|
Sinapic Aldehyde
Sinapaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula HO(CH3O)2C6H2CH=CHCHO. It is a derivative of cinnamaldehyde, featuring one hydroxy group and two methoxy groups as substituents. It is an intermediate in the formation of sinapyl alcohol, a lignol that is a major precursor to lignin. Biosynthetic role In sweetgum (''Liquidambar styraciflua''), sinapaldehyde arises in two steps from coniferyl aldehyde beginning with hydroxylation mediated by coniferyl aldehyde 5-hydroxylase. The diphenol is then methylated at the 5-OH by the action of caffeate ''O''-methyltransferase. Sinapaldehyde is reduced to the alcohol by the action of dehydrogenase enzymes. In '' Arabidopsis thaliana'', the enzyme dihydroflavonol 4-reductase uses NADP+ to reduce sinapaldehyde to sinapyl alcohol. It is found in '' Senra incana'' (Hibisceae). It is a low molecular weight phenol that is susceptible to extraction from cork stoppers into wine.Polyphenolic Composition of ''Quercus suber'' Cork from D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamaldehyde
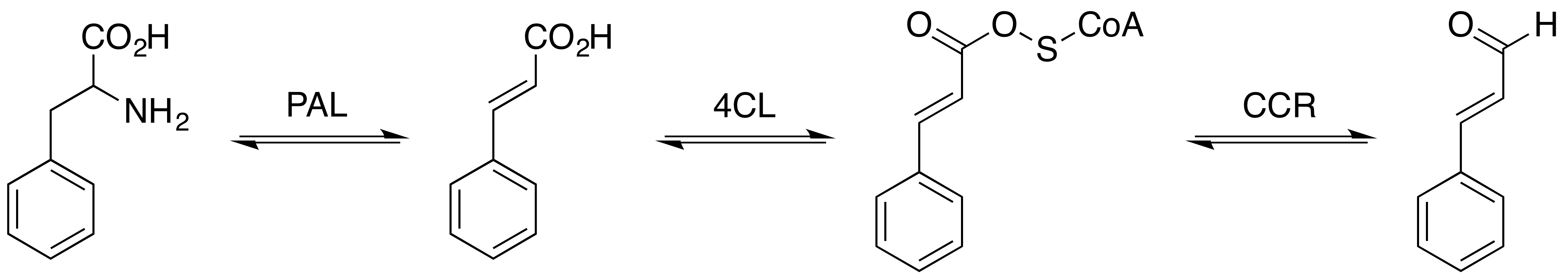
Cinnamaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula(C9H8O) C6H5CH=CHCHO. Occurring naturally as predominantly the ''trans'' (''E'') isomer, it gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. It is a phenylpropanoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. This pale yellow, viscous liquid occurs in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus '' Cinnamomum''. The essential oil of cinnamon bark is about 90% cinnamaldehyde. Cinnamaldehyde decomposes to styrene because of oxidation as a result of bad storage or transport conditions. Styrene especially forms in high humidity and high temperatures. This is the reason why cinnamon contains small amounts of styrene. Structure and synthesis Cinnamaldehyde was isolated from cinnamon essential oil in 1834 by Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot and synthesized in the laboratory by the Italian chemist Luigi Chiozza in 1854. The natural product is ''trans''-cinnamaldehyde. The molecule consists of a benzene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome around 135 megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is a popular tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual (rarely biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering stem. The basal leaves are green to slightly purplish in color, 1.5–5 cm long, and 2–10 mm broad, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canolol
Canolol is a phenolic compound found in crude canola oil. It is produced by decarboxylation of sinapic acid during canola seed roasting.Isolation and Identification of a Potent Radical Scavenger (Canolol) from Roasted High Erucic Mustard Seed Oil from Nepal and Its Formation during Roasting. Kshitij Shrestha, Christian V Stevens, Bruno De Meulenaer, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2012, 60 (30), pp 7506–7512, See also *Phenolic content in wine * Syringaldehyde *Syringol *Syringic acid * Acetosyringone * Sinapyl alcohol * Sinapaldehyde *Sinapinic acid Sinapinic acid, or sinapic acid (Sinapine - Origin: L. Sinapi, sinapis, mustard, Gr., cf. F. Sinapine.), is a small naturally occurring hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a member of the phenylpropanoid family. It is a commonly used matrix in MALDI mass ... * Sinapine References O-methylated natural phenols Vinyl compounds Vegetable oils {{phenol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinapine
Sinapine is an alkaloidal amine found in some seeds, particularly oil seeds of plants in the family Brassicaceae. It is the choline ester of sinapic acid. Sinapine was discovered by Etienne Ossian Henry in 1825. Occurrence Sinapine typically occurs in the outer seed coat of oil crops and is plentiful in some types of press cake leftover after vegetable oil extraction. Typical oil seed cake residues high in sinapine include ''Brassica juncea'' (1.22% by mass), and rapeseed (0.39-1.06% by mass). Isolation The typical protocol for extracting Sinapine from seed cakes entails defatting the cake with hexane via a Soxhlet apparatus followed by extraction with 70% methanol held at 75 °C. Metabolism Sinapine esterase is an enzyme whose two substrates are sinapine and H2O and whose two products are sinapic acid and choline. Sinapoylglucose—choline O-sinapoyltransferase is an enzyme whose two substrates are 1-''O''-sinapoyl-β-D-glucose and choline, whereas its two pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinapinic Acid
Sinapinic acid, or sinapic acid (Sinapine - Origin: L. Sinapi, sinapis, mustard, Gr., cf. F. Sinapine.), is a small naturally occurring hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a member of the phenylpropanoid family. It is a commonly used matrix in MALDI mass spectrometry. It is a useful matrix for a wide variety of peptides and proteins. It serves well as a matrix for MALDI due to its ability to absorb laser radiation and to also donate protons (H+) to the analyte of interest. Sinapic acid can form dimers with itself (one structure) and ferulic acid (three different structures) in cereal cell walls and therefore may have a similar influence on cell-wall structure to that of the diferulic acids. Sinapine is an alkaloidal amine found in black mustard seeds. It is considered a choline ester of sinapinic acid. Natural occurrences Sinapinic acid can be found in wine and vinegar. Metabolism Sinapate 1-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that uses UDP-glucose and sinapate to produce UDP and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetosyringone
Acetosyringone is a phenolic natural product and a chemical compound related to acetophenone and 2,6-dimethoxyphenol. It was first described in relation to lignan/phenylpropanoid-type phytochemicals, with isolation from a variety of plant sources, in particular, in relation to wounding and other physiologic changes. Occurrence and biological role Historically, this substance has been best known for its involvement in plant-pathogen recognition, especially its role as a signal attracting and transforming unique, oncogenic bacteria in genus ''Agrobacterium''. The ''virA'' gene on the Ti plasmid of ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and the Ri plasmid of '' Agrobacterium rhizogenes'' is used by these soil bacteria to infect plants, via its encoding for a receptor for acetosyringone and other phenolic phytochemicals exuded by plant wounds. This compound also allows higher transformation efficiency in plants, as shown in ''A. tumefaciens''-mediated transformation procedures, and so is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringic Acid
Syringic acid is a naturally occurring phenolic compound and dimethoxybenzene that is commonly found as a plant metabolite. Natural occurrence Syringic acid can be found in several plants including ''Ardisia elliptica'' and '' Schumannianthus dichotomus''. Synthesis Syringic acid can be prepared by selectively hydrolyzing ( demethylating) eudesmic acid with 20% sulfuric acid. Presence in food Syringic acid can be found in several fruits including olives, dates, spices, pumpkin, grapes, acai palm, honey, red wine, among others. Its presence in the ancient Egyptian drink shedeh could confirm it was made out of grape, as syringic acid is released by the breakdown of the compound malvidin, also found in red wine. It is also found in vinegar. Applications Various studies have found syringic acid to exhibit useful pharmaceutical properties such as anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, anti-inflammation, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic. Syringic acid can be enzymatically polymerise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringol
Syringol is the organic compound with the formula HO(CH3O)2C6H3. The molecule is a phenol, with methoxy groups in the flanking (2 and 6) positions. It is the symmetrically dimethylated derivative of pyrogallol. It is a colorless solid, although typical samples are brown owing to air-oxidized impurities. Together with guaiacol, syringol and its derivatives are produced by the pyrolysis of lignin. Specifically, syringol is derived from the thermal decomposition of the sinapyl alcohol component. As such, syringol is an important component of wood smoke. Syringyl/guaiacyl ratio Lignin, comprising a major fraction of biomass, is sometimes classified according to the syringyl component. Pyrolysis of lignin derived from sinapyl alcohol affords syringol. The conversion involves replacement of the propenyl alcohol substituent of the sinapyl alcohol by hydrogen. A high syringyl (or S) content is indicative of lignin from angiosperms. In contrast, pyrolysis of lignin from gymnosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringaldehyde
Syringaldehyde is an organic compound that occurs in trace amounts widely in nature. Some species of insects use syringaldehyde in their chemical communication systems. ''Scolytus multistriatus'' uses it as a signal to find a host tree during oviposition. Because it contains many functional groups, it can be classified in many ways - aromatic, aldehyde, phenol. It is a colorless solid (impure samples appear yellowish) that is soluble in alcohol and polar organic solvents. Its refractive index is 1.53. Natural sources Syringaldehyde can be found naturally in the wood of spruce and maple trees. Syringaldehyde is also formed in oak barrels and extracted into whisky, which it gives spicy, smoky, hot and smoldering wood aromas. Preparation This compound may be prepared from syringol by the Duff reaction: : See also *Phenolic content in wine *Syringol *Syringic acid *Acetosyringone * Sinapyl alcohol *Sinapinic acid *Sinapaldehyde *Sinapine *Canolol Canolol is a phenolic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenolic Content In Wine
The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids. Origin of the phenolic compounds The natural phenols are not evenly distributed within the fruit. Phenolic acids are largely present in the pulp, anthocyanins and stilbenoids in the skin, and other phenols (catechins, proanthocyanidins and flavonols) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (material)
Cork is an impermeable buoyant material, the phellem layer of bark tissue that is harvested for commercial use primarily from '' Quercus suber'' (the cork oak), which is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa. Cork is composed of suberin, a hydrophobic substance. Because of its impermeable, buoyant, elastic, and fire retardant properties, it is used in a variety of products, the most common of which is wine stoppers. The montado landscape of Portugal produces approximately half of the cork harvested annually worldwide, with Corticeira Amorim being the leading company in the industry. Cork was examined microscopically by Robert Hooke, which led to his discovery and naming of the cell. Cork composition varies depending on geographic origin, climate and soil conditions, genetic origin, tree dimensions, age (virgin or reproduction), and growth conditions. However, in general, cork is made up of suberin (average of about 40%), lignin (22%), polysaccharides (cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |