|
Scikit-learn
scikit-learn (formerly scikits.learn and also known as sklearn) is a free and open-source machine learning library for the Python programming language. It features various classification, regression and clustering algorithms including support-vector machines, random forests, gradient boosting, ''k''-means and DBSCAN, and is designed to interoperate with the Python numerical and scientific libraries NumPy and SciPy. Scikit-learn is a NumFOCUS fiscally sponsored project. Overview The scikit-learn project started as scikits.learn, a Google Summer of Code project by French data scientist David Cournapeau. The name of the project derives from its role as a "scientific toolkit for machine learning", originally developed and distributed as a third-party extension to SciPy. The original codebase was later rewritten by other developers. In 2010, contributors Fabian Pedregosa, Gaël Varoquaux, Alexandre Gramfort and Vincent Michel, from the French Institute for Research in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support Vector Machine
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised max-margin models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories, SVMs are one of the most studied models, being based on statistical learning frameworks of VC theory proposed by Vapnik (1982, 1995) and Chervonenkis (1974). In addition to performing linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform non-linear classification using the ''kernel trick'', representing the data only through a set of pairwise similarity comparisons between the original data points using a kernel function, which transforms them into coordinates in a higher-dimensional feature space. Thus, SVMs use the kernel trick to implicitly map their inputs into high-dimensional feature spaces, where linear classification can be performed. Being max-margin models, SVMs are resilient to noisy data (e.g., misclassified examples). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Cournapeau
David Cournapeau is a data scientist. He is the original author of the scikit-learn package, an open source machine learning library in the Python programming language. Early life and education Cournapeau graduated with a MSc in Electrical Engineering from Telecom Paristech, Paris in 2004, and obtained his PhD in Computer Science at Kyoto University, Japan, in the domain of speech recognition. Career The scikit-learn project started as scikits.learn, a Google Summer of Code project by David Cournapeau. After having worked for Silveregg, a SaaS Japanese company delivering recommendation systems for Japanese online retailers, he worked for 6 years at Enthought, a scientific consulting company. He joined Cogent Labs, a Japanese Deep Learning/AI company, in 2017. He is a Machine Learning Engineering Manager at Mercari, Inc. Cournapeau has also been involved in the development of other central numerical Python libraries: NumPy and SciPy SciPy (pronounced "sigh pie") is a free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBSCAN
Density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) is a data clustering algorithm proposed by Martin Ester, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Jörg Sander, and Xiaowei Xu in 1996. It is a Cluster analysis#Density-based clustering, density-based clustering non-parametric algorithm: given a set of points in some space, it groups together points that are closely packed (points with many Fixed-radius near neighbors, nearby neighbors), and marks as outliers points that lie alone in low-density regions (those whose nearest neighbors are too far away). DBSCAN is one of the most commonly used and cited clustering algorithms. In 2014, the algorithm was awarded the Test of Time Award (an award given to algorithms which have received substantial attention in theory and practice) at the leading data mining conference, ACM SIGKDD. , the follow-up paper "DBSCAN Revisited, Revisited: Why and How You Should (Still) Use DBSCAN" appears in the list of the 8 most downloaded articles of the presti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Institute For Research In Computer Science And Automation
The National Institute for Research in Digital Science and Technology (Inria) () is a French national research institution focusing on computer science and applied mathematics. It was created under the name French Institute for Research in Computer Science and Automation (IRIA) () in 1967 at Rocquencourt near Paris, part of Plan Calcul. Its first site was the historical premises of SHAPE (central command of NATO military forces), which is still used as Inria's main headquarters. In 1980, IRIA became INRIA. Since 2011, it has been styled ''Inria''. Inria is a Public Scientific and Technical Research Establishment (EPST) under the double supervision of the French Ministry of National Education, Advanced Instruction and Research and the Ministry of Economy, Finance and Industry. Administrative status Inria has nine research centers distributed across France (in Bordeaux, Grenoble- Inovallée, Lille, Lyon, Nancy, Paris- Rocquencourt, Rennes, Saclay, and Sophia Antipolis) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-means Clustering
''k''-means clustering is a method of vector quantization, originally from signal processing, that aims to partition of a set, partition ''n'' observations into ''k'' clusters in which each observation belongs to the cluster (statistics), cluster with the nearest mean (cluster centers or cluster centroid), serving as a prototype of the cluster. This results in a partitioning of the data space into Voronoi cells. ''k''-means clustering minimizes within-cluster variances (squared Euclidean distances), but not regular Euclidean distances, which would be the more difficult Weber problem: the mean optimizes squared errors, whereas only the geometric median minimizes Euclidean distances. For instance, better Euclidean solutions can be found using k-medians clustering, ''k''-medians and k-medoids, ''k''-medoids. The problem is computationally difficult (NP-hardness, NP-hard); however, efficient heuristic algorithms converge quickly to a local optimum. These are usually similar to the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Forests
Random forests or random decision forests is an ensemble learning method for classification, regression and other tasks that works by creating a multitude of decision trees during training. For classification tasks, the output of the random forest is the class selected by most trees. For regression tasks, the output is the average of the predictions of the trees. Random forests correct for decision trees' habit of overfitting to their training set. The first algorithm for random decision forests was created in 1995 by Tin Kam Ho using the random subspace method, which, in Ho's formulation, is a way to implement the "stochastic discrimination" approach to classification proposed by Eugene Kleinberg. An extension of the algorithm was developed by Leo Breiman and Adele Cutler, who registered "Random Forests" as a trademark in 2006 (, owned by Minitab, Inc.). The extension combines Breiman's " bagging" idea and random selection of features, introduced first by Ho and later inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scikit-image
scikit-image (formerly scikits.image) is an open-source image processing library for the Python programming language. It includes algorithms for segmentation, geometric transformations, color space manipulation, analysis, filtering, morphology, feature detection, and more. It is designed to interoperate with the Python numerical and scientific libraries NumPy and SciPy. Overview The scikit-image project started as scikits.image, by Stéfan van der Walt. Its name stems from the notion that it is a "SciKit" (SciPy Toolkit), a separately-developed and distributed third-party extension to SciPy. The original codebase was later extensively rewritten by other developers. Of the various scikits, scikit-image as well as scikit-learn were described as "well-maintained and popular" . Scikit-image has also been active in the Google Summer of Code. Implementation scikit-image is largely written in Python, with some core algorithms written in Cython Cython () is a superset of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
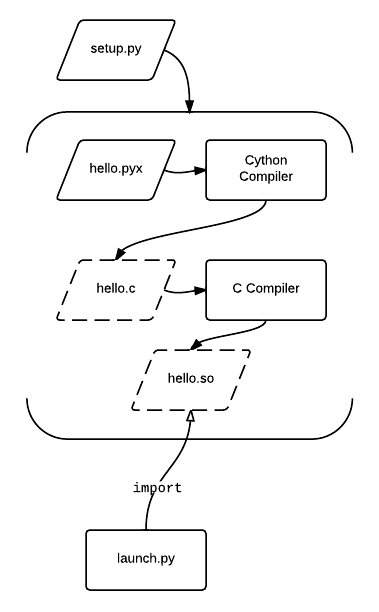
Cython
Cython () is a superset of the programming language Python, which allows developers to write Python code (with optional, C-inspired syntax extensions) that yields performance comparable to that of C. Cython is a compiled language that is typically used to generate CPython extension modules. Annotated Python-like code is compiled to C and then automatically wrapped in interface code, producing extension modules that can be loaded and used by regular Python code using the import statement, but with significantly less computational overhead at run time. Cython also facilitates wrapping independent C or C++ code into python-importable modules. Cython is written in Python and C and works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, producing C source files compatible with CPython 2.6, 2.7, and 3.3 and later versions. The Cython source code that Cython compiles (to C) can use both Python 2 and Python 3 syntax, defaulting to Python 2 syntax in Cython 0.x and Python 3 syntax in Cython 3.x. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSD-new
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses. BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all. Terms In addition to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |