|
Sodium Pertechnetate
Sodium pertechnetate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaTcO4. This colourless salt contains the pertechnetate anion, . The radioactive anion is an important radiopharmaceutical for diagnostic use. The advantages to include its short half-life of 6 hours and the low radiation exposure to the patient, which allow a patient to be injected with activities of more than 30 millicuries. is a precursor to a variety of derivatives that are used to image different parts of the body. Chemistry is the starting material for most of the chemistry of technetium. Pertechnetate salts are usually colorless. is produced by oxidizing technetium with nitric acid or with hydrogen peroxide. The pertechnetate anion is similar to the permanganate anion but is a weaker oxidizing agent. It is tetrahedral and diamagnetic. The standard electrode potential for / is only +0.738 V in acidic solution, as compared to +1.695 V for /. Because of its diminished oxidizing power, is stable in alkaline so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheelite
Scheelite is a calcium tungstate mineral with the chemical formula Ca W O4. It is an important ore of tungsten (wolfram). Scheelite is originally named after Swedish chemist K. Scheele (1742-1786). Well-formed crystals are sought by collectors and are occasionally fashioned into gemstones when suitably free of flaws. Scheelite has been synthesized using the Czochralski process; the material produced may be used to imitate diamond, as a scintillator, or as a solid-state lasing medium. It was also used in radium paint in the same fashion as was zinc sulphide, and Thomas Edison invented a fluoroscope with a calcium tungstate-coated screen, making the images six times brighter than those with barium platinocyanide; the latter chemical allowed Röntgen to discover X-rays in early November 1895. Properties Its crystals are in the tetragonal crystal system, appearing as dipyramidal pseudo-octahedra. Colors include golden yellow, brownish green to dark brown, pinkish to reddis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidizing Agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens. In one sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that undergoes a chemical reaction in which it gains one or more electrons. In that sense, it is one component in an oxidation–reduction (redox) reaction. In the second sense, an oxidizing agent is a chemical species that transfers electronegative atoms, usually oxygen, to a substrate. Comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Compounds
Sodium atoms have 11 electrons, one more than the stable configuration of the noble gas neon. As a result, sodium usually forms ionic compounds involving the Na+ cation. Sodium is a reactive alkali metal and is much more stable in ionic compounds. It can also form intermetallic compounds and organosodium compounds. Sodium compounds are often soluble in water. Metallic sodium Metallic sodium is generally less reactive than potassium and more reactive than lithium. Sodium metal is highly reducing, with the standard reduction potential for the Na+/Na couple being −2.71 volts, though potassium and lithium have even more negative potentials. The thermal, fluidic, chemical, and nuclear properties of molten sodium metal have caused it to be one of the main coolants of choice for the fast breeder reactor. Such nuclear reactors are seen as a crucial step for the production of clean energy. Salts and oxides Sodium compounds are of immense commercial importance, being particularly cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Radioanalytical And Nuclear Chemistry
The ''Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Springer Science+Business Media. It publishes original papers, review papers, short communications and letters on nuclear chemistry. Some of the subjects covered are nuclear chemistry, radiation chemistry, nuclear power plant chemistry, radioanalytical chemistry, and environmental radiochemistry. Impact factor The ''Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry'' had a 2014 impact factor of 1.034, ranking it 15th out of 34 in the subject category "Nuclear Science and Technology", 57th out of 74 in "Analytical Chemistry", and 31st out of 44 in "Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry". Editor The founding |
Journal Of Chromatography B
The ''Journal of Chromatography B'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research papers in analytical chemistry, with a focus on chromatography techniques and methods in the biological and life sciences. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', 'Journal of Chromatography B'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.205, ranking it 36th out of 83 in the category of Chemistry, Analytical. See also * Journal of Chromatography A References Publications established in 1958 Elsevier academic journals Chemistry journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large or hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of the barrier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microanatomy T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
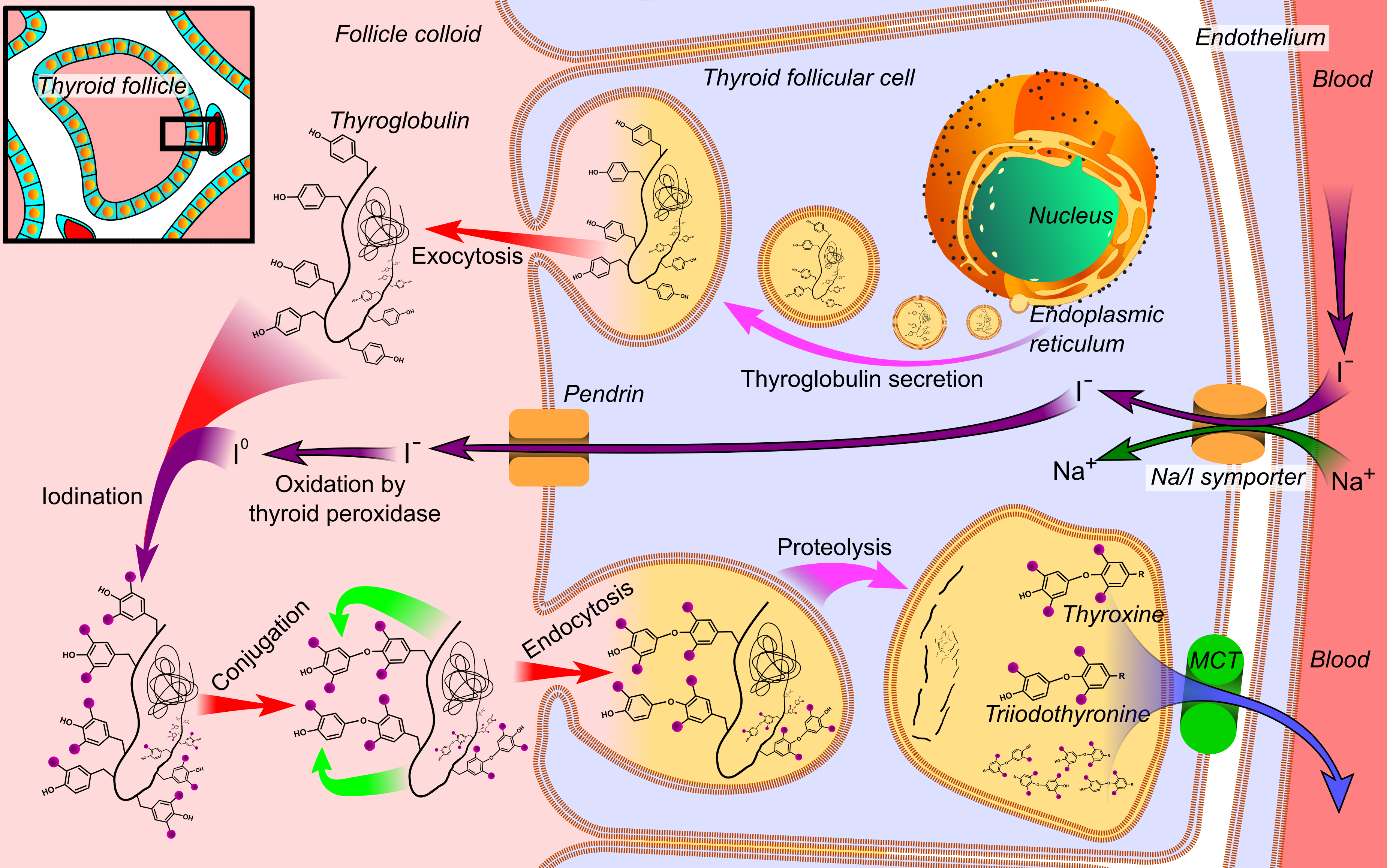
Thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment of the thyroid follicles, accounting for approximately half of the protein content of the thyroid gland. Human TG (hTG) is a homodimer of subunits each containing 2768 amino acids as synthesized (a short signal peptide of 19 aminoacids may be removed from the N-terminus in the mature protein). Thyroglobulin is in all vertebrates the main precursor to thyroid hormones, which are produced when thyroglobulin's tyrosine residues are combined with iodine and the protein is subsequently cleaved. Each thyroglobulin molecule contains approximately 100–120 tyrosine residues, but only a small number (20) of these are subject to iodination by thyroperoxidase in the follicular colloid. Therefore, each Tg molecule forms approximately 10 thyroid h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanganate
A permanganate () is a chemical compound containing the manganate(VII) ion, , the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion is a transition metal oxo complex with tetrahedral geometry. Permanganate solutions are purple in color and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction is dependent upon the organic contaminants present and the oxidant utilized. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidized by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−). :8 + 3 → 6 + 8 + + 4 + 9 In an acidic solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the pale pink +2 oxidation state of the manganese(II) (Mn2+) ion. :8 + + 5 e− → Mn2+ + 4 H2O In a strongly basic solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the green +6 oxidation state of the manganate ion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Permanganate
Sodium permanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na MnO4. It is closely related to the more commonly encountered potassium permanganate, but it is generally less desirable, because it is more expensive to produce. It is mainly available as the monohydrate. This salt absorbs water from the atmosphere and has a low melting point. Being about 15 times more soluble than KMnO4, sodium permanganate finds some applications where very high concentrations of MnO4− are sought. Preparation and properties Sodium permanganate cannot be prepared analogously to the route to KMnO4 because the required intermediate manganate salt, Na2MnO4, does not form. Thus less direct routes are used including conversion from KMnO4.Arno H. Reidies "Manganese Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Sodium permanganate behaves similarly to potassium permanganate. It dissolves readily in water to give deep purple solutions, evaporation of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |