|
Sulfonamides
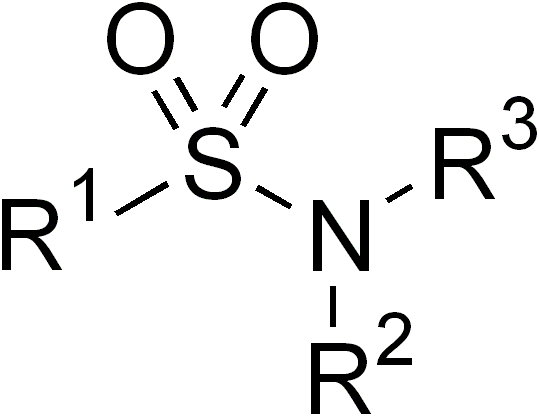
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
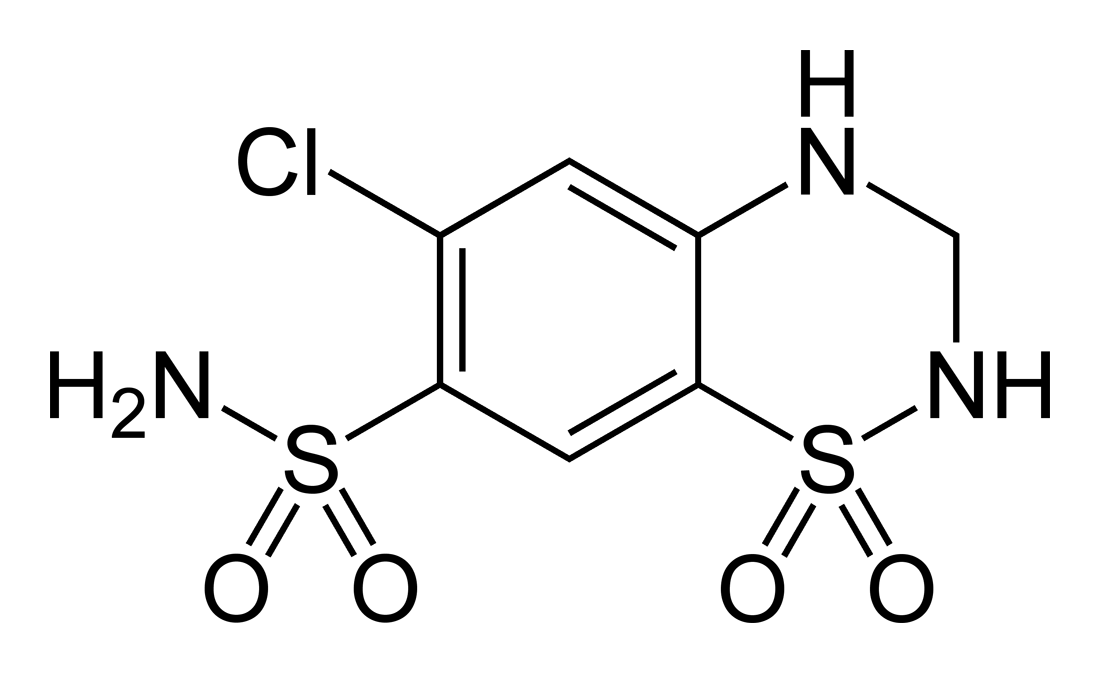
Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ or SMX) is an antibiotic. It is used for bacterial infections such as urinary tract infections, bronchitis, and prostatitis and is effective against both gram negative and positive bacteria such as ''Listeria monocytogenes'' and ''E. coli''. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and skin rashes. It is a sulfonamide and bacteriostatic. It resembles a component of folic acid. It prevents folic acid synthesis in the bacteria that must synthesize their own folic acid. Mammalian cells, and some bacteria, do not synthesize but require preformed folic acid (vitamin B9); they are therefore insensitive to sulfamethoxazole. It was introduced to the United States in 1961. It is now mostly used in combination with trimethoprim (abbreviated SMX-TMP). The SMX-TMP combination is on the WHO Model List of Essential medicines as a first-choice treatment for urinary tract infections. Other names include: sulfamethalazole, sulfisomezole,PubChem"Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultam
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfanilamide
Sulfanilamide (also spelled sulphanilamide) is a sulfonamide antibacterial drug. Chemically, it is an organic compound consisting of an aniline derivatized with a sulfonamide group. Powdered sulfanilamide was used by the Allies in World War II to reduce infection rates and contributed to a dramatic reduction in mortality rates compared to previous wars. Sulfanilamide is rarely if ever used systemically due to toxicity and because more effective sulfonamides are available for this purpose. Modern antibiotics have supplanted sulfanilamide on the battlefield; however, sulfanilamide remains in use today in the form of topical preparations, primarily for treatment of vaginal yeast infections mainly vulvovaginitis which is caused by '' Candida albicans''. The term "sulfanilamides" is also sometimes used to describe a family of molecules containing these functional groups. Examples include: * Furosemide, a loop diuretic * Sulfadiazine, an antibiotic * Sulfamethoxazole, an antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulthiame
Sultiame (or sulthiame) is a sulfonamide and inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. It is used as an anticonvulsant. History Sultiame was first synthesised in the laboratories of Bayer AG in the mid 1950s and eventually launched as Ospolot in Europe and other markets the early 1960s. It never became a registered drug in the United States. The brand was transferred to Desitin GmbH in 1993 and is sold in several European countries, in Israel, Japan, and Australia. Sultiame became established as a second-line drug for treatment of partial epilepsy in the 1960s and 1970s and was often used in combination with the established anticonvulsant phenytoin. Temporal lobe seizures appeared particularly responsive to sultiame. Doubts subsequently arose as to whether sultiame has intrinsic anticonvulsant properties. After discovering sultiame's ability to raise the blood levels of phenytoin, it was assumed that sultiame would only act in combination with phenytoin. This finding, together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfur
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries. Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium, and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium, and carbon–tellurium compounds. A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Syntheses
''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and experiments reported in an article must be successfully repeated in the laboratory of a member of the editorial board as a check for reproducibility prior to publication. The journal is published by Organic Syntheses, Inc., a non-profit corporation. An annual print version is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of Organic Syntheses, Inc. History Prior to World War I, work on synthetic organic chemistry in the United States had been quite limited, and most of the reagents used in laboratories had to be imported from Europe. When export stoppages and trade embargoes cut off this source, Clarence Derick, a professor of chemistry at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, began an effort to synthesize these needed chemicals in indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Sweeteners
A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie () or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be derived through manufacturing of plant extracts or processed by chemical synthesis. Sugar substitute products are commercially available in various forms, such as small pills, powders, and packets. In North America, common sugar substitutes include aspartame, monk fruit extract, saccharin, sucralose, and stevia; cyclamate is also used outside the United States. These sweeteners are a fundamental ingredient in diet drinks to sweeten them without adding calories. Additionally, sugar alcohols such as erythritol, xylitol, and sorbitol are derived from sugars. Approved artificial sweeteners do not cause cancer. Reviews and dietetic professionals have concluded that moderate use of non-nutritive sweeteners as a safe replacement for suga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |