|
Systems Integrator
A systems integrator (or system integrator) is a person or company that specializes in bringing together component subsystems into a whole and ensuring that those subsystems function together, a practice known as system integration. They also solve problems of automation. Systems integrators may work in many fields but the term is generally used in the information technology (IT) field such as computer networking, the defense industry, the mass media, enterprise application integration, business process management or manual computer programming. Data quality issues are an important part of the work of systems integrators. Required skills A system integration engineer needs a broad range of skills and is likely to be defined by a breadth of knowledge rather than a depth of knowledge. These skills are likely to include software, systems and enterprise architecture, software and hardware engineering, interface protocols, and general problem solving skills. It is likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Integration
System integration is defined in engineering as the process of bringing together the component sub- systems into one system (an aggregation of subsystems cooperating so that the system is able to deliver the overarching functionality) and ensuring that the subsystems function together as a system, and in information technology as the process of linking together different computing systems and software applications physically or functionally, to act as a coordinated whole. The system integrator integrates discrete systems utilizing a variety of techniques such as computer networking, enterprise application integration, business process management or manual programming. System integration involves integrating existing, often disparate systems in such a way "that focuses on increasing value to the customer" (e.g., improved product quality and performance) while at the same time providing value to the company (e.g., reducing operational costs and improving response time). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical User Interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, instead of text-based UIs, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of CLIs ( command-line interfaces), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower- display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where HUD (''head-up display'') is preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric display ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Application Integration
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications. Overview Enterprise application integration is an integration framework composed of a collection of technologies and services which form a middleware or "middleware framework" to enable integration of systems and applications across an enterprise. Many types of business software such as supply chain management applications, ERP systems, CRM applications for managing customers, business intelligence applications, payroll, and human resources systems typically cannot communicate with one another in order to share data or business rules. For this reason, such applications are sometimes referred to as islands of automation or information silos. This lack of communication leads to inefficiencies, wherein identical data are stored in multiple locations, or straightforward processes are unable to be automated. Enterp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture For Control Networks
Architecture for Control Networks (ACN) is a suite of network protocols for control of entertainment technology equipment, particularly as used in live performance or large-scale installations. For example, lighting, audio or special effects equipment. ACN is maintained by Entertainment Services and Technology Association and its first official release was ANSI Standard E1.17-2006 - Entertainment Technology - Architecture for Control Networks. The standard was subsequently revised and released as ANSI E1.17-2010. ACN was initially designed to be layered on top of UDP/IP and therefore will run over most IP transports including standard, inexpensive Ethernet and 802.11 ( Wi-Fi) networks. Protocol architecture ACN defines a common protocol architecture, two major network protocols (SDT, DMP), a device description language (DDL) and a number of ‘E1.17 Profiles for Interoperability’ (known as ''EPI''s or '' interoperability profiles'') which define how elements of the ACN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art-Net
Art-Net is a royalty-free communications protocol for transmitting the DMX512-A lighting control protocol and Remote Device management (RDM) protocol over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) of the Internet protocol suite. It is used to communicate between "nodes" (e.g., intelligent lighting instruments) and a "server" (a lighting desk or general purpose computer running lighting control software). Facilities Art-Net is a simple implementation of DMX512-A protocol over UDP in which lighting control information is conveyed in IP packets, typically on a private local area network such as Ethernet. Supported functions include transmitting and receiving lighting data (e.g., fader levels for individual lights, positions of movable lights); management functions such as detecting nodes, updating node control parameters, and transmitting timecodes; and functions that allow nodes to "subscribe" to "publisher" nodes so that, for example, nodes A and B can subscribe to node C (C wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDM (lighting)
{{manual, date=February 2016 Remote Device Management (RDM) is a protocol enhancement to USITT DMX512 that allows bi-directional communication between a lighting or system controller and attached RDM compliant devices over a standard DMX line. This protocol will allow configuration, status monitoring, and management of these devices in such a way that does not disturb the normal operation of standard DMX512 devices that do not recognize the RDM protocol. The standard was originally developed by the Entertainment Services and Technology Association - Technical Standards (ESTAand is officially known as "ANSI E1.20, Remote Device Management Over DMX512 Networks. Technical Details RDM Physical layer The RDM protocol and the RDM physical layer were designed to be compatible with legacy equipment. All compliant legacy DMX512 receivers should be usable in mixed systems with an RDM controller (console) and RDM responders (receivers). DMX receivers and RDM responders can be used wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMX512-A
DMX512 is a technical standard, standard for digital communication networks that are commonly used to control lighting and effects. It was originally intended as a standardized method for controlling stage lighting dimmers, which, prior to DMX512, had employed various incompatible proprietary protocols. It quickly became the primary method for linking controllers (such as a lighting console) to dimmers and special effects devices such as fog machines and intelligent lighting, intelligent lights. DMX512 has also expanded to uses in non-theatrical interior and architectural lighting, at scales ranging from strings of Christmas lights to electronic billboards and stadium or arena concerts. It can now be used to control almost anything, reflecting its popularity in all types of venues. DMX512 uses a unidirectional EIA-485, EIA-485 (RS-485) differential signaling at its physical layer, in conjunction with a variable-size, packet-based communication protocol. DMX512 does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
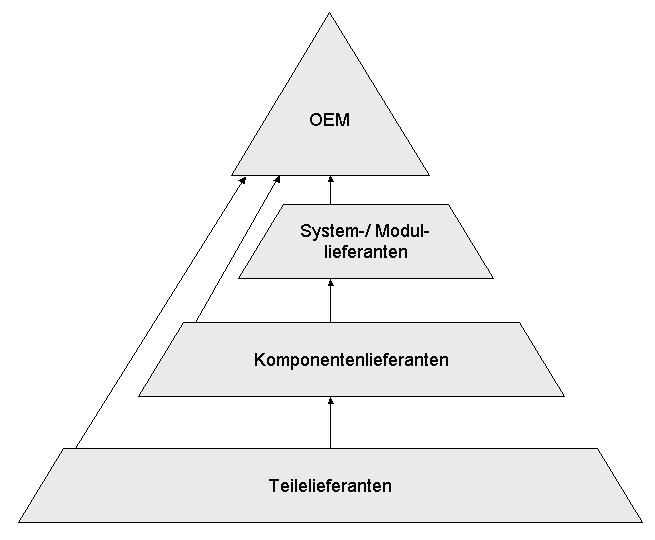
OEMs
An original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is generally perceived as a company that produces non-aftermarket parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. It is a common industry term recognized and used by many professional organizations such as SAE International, ISO, and others. However, the term is also used in several other ways, which causes ambiguity. It sometimes means the maker of a system that includes other companies' subsystems, an end-product producer, an automotive part that is manufactured by the same company that produced the original part used in the automobile's assembly, or a value-added reseller.Ken Olsen: PDP-1 and PDP-8 (page 3) , economicadventure.com Automotive parts When referring to auto parts, OEM refers to the manufactur ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer PCs and tablets, Windows 11 Enterprise for corporations, and Windows Server 2022 for servers. Genealogy By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIX
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM (AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the "Unix philosophy". According to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Systems
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

