|
Sophora
''Sophora'' is a genus of about 45 species of small trees and shrubs in the pea family Fabaceae. The species have a pantropical distribution. The generic name is derived from ''sophera'', an Arabic name for a pea-flowered tree. The genus formerly had a broader interpretation including many other species now treated in other genera, notably ''Styphnolobium'' (pagoda tree genus), which differs in lacking nitrogen fixing bacteria (rhizobia) on the roots, and ''Dermatophyllum'' (the mescalbeans). ''Styphnolobium'' has galactomannans as seed polysaccharide reserve, in contrast ''Sophora'' contains arabinogalactans, and ''Dermatophyllum'' amylose. The New Zealand ''Sophora'' species are known as kowhai. The seeds of species such as ''Sophora affinis'' and ''Sophora chrysophylla'' are reported to be poisonous. Fossil record One ''Sophora'' fossil seed pod from the middle Eocene epoch has been described from the Miller clay pit in Henry County, Tennessee, United States. Species ''Sop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Styphnolobium Japonicum
''Styphnolobium japonicum'', the Japanese pagoda tree (also known as the Chinese scholar tree and pagoda tree; syn. ''Sophora japonica'') is a species of tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae. It was formerly included within a broader interpretation of the genus '' Sophora''. The species of ''Styphnolobium'' differ from ''Sophora'' in lacking the ability to form symbioses with rhizobia (nitrogen fixing bacteria) on their roots. It also differs from the related genus ''Calia'' (mescalbeans) in having deciduous leaves and flowers in axillary, not terminal, racemes. The leaves are alternate, pinnate, with nine to 21 leaflets, and the flowers in pendulous racemes similar to those of the black locust. Distribution ''Styphnolobium japonicum'' is native to China; despite the name, it was introduced in Japan. It is a popular ornamental tree in Europe, North America and South Africa, grown for its white flowers, borne in late summer after most other flowering trees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobia
Rhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. In general, they are gram negative, motile, non- sporulating rods. Rhizobia are a "group of soil bacteria that infect the roots of legumes to form root nodules". Rhizobia are found in the soil and after infection, produce nodules in the legume where they fix nitrogen gas (N2) from the atmosphere turning it into a more readily useful form of nitrogen. From here, the nitrogen is exported from the nodules and used for growth in the legume. Once the legume dies, the nodule breaks down and releases the rhizobia back into the soil where they can live individually or reinfect a new legume host. History The first known species of rhizobia, '' Rhizobium leguminosarum'', was identified in 1889, and all further species were initially placed in the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophora Tomentosa
Sophora tomentosa, also known as necklacepod, yellow necklacepod, and occasionally as silver bush, is a pantropical shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae. It commonly ranges in height from 4 to 10 feet and often occurs in coastal conditions and near wetlands. The common name Necklacepod is derived from the characteristic string of seed pods that develop after its yellow flowers germinate into seeds. Necklacepod is a nectar plant for bees, butterflies, and in parts of the Americas hummingbirds as well. It is suggested for use by native plant enthusiasts in Florida as a good landscape plant for xeriscaping but it only naturally occurs in coastal counties in the central and southern part of the state, while closely related varieties occur in Texas Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular nitrogen (), with a strong triple covalent bond, in the air is converted into ammonia () or related nitrogenous compounds, typically in soil or aquatic systems but also in industry. Atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen, a relatively nonreactive molecule that is metabolically useless to all but a few microorganisms. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is an important microbials mediated process that converts dinitrogen (N2) gas to ammonia (NH3) using the nitrogenase protein complex (Nif). Nitrogen fixation is essential to life because fixed inorganic nitrogen compounds are required for the biosynthesis of all nitrogen-containing organic compounds, such as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates and nucleic acids. As part of the nitrogen cycle, it is essential for agriculture and the manufacture of fertilizer. It is also, indirectly, relevant to the manufacture of all nitrogen chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry County, Tennessee
Henry County is a county located on the northwestern border of the U.S. state of Tennessee, and is considered part of West Tennessee. As of the 2020 census, the population was 32,199. Its county seat is Paris. The county is named for the Virginia orator and American Founding Father Patrick Henry. Henry County comprises the Paris, TN Micropolitan Statistical Area. West Tennessee lands and commodity culture were associated with the lowlands and delta of the Mississippi River, which created fertile areas that supported cotton culture. During the antebellum era, numerous enslaved African Americans provided labor for the cotton plantations. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which are land and (5.3%) are covered by water. Adjacent counties * Calloway County, Kentucky (north) * Stewart County (northeast) * Benton County (southeast) * Carroll County (south) * Weakley County (west) *Graves County, Kentucky (northwest) National prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Epoch
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Journal Of Botany
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from '' Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation) * Northeast Wrestling, a professional wrestling promotion in the northeastern United States Transport * New Orleans Lakefront A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōwhai
Kōwhai ( or ) are small woody legume trees within the genus ''Sophora'' in the family Fabaceae that are native to New Zealand. There are eight species, with ''Sophora microphylla'' and '' S. tetraptera'' being the most recognised as large trees. Their natural habitat is beside streams and on the edges of forest, in lowland or mountain open areas. Kōwhai trees grow throughout the country and are a common feature in New Zealand gardens. Outside of New Zealand, kōwhai tend to be restricted to mild temperate maritime climates. The blooms of the kōwhai are widely regarded as being New Zealand's unofficial national flower.Kōwhai: Native plants (doc.govt.nz) As such, it is often incorporated as a visual shorthand for the country, such as in Meghan Markle's wedding veil which included distinctive flora representing all Commonwealth nations. The Māori word ''kōwhai'' is related to other words in some Polynesian languages that refer to different species that look superficially si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
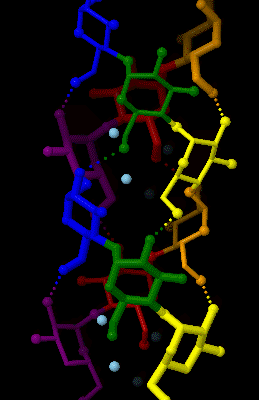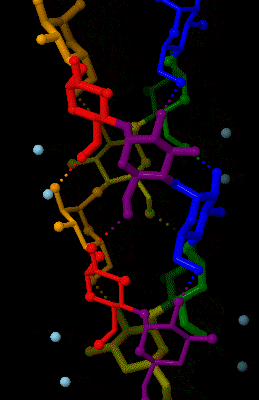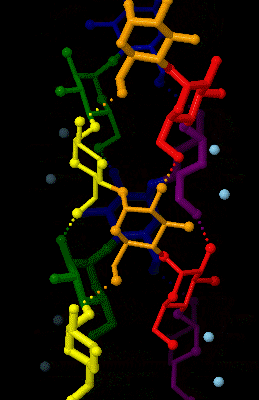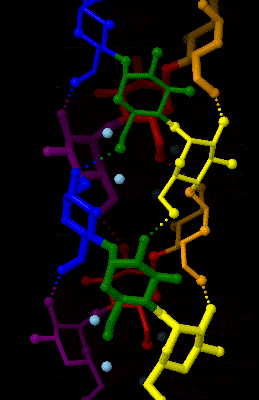
Amylose
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation or two different helical forms. It can bind with itself in a double helix (A or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |