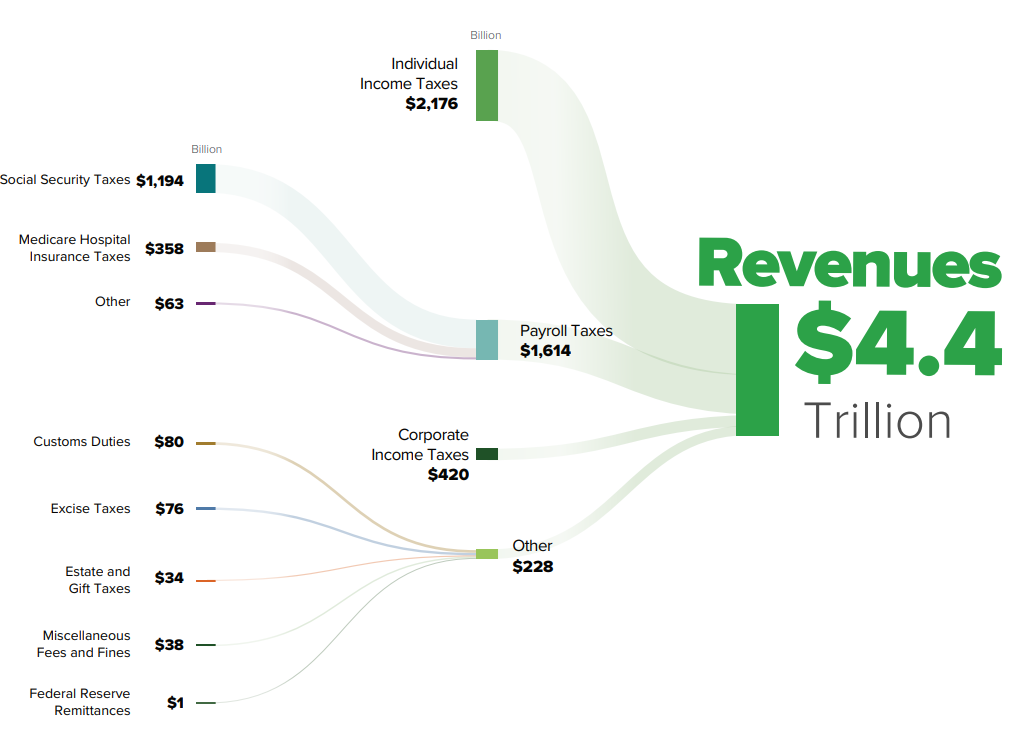
Taxation In The United States
The United States has separate Federal government of the United States, federal, U.S. state, state, and Local government in the United States, local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, Capital gains tax in the United States, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP. Income tax in the United States, U.S. tax and transfer policies are Progressive tax, progressive and therefore reduce effective income inequality in the United States, income inequality, as rates of tax generally increase as taxable income increases. As a group, the lowest earning workers, especially those with dependents, pay no income taxes and may actually receive a small subsidy from the federal government (from child credits and the Earned Income Tax Credit). Taxes fall m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profit (accounting)
Profit, in accounting, is an income distributed to the ownership , owner in a Profit (economics) , profitable market production process (business). Profit is a measure of profitability which is the owner's major interest in the income-formation process of market production. There are several profit measures in common use. Income formation in market production is always a balance between income generation and income distribution. The income generated is always distributed to the Stakeholder (corporate), stakeholders of production as economic value within the review period. The profit is the share of income formation the owner is able to keep to themselves in the income distribution process. Profit is one of the major sources of economics , economic well-being because it means incomes and opportunities to develop production. The words "income", "profit" and "earnings" are synonyms in this context. Other terms See also * Gross income * Net profit * Profitability index * Rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Income
In economics, personal income refers to the total earnings of an individual from various sources such as wages, investment ventures, and other sources of income. It encompasses all the products and money received by an individual. Personal income can be defined in different ways: * It refers to the income received by individuals or households in a country from all sources during a specific year. * It includes earned income or transferred income received by households within the country or even from outside sources. * It represents the total capital an individual receives from various sources over a certain period or throughout their life. Personal income encompasses various forms of income beyond just wages. It can include dividends, transfers, pension payments, government benefits, and rental income, among others. Taxes charged to an individual are typically not deducted when calculating personal income. Personal income serves as an indicator of the real well-being of people an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dividends
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders, after which the stock exchange decreases the price of the stock by the dividend to remove volatility. The market has no control over the stock price on open on the ex-dividend date, though more often than not it may open higher. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-invested in the business (called retained earnings). The current year profit as well as the retained earnings of previous years are available for distribution; a corporation is usually prohibited from paying a dividend out of its capital. Distribution to shareholders may be in cash (usually by bank transfer) or, if the corporation has a dividend reinvestment plan, the amount can be paid by the issue of further shares or by share repurchase. In some cases, the distribution may be of assets. The dividend received by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation And Amortization
A company's earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (commonly abbreviated EBITDA, pronounced ) is a measure of a company's profitability of the operating business only, thus before any effects of indebtedness, state-mandated payments, and costs required to maintain its asset base. It is derived by subtracting from revenues all costs of the operating business (e.g. wages, costs of raw materials, services ...) but not decline in asset value, cost of borrowing and obligations to governments. Although lease have been capitalised in the balance sheet (and depreciated in the profit and loss statement) since IFRS 16, its expenses are often still adjusted back into EBITDA given they are deemed operational in nature. Though often shown on an income statement, it is not considered part of the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (United States), Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) by the Securities and Exchange Commission, SEC, hence the SEC require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Revenue Code
The Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (IRC), is the domestic portion of federal statutory tax law in the United States. It is codified in statute as Title 26 of the United States Code. The IRC is organized topically into subtitles and sections, covering federal income tax in the United States, payroll taxes, estate taxes, gift taxes, and excise taxes; as well as procedure and administration. The Code's implementing federal agency is the Internal Revenue Service. Origins of tax codes in the United States Prior to 1874, U.S. statutes (whether in tax law or other subjects) were not codified. That is, the acts of Congress were not organized and published in separate volumes based on the subject matter (such as taxation, bankruptcy, etc.). Codifications of statutes, including tax statutes, undertaken in 1873 resulted in the Revised Statutes of the United States, approved June 22, 1874, effective for the laws in force as of December 1, 1873. Title 35 of the Revised Statutes was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital-structure
In corporate finance, capital structure refers to the mix of various forms of external funds, known as capital, used to finance a business. It consists of shareholders' equity, debt (borrowed funds), and preferred stock, and is detailed in the company's balance sheet. The larger the debt component is in relation to the other sources of capital, the greater financial leverage (or gearing, in the United Kingdom) the firm is said to have. Too much debt can increase the risk of the company and reduce its financial flexibility, which at some point creates concern among investors and results in a greater cost of capital. Company management is responsible for establishing a capital structure for the corporation that makes optimal use of financial leverage and holds the cost of capital as low as possible. Capital structure is an important issue in setting rates charged to customers by regulated utilities in the United States. The utility company has the right to choose any capital stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade-Off Theory
The trade-off theory of capital structure is the idea that a company chooses how much debt finance and how much equity finance to use by balancing the costs and benefits. The classical version of the hypothesis goes back to Kraus and Litzenberger who considered a balance between the dead-weight costs of bankruptcy and the tax saving benefits of debt. Often agency costs are also included in the balance. This theory is often set up as a competitor theory to the pecking order theory of capital structure. A review of the trade-off theory and its supporting evidence is provided by Ai, Frank, and Sanati. An important purpose of the theory is to explain the fact that corporations usually are financed partly with debt and partly with equity. It states that there is an advantage to financing with debt, the tax benefits of debt and there is a cost of financing with debt, the costs of financial distress including bankruptcy costs of debt and non-bankruptcy costs (e.g. staff leaving, supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Structure
In corporate finance, capital structure refers to the mix of various forms of external funds, known as capital, used to finance a business. It consists of shareholders' equity, debt (borrowed funds), and preferred stock, and is detailed in the company's balance sheet. The larger the debt component is in relation to the other sources of capital, the greater financial leverage (or gearing, in the United Kingdom) the firm is said to have. Too much debt can increase the risk of the company and reduce its financial flexibility, which at some point creates concern among investors and results in a greater cost of capital. Company management is responsible for establishing a capital structure for the corporation that makes optimal use of financial leverage and holds the cost of capital as low as possible. Capital structure is an important issue in setting rates charged to customers by regulated utilities in the United States. The utility company has the right to choose any capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |