|
Taifa Of Málaga
The Taifa of Málaga () was an Andalusī Islamic taifa kingdom located in what is now southern Spain. It existed during four distinct time periods: from 1026 to 1057, 1073 to 1090, 1145 to 1153, and 1229 to 1239, when the polity was finally conquered by the Emirate of Granada. History First taifa The taifa was created in 1026 when Yahya I al-Mu'tali, a Berberized Arab of the Hammudid dynasty who had been invited to assume the title of caliph of Córdoba, returned to his secure stronghold of Málaga and subsequently was banished definitively by the Córdobans. After his expulsion, he united under his rule the coras of Málaga and Algeciras, initially with the support of the Zirids of Granada, and thereupon declared the independent Taifa of Málaga. He regained the title of caliph, which thenceforth was exclusive to the Málagan rulers. His rule, which lasted until his death in 1035, was characterized by struggle with the Abbadid dynasty kings of the Taifa of Seville. Yahya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taifa Of Granada
The Taifa of Granada (, ) or Zirid Kingdom of Granada was a Muslim kingdom that was formed in al-Andalus (in present-day Spain) in 1013 following the deposition of Umayyad Caliph Hisham II in 1009. The kingdom was centered on Granada, its capital, and it also extended its control to Málaga for a period. Four kings succeeded each other during its nearly 80 years of existence, all of them belonging to an offshoot of the Zirid dynasty of North Africa, a Sanhaja Berber clan. The Taifa of Granada was considered to be the wealthiest out of all of the taifa kingdoms.The Art of Medieval Spain, A.D. 500-1200 Jerrilynn D. Dodds, Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York, N.Y.). Metropolitan Museum of Art. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taifa Of Almería
The Taifa of Almería (, ) was a Muslim medieval Arab kingdom located in what is now the province of Almería in Spain. The taifa originated in 1012 and lasted until 1091. In this period the city of Almería reached its historical splendour under powerful local emirs like Khayran, the first fully independent Emir of Almería and Cartagena, and Abu Yahyà Muhammad ben Ma'n. Almería declared independence of its province from Caliphate of Cordoba around 1012. It remained as an independent kingdom, although several campaigns of the Taifa of Seville diminished its territory in the north. The kingdom was important due to its strategic location, its harbour, and a developed and very important textile industry, with around five thousand looms, being also a center of silk industry, which originated a very strong commerce with other parts of Europe and which remained until the Muslims were expelled in early 17th century. The emirs of Granada, Seville and Valencia tried to conquer the li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Écija (1039)
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taifa Of Algeciras
The Taifa of Algeciras () was a medieval Muslim taifa kingdom in what is now southern Spain and Gibraltar, that existed from 1035 to 1058. History The ''taifa'' was created in 1013, in the wake of the disintegration of the caliphate of Córdoba which began after 1009. When Sulayman ibn al-Hakam took control of the caliphate, he gave Algeciras to the Hammudids, a dynasty who had helped him in gaining the power. The first king of Algeciras was al-Qasim al-Ma'mun, who later was also caliph. His cousin Yahya al-Mu'tali annexed Algeciras to the taifa of Málaga in 1035. In 1039 Muhammad ibn al-Qasim, son of al-Qasim, was proclaimed emir of Algeciras. In 1055 al-Mu'tamid ibn Abbad, lord of Seville, appeared under Algeciras' walls, forcing Muhammad to leave the taifa, which was annexed to that of Seville.Kevin Lane, Clive Finlayson, Uwe Vagelpohl, Francisco José Giles Guzmàn, Francisco Giles Pachec"Myths, Moors and Holy War: Reassessing the History and Archaeology of Gibraltar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taifa Of Carmona
The Taifa of Carmona () was a medieval Berber taifa kingdom. It existed for two distinct periods: first from 1013 to 1066 when it was conquered by the Taifa of Seville, and secondly from around 1143 to 1150 when it was finally conquered by the Almohad Caliphate. The taifa was established and ruled by the Zenata Berber Birzalid dynasty. Origins The Banu Birzal was a Zenata Berber tribe settled in the Zab region and belonging to the confederations of the central Maghreb (Maghreb al-Awsat). Xavier Ballestín Edicions Universitat Barcelona, List of emirs Birzalid dynasty *'Abd Allah: 1013/4–1023/4 *Muhamma ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taifa Of Seville
The Taifa of Seville ( ''Ta'ifat-u Ishbiliyyah'') was an Arab kingdom which was ruled by the Abbadid dynasty. It was established in 1023 and lasted until 1091, in what is today southern Spain and Portugal. It gained independence from the Caliphate of Cordoba and it expanded the territory it ruled in the mid-11th century. The emerging power of Castile led Seville to ask military assistance from the Almoravids, who then occupied Seville. History The ''taifa'' (principality) began as a small, weakly-defended territory comprising parts of the modern Spanish provinces of Seville, Huelva, and Cádiz, but quickly emerged as the most powerful taifa of the time, after its rulers began a policy of expansion. The first emir of Seville was Abu al-Qasim Muhammad ibn Abbad, Abu al-Qasim (1023–1042). He was qadi of Seville Seville ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Spain, Spanish autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Sevil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abbadid Dynasty
The Abbadid dynasty or Abbadids () was an Arab dynasty from the tribe of Banu Lakhm of al-Hirah, which ruled the Taifa of Seville in al-Andalus following the fall of the Caliphate of Cordoba in 1031. After the collapse, they were the most powerful Taifa and before long absorbed most of the others. Abbadid rule lasted from about 1023 until 1091, but during the short period of its existence it exhibited singular energy and typified its time. Overview During their reign, the Abbadids also made significant contributions to the development of science, military technology and medicine. Their patronage of scholars and researchers helped to create a culture of learning that encouraged scientific inquiry and experimentation. The Abbadids' interest in science is evident in the many scientific works that were written during their reign, including the famous Book of Optics by the polymath Ibn al-Haytham. In addition to their patronage of the arts, sciences, and literature, the Abbadids also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
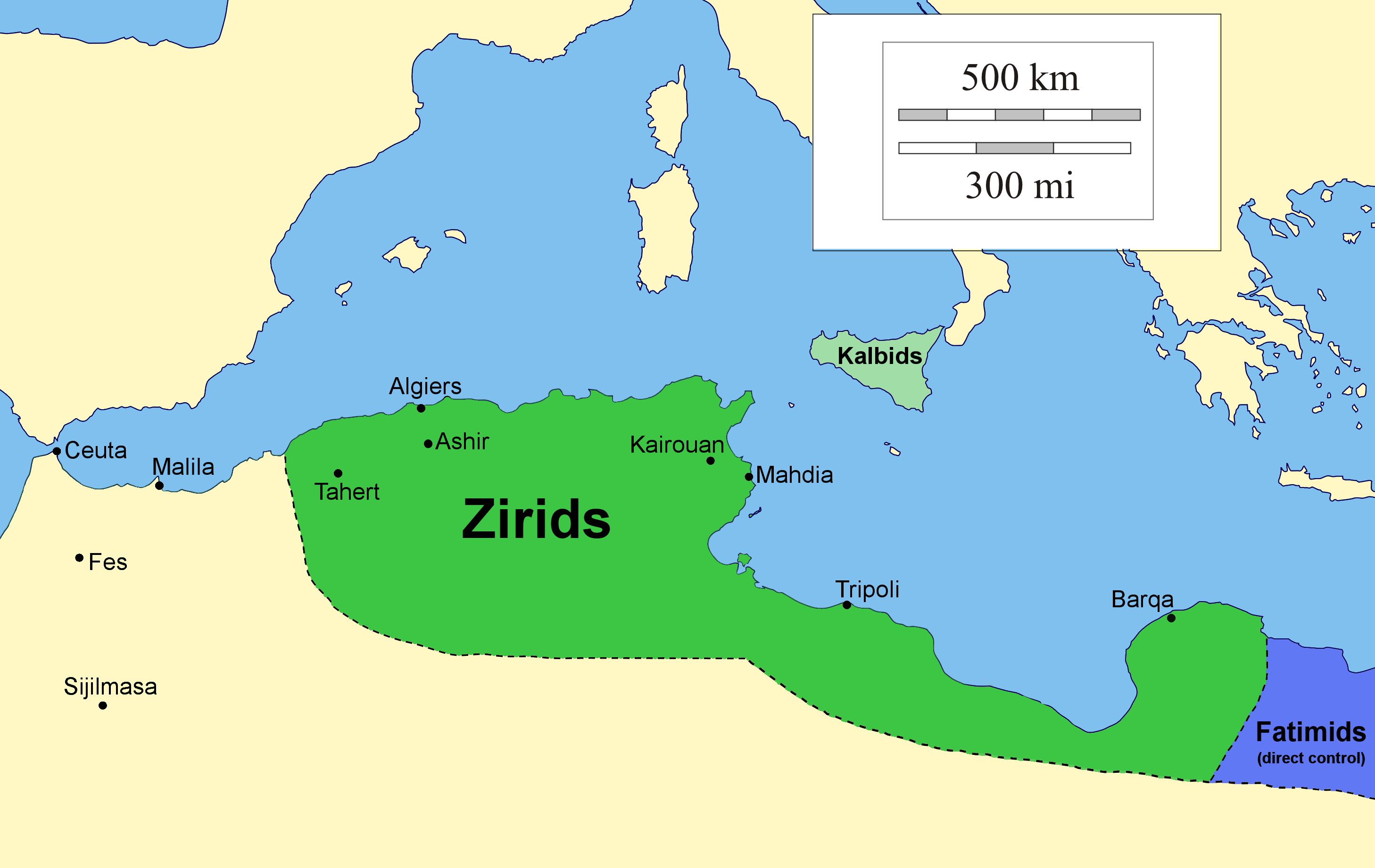
Zirid Dynasty
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148. Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of the Fatimid Caliphate and the eponymous founder of the dynasty, the Zirids were emirs who ruled in the name of the Fatimids. The Zirids gradually established their autonomy in Ifriqiya through military conquest until officially breaking with the Fatimids in the mid-11th century. The rule of the Zirid emirs opened the way to a period in North African history where political power was held by Berber dynasties such as the Almoravid dynasty, Almohad Caliphate, Zayyanid dynasty, Marinid Sultanate and Hafsid dynasty. Under Buluggin ibn Ziri the Zirids extended their control westwards and briefly occupied Fez and much of present-day Morocco after 980, but encountered resistance from the local Zenata Berbers who gave their allegiance to the Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algeciras
Algeciras () is a city and a municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, Andalusia. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, near the Strait of Gibraltar, it is the largest city on the Bay of Gibraltar (). The Port of Algeciras is List of busiest ports in Europe, one of the largest ports in Europe and the world in three categories: List of world's busiest container ports, container, List of world's busiest ports by cargo tonnage, cargo and transshipment. The urban area straddles the small Río de la Miel, which is the southernmost river of continental Europe. As of 1 January 2020, the municipality had a registered population of 123,078, second in its province after Jerez de la Frontera and greater than Cádiz city population. It forms part of the Comarcas of Spain, ''comarca'' of Campo de Gibraltar. The surrounding metro area also includes the municipalities of Los Barrios, La Línea de la Concepción, Castellar de la Frontera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kura (al-Andalus)
The ''Kūra'' was one of the territorial demarcations into which al-Andalus, the ancient Islamic Iberian Peninsula, was divided during the Emirate and Caliphate of Córdoba. It coexisted with another territorial demarcation called March ("''thagr''"), which overlapped the ''Kūra'' in the areas bordering the Christian kingdoms. Both underpinned the al-Andalus territorial organization during the aforementioned periods. According to the RAE dictionary, the word '' Kūra'' (, ) comes from the Greek ''χῶρα'', with the meaning of territory. Territorial organization of al-Andalus The Andalusian Caliphate was organized into six large districts, three inland and three on the borders, all with their respective ''Kūra''. The interior demarcations or regions (nabiya) were: al-Gharb, which covered the present-day province of Huelva and southern Portugal; al-Mawsat or ''central lands'', which extended through the valleys of the Guadalquivir and the Genil, plus the mountainous areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caliphate Of Córdoba
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, formally abolished as part of the Atatürk's reforms, 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |