|
Southern Bent-wing Bat
The southern bent-wing bat (''Miniopterus orianae bassanii'') is one of two subspecies of the Australasian bent-wing bat. Its population size has declined rapidly since the 1950s, and it is classified as critically endangered by the Australian government. Taxonomy In 2000, the common bent-wing bat of Australia was revised into three subspecies, including the southern bent-wing bat.Cardinal, B. R., & Christidis, L. (2000). Mitochondrial DNA and morphology reveal three geographically distinct lineages of the large bentwing bat (Miniopterus schreibersii) in Australia. Australian Journal of Zoology, 48(1), 1-19. However, it is now recognized as a subspecies of the Australasian bent-wing bat (''Miniopterus orianae''). There is evidence to suggest that it is reproductively isolated from the other Australian subspecies, and warrants elevation to its own species based on genetics. Etymology The subspecies name is derived from the border between this subspecies and the eastern bent-wing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasian Bent-wing Bat
The Australasian bent-wing bat (''Miniopterus orianae'') is a species of vesper bat in the family Miniopteridae. It is found in Australia and in Southeast Asia. Taxonomy The Australasian bent-wing bat was described as a new species in 1922 by British zoologist Oldfield Thomas. The holotype had been collected on 9 July 1922 by Oriana F. Wilson, widow of Antarctic explorer Edward Adrian Wilson. Thomas named the species ''Miniopterus orianae''. This species was once considered a subspecies of common bent-wing bat. It is now accepted that the Australasian bent-winged bat and the Eastern bent-winged bat are two distinct species. The Australasian bent-wing bat has three subspecies: ''M. orianae bassanii'' (the southern bent-wing bat), ''M. o. orianae'' (the northern bent-wing bat), and ''M. o. oceanensis'' (the eastern bent-wing bat). Ecology It is known to harbor the blood parasite ''Polychromophilus melanipherus'', though one study found that bats with the blood parasite did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protector Of Aborigines
The role of Protector of Aborigines was first established in South Australia in 1836. The role became established in other parts of Australia pursuant to a recommendation contained in the ''Report of the Parliamentary Select Committee on Aboriginal Tribes, (British settlements.)'' of the UK's Parliamentary Select Committee on Aboriginal Tribes. On 31 January 1838, Lord Glenelg, Secretary of State for War and the Colonies sent Governor Gipps of NSW the report. The report recommended that protectors of Aborigines should be engaged. They would be required to learn the Aboriginal language and their duties would be to watch over the rights of Indigenous Australians (mostly mainland Aboriginal Australians, but also Torres Strait Islander people), guard against encroachment on their property and to protect them from acts of cruelty, oppression and injustice. In many colonial, state, territory and similar jurisdictions a chief protector was appointed. Matthew Moorhouse became the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
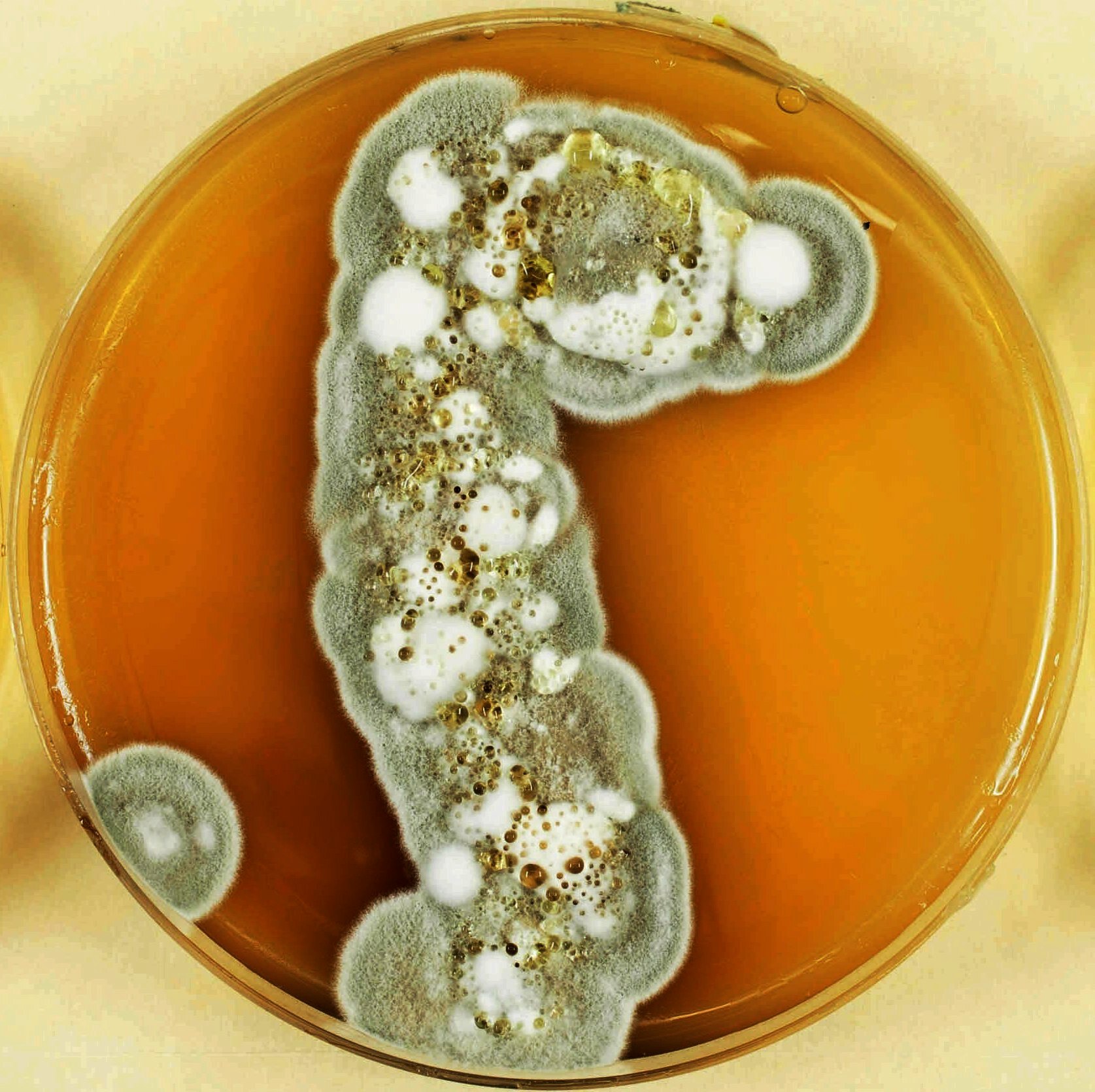
Pseudogymnoascus Destructans
''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' (formerly known as ''Geomyces destructans'') is a psychrophilic (cold-loving) fungus that causes white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fatal disease that has devastated bat populations in parts of the United States and Canada. Unlike species of ''Geomyces'', ''P. destructans'' forms asymmetrically curved conidia. ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' grows very slowly on artificial media and cannot grow at temperatures above 20 °C. It can grow around 4 °C to 20 °C, which encompasses the temperatures found in winter bat hibernacula. Phylogenic evaluation has revealed this organism should be reclassified under the family ''Pseudeurotiaceae'', changing its name to ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans''. History In 2008, Blehert ''et al.'' described the fungus associated with white-nose syndrome as a member of the genus ''Geomyces''. In 2009, Gargas ''et al.'' were the first to describe the fungus as a unique species; the specific name they chose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-nose Syndrome
White-nose syndrome (WNS) is a fungal disease in North American bats which has resulted in the dramatic decrease of the bat population in the United States and Canada, reportedly killing millions as of 2018. The condition is named for a distinctive fungal growth around the muzzles and on the wings of hibernating bats. It was first identified from a February 2006 photo taken in a cave located in Schoharie County, New York. The syndrome has rapidly spread since then. In early 2018, it was identified in 33 U.S. states and seven Canadian provinces; plus the fungus, albeit sans syndrome, had been found in three additional states. Most cases are in the eastern half of both countries, but in March 2016, it was confirmed in a little brown bat in Washington state. In 2019, evidence of the fungus was detected in California for the first time, although no affected bats were found. The disease is caused by the fungus ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'', which colonizes the bat's skin. No obvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) is a chemical compound formed by the loss of hydrogen chloride (dehydrohalogenation) from DDT, of which it is one of the more common breakdown products. Due to DDT's massive prevalence in society and agriculture during the mid 20th century, DDT and DDE are still widely seen in animal tissue samples. DDE is particularly dangerous because it is fat-soluble like other organochlorines; thus, it is rarely excreted from the body, and concentrations tend to increase throughout life. The major exception is the excretion of DDE in breast milk, which transfers a substantial portion of the mother's DDE burden to the young animal or child. Along with accumulation over an organism's lifetime, this stability leads to bioaccumulation in the environment, which amplifies DDE's negative effects. Synthesis DDE is created by dehydrohalogenation of DDT. The loss of HCl results in a double bond on the central (previously quaternary) carbon atoms. Toxicity DDE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane (DDD) is an organochlorine insecticide that is slightly irritating to the skin.Merck Index, 11th ed, p482 DDD is a metabolite of DDT.“p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane (DDD) (CASRN 72-54-8).” ''Integrated Risk Information System''. 25 Jan. 2007. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 23 Apr. 2007 . DDD is colorless and crystalline;Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” ''Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. it is closely related chemically and is similar in properties to DDT, but it is considered to be less toxic to animals than DDT.Guralnik, David B., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” ''Webster’s New World Dictionary of the American Language''. Second College Edition. New York, NY: Prentice Hall Press, 1986. The molecular formula for DDD is (ClC6H4)2CHCHCl2 or C14H10Cl4, whereas the formula for DDT is (ClC6H4)2CHCCl3 or C14H9Cl5. DDD is in the “ Group B2” classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a lesser extent, sought for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials. The 19th-century seabird guano trade played a pivotal role in the development of modern input-intensive farming. The demand for guano spurred the human colonization of remote bird islands in many parts of the world. Unsustainable seabird guano mining processes can result in permanent habitat destruction and the loss of millions of seabirds. Bat guano is found in caves throughout the world. Many cave ecosystems are wholly dependent on bats to provide nutrients via their guano which supports bacteria, fungi, invertebrates, and vertebrates. The loss of bats from a cave can result in the extinction of species that rely on their guano. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Genetics
Conservation genetics is an interdisciplinary subfield of population genetics that aims to understand the dynamics of genes in populations principally to avoid extinction. Therefore, it applies genetic methods to the conservation and restoration of biodiversity. Researchers involved in conservation genetics come from a variety of fields including population genetics, molecular ecology, biology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. Genetic diversity is one of the three fundamental levels of biodiversity, so it is directly important in conservation. Genetic variability influences both the health and long-term survival of populations because decreased genetic diversity has been associated with reduced fitness, such as high juvenile mortality, diminished population growth, reduced immunity, and ultimately, higher extinction risk. Genetic diversity Genetic diversity is the variability of genes in a species. A number of means can express the level of genetic diversity: observed hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian D
Ian or Iain is a name of Scottish Gaelic origin, derived from the Hebrew given name (Yohanan, ') and corresponding to the English name John. The spelling Ian is an Anglicization of the Scottish Gaelic forename ''Iain''. It is a popular name in Scotland, where it originated, as well as other English-speaking countries. The name has fallen out of the top 100 male baby names in the United Kingdom, having peaked in popularity as one of the top 10 names throughout the 1960s. In 1900, Ian was the 180th most popular male baby name in England and Wales. , the name has been in the top 100 in the United States every year since 1982, peaking at 65 in 2003. Other Gaelic forms of "John" include "Seonaidh" ("Johnny" from Lowland Scots), "Seon" (from English), "Seathan", and "Seán" and "Eoin" (from Irish). Its Welsh counterpart is Ioan, its Cornish equivalent is Yowan and Breton equivalent is Yann. Notable people named Ian As a first name (alphabetical by family name) *Ian Agol (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Augustus Robinson
George Augustus Robinson (22 March 1791 – 18 October 1866) was a British-born colonial official and self-trained preacher in colonial Australia. In 1824, Robinson travelled to Hobart, Van Diemen’s Land, where he attempted to negotiate a peace between European settlers and Aboriginal Tasmanians prior to the outbreak of the Black War. He was appointed Chief Protector of Aborigines by the Aboriginal Protection Board in Port Phillip District, New South Wales in 1839, a position he held until 1849. Early life Robinson was born on 22 March 1791, probably in London, England, to William Robinson, a construction worker, and Susannah Robinson (''née'' Perry). He followed his father into the building trade, married Maria Amelia Evans on 28 February 1814, and had five children over the next ten years. He was connected with the engineering department at the Chatham Dockyard and had some involvement with the construction of martello towers along England's coast, possibly as a supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skipton, Victoria
Skipton is a town in the Western District of Victoria, Australia. The town is situated on the Glenelg Highway 166 kilometres west of the state capital, Melbourne and 52 kilometres south west of the regional centre, Ballarat. Skipton is in the Shire of Corangamite LGA and is on the banks of Mount Emu Creek. At the , Skipton had a population of 586, considerably less than the population of 927 at the . Skipton is named after Skipton, in Yorkshire, England and is known as "the home of the platypus". History Skipton was first established in 1839 as a pastoral run and a town site was surveyed in 1852. The town was settled some years later, with a local Post Office opening on the 6th of March 1858. The town held the first agricultural show in the Western District in 1859. Skipton once had a Magistrates' Court, but it closed on the 1st of January 1983. Culture Economy Fine wool is the main agricultural product of the Skipton area. Skipton Variety Market is held on every second Sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |