|
Statocyst
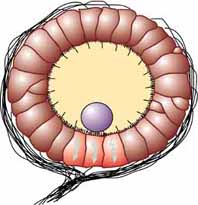
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in '' Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs ( setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in '' Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs ( setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Organs Of Gastropods
The sensory organs of gastropods (snails and slugs) include olfactory organs, eyes, statocysts and mechanoreceptors. Gastropods have no sense of hearing.Chase R.: ''Sensory Organs and the Nervous System''. in Barker G. M. (ed.): ''The biology of terrestrial molluscs''. CABI Publishing, Oxon, UK, 2001, . 1–146, cited pages: 179–211. Olfactory organs In terrestrial gastropods the most important sensory organs are the olfactory organs which are located on the tips of the 4 tentacles. Some terrestrial gastropods can track the odor of food using their tentacles ( tropotaxis) and the wind ( anemotaxis). In opisthobranch marine gastropods, the chemosensory organs are two protruding structures on top of the head. These are known as rhinophores. An opisthobranch sea slug ''Navanax inermis'' has chemoreceptors on the sides of its mouth to track mucopolysaccharides in the slime trails of prey, and of potential mates. The freshwater snail ''Bithynia tentaculata'' is capable of de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolith
An otolith ( grc-gre, ὠτο-, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called statoconium or otoconium or statolith, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the ''otolith organs''. These organs are what allows an organism, including humans, to perceive linear acceleration, both horizontally and vertically (gravity). They have been identified in both extinct and extant vertebrates. Counting the annual growth rings on the otoliths is a common technique in estimating the age of fish. Description Endolymphatic infillings such as otoliths are structures in the saccule and utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular labyrinth of all vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds). In vertebrates, the saccule and utricle together make the ''otolith organs''. Both statoconia and otoliths are used as gravity, balance, movement, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by jet propulsion, and largely locate their prey by sight. They are among the most intelligent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidarian Anatomy
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scyphozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda ( Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by '' Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
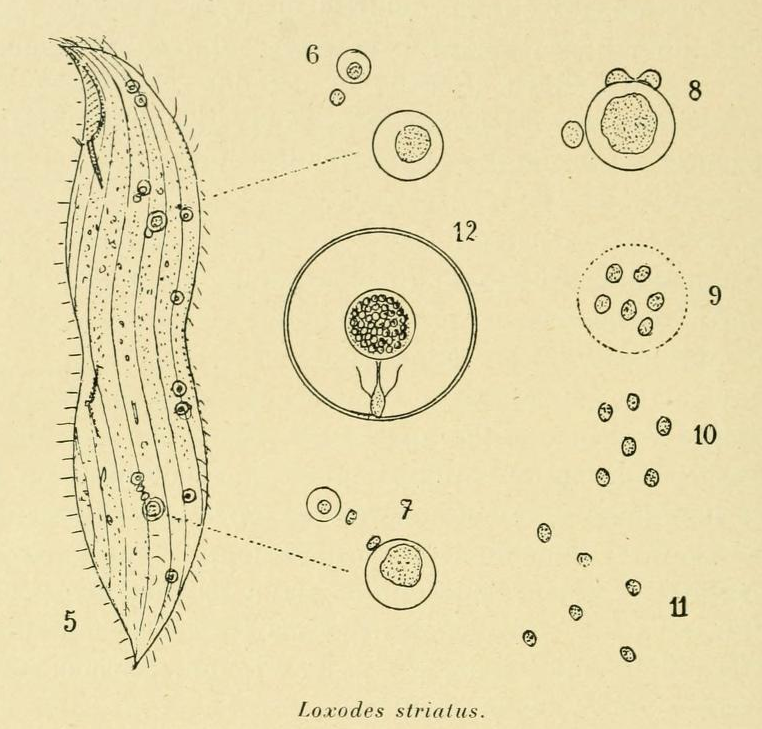
Loxodidae
Loxodidae is a family of karyorelict ciliates. Loxodidae members possess an elongated, laterally flattened shape. They share two key characters: a beak-like anterior rostrum interrupting the perioral kineties, and peculiar cytoplasmic organelles named Müller vesicles. The extensive development of lacunae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum leads to strong vacuolization of the endoplasm. This feature is associated to a lack of contractile vacuoles in all loxodids. The term ''Loxodidae'' derives from the ancient Greek (), meaning "oblique, tilted". Gravitaxis Loxodidae members possess the ability to orient themselves in oxygen gradients. They use gravity as a stimulus for this spatial orientation, a phenomenon called gravitaxis or geotaxis. Loxodid ciliates must therefore have developed mechanoreceptors informing them about what is up or down. A likely candidate structure for their gravitaxis is the Müller vesicle. Müller vesicle Müller vesicles (also known as Mülle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Müllerian Vesicle
Loxodidae is a family of karyorelict ciliates. Loxodidae members possess an elongated, laterally flattened shape. They share two key characters: a beak-like anterior rostrum interrupting the perioral kineties, and peculiar cytoplasmic organelles named Müller vesicles. The extensive development of lacunae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum leads to strong vacuolization of the endoplasm. This feature is associated to a lack of contractile vacuoles in all loxodids. The term ''Loxodidae'' derives from the ancient Greek (), meaning "oblique, tilted". Gravitaxis Loxodidae members possess the ability to orient themselves in oxygen gradients. They use gravity as a stimulus for this spatial orientation, a phenomenon called gravitaxis or geotaxis. Loxodid ciliates must therefore have developed mechanoreceptors informing them about what is up or down. A likely candidate structure for their gravitaxis is the Müller vesicle. Müller vesicle Müller vesicles (also known as Mül ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


.jpg)