|
Scent Glands
Scent gland are exocrine glands found in most mammals. They produce semi-viscous secretions which contain pheromones and other semiochemical compounds. These odor-messengers indicate information such as status, territorial marking, mood, and sexual behaviour. The odor may be subliminal—not consciously detectable. Though it is not their primary function, the salivary glands may also function as scent glands in some animals. In even-toed ungulates The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) have many specialized skin glands, the secretions of which are involved in semiochemical communication. These glands include the sudoriferous glands (located on the forehead, between the antlers and eyes), the preorbital glands (extending from the medial canthus of each eye), the nasal glands (located inside the nostrils), the interdigital glands (located between the toes), the preputial gland (located inside the foreskin of the penis), the metatarsal glands (located outside of the hind legs), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Gland
Anal may refer to: Related to the anus *Related to the anus of animals: ** Anal fin, in fish anatomy ** Anal vein, in insect anatomy ** Anal scale, in reptile anatomy *Related to the human anus: ** Anal sex, a type of sexual activity involving stimulation of the anus ** Anal stage, a term used by Sigmund Freud to describe the development during the second year of life ** Anal expulsive, people who have a carefree attitude ** Anal retentive, a person overly uptight or distressed over ordinarily minor problems Places * Anal Island, an island of the Marshall Islands * Añal, New Mexico, a ghost town Other uses * Anāl people, an ethnic group of northeast India and Myanmar **Anāl language, the Sino-Tibetan language they speak * Ammonal, or ANAL, an explosive made from ammonium nitrate (AN) and aluminium (AL) powder * '' All Nippon Air Line'', a 2008 boys love manga * Anal Arasu, Indian fight master/action choreographer See also * IANAL, a colloquial acronym for "I am not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canthus
The canthus (pl. canthi, palpebral commissures) is either corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet. More specifically, the inner and outer canthi are, respectively, the medial and lateral ends/angles of the palpebral fissure. The bicanthal plane is the transversal plane linking both canthi and defines the upper boundary of the midface. Etymology The word ' is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ('), meaning 'corner of the eye'. Population distribution The eyes of those of East Asian and some Southeast Asian people tend to have the inner canthus veiled by the epicanthus. In the Caucasian or double eyelid, the inner corner tends to be exposed completely. Commissures * The ''lateral palpebral commissure'' (commissura palpebrarum lateralis; external canthus) is more acute than the medial, and the eyelids here lie in close contact with the bulb of the eye. * The ''medial palpebral commissure'' (commissura palpebrarum medialis; internal canthus) is prolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-tailed Deer
Two forms of black-tailed deer or blacktail deer that occupy coastal woodlands in the Pacific Northwest of North America are subspecies of the mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus''). They have sometimes been treated as a species, but virtually all recent authorities maintain they are subspecies.Novak, R. M. (1999). ''Walker's Mammals of the World.'' 6th edition. Heffelfinger, J. (version 2 March 2011). Tails with a dark side: The truth about whitetail – mule deer hybrids.''Reid, F. A. (2006). ''Mammals of North America.'' 4th edition. Geist, V. (1998). ''Deer of the world: their evolution, behaviour, and ecology.'' Feldhamer, G. A., B. C. Thompson, and J. A. Chapman, editors (2003). Wild mammals of North America: biology, management, and conservation'' 2nd edition. The Columbian black-tailed deer (''Odocoileus hemionus columbianus'') is found in western North America, from Northern California into the Pacific Northwest of the United States and coastal British Columbia in Canada.B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Urine
Urination, also known as micturition, is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, and pissing. In healthy humans (and many other animals), the process of urination is under voluntary control. In infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury, urination may occur as a reflex. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day. In some animals, in addition to expelling waste material, urination can mark territory or express submissiveness. Physiologically, urination involves coordination between the central, autonomic, and somatic nervous systems. Brain centres that regulate urination include the pontine micturition center, periaqueductal gray, and the cerebral cortex. In placental mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rub-urination
Self-anointing in animals, sometimes called anointing or anting, is a behaviour whereby a non-human animal smears odoriferous substances over themselves. These substances are often the secretions, parts, or entire bodies of other animals or plants. The animal may chew these substances and then spread the resulting saliva mixture over their body, or they may apply the source of the odour directly with an appendage, tool or by rubbing their body on the source. The functions of self-anointing differ between species, but it may act as self-medication, repel parasites, provide camouflage, aid in communication, or make the animal poisonous. Primates Several primate species self-anoint with various items such as millipedes, leaves and fruit. They sometimes drool while doing this. Both capuchin monkeys and squirrel monkeys perform urine washing, when they deposit a small quantity of urine onto the palm of a hand and then rub it on the sole of the opposite foot. It is thought to have m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
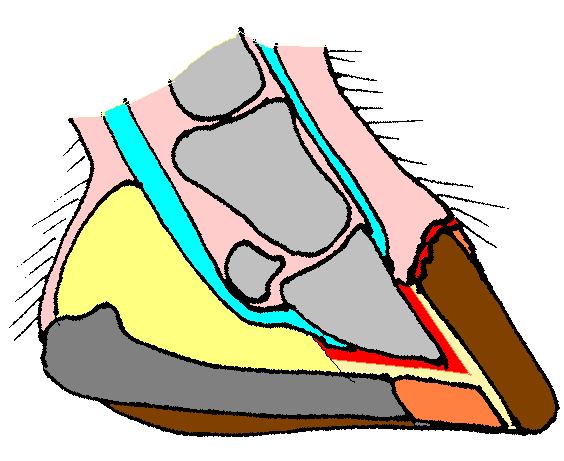
Hoof
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the ruminants with two digits, are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goat, and sheep. The feet of perissodactyl mammals have an odd number of toes, e.g. the horse, the rhinoceros, and the tapir. Hooves are limb structures restricted to placental mammals, which have long pregnancies; however, the marsupial ''Chaeropus'' had hooves. Description The hoof surrounds the distal end of the second phalanx, the distal phalanx, and the navicular bone. The hoof consists of the hoof wall, the bars of the hoof, the sole and frog and soft tissue shock absorption structures. The weight of the animal is normally borne by both the sole and the edge of the hoof wall. Hooves perform many functions, including supporting the weight of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
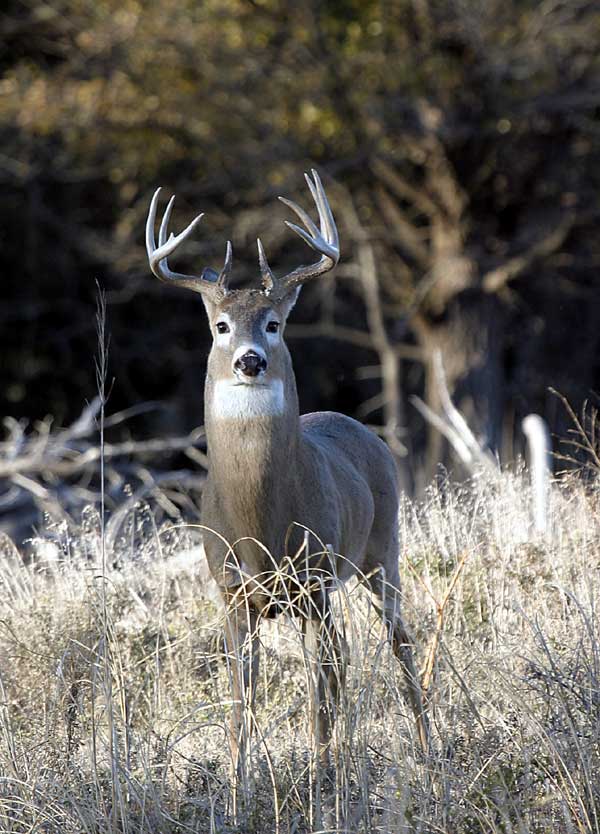
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black-tailed or mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') from that point west except for mixed deciduous riparian corridors, river valley bottomlands, and lower foothills of the northern Rocky Mountain region from Wyoming west to eastern Washington and eastern Oregon and north to nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black-tailed or mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') from that point west except for mixed deciduous riparian corridors, river valley bottomlands, and lower foothills of the northern Rocky Mountain region from Wyoming west to eastern Washington and eastern Oregon and north to nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family ( Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer (Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in herald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hock (anatomy)
The hock, or gambrel, is the joint between the tarsal bones and tibia of a digitigrade or unguligrade quadrupedal mammal, such as a horse, cat, or dog. This joint may include articulations between tarsal bones and the fibula in some species (such as cats), while in others the fibula has been greatly reduced and is only found as a vestigial remnant fused to the distal portion of the tibia (as in horses).{{citation needed, date=January 2016 It is the anatomical homologue of the ankle of the human foot. While homologous joints occur in other tetrapods, the term is generally restricted to mammals, particularly long-legged domesticated species. Horse Although the ''tarsus'' refers specifically to the bones and joints of the hock, most people working with horses refer to the ''hock'' in such a way to include the bones, joints, and soft tissue of the area. The hock is especially important in equine anatomy, due to the great strain it receives when the horse is worked. Jumping, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsal Gland (ungulate)
Tarsal may refer to: * Tarsal artery (other) * Tarsal bone * Tarsal glands * tarsus (skeleton) (skeleton) * tarsus (eyelids) (eye) * superior tarsal muscle The superior tarsal muscle is a smooth muscle adjoining the levator palpebrae superioris muscle that helps to raise the upper eyelid. Structure The superior tarsal muscle originates on the underside of levator palpebrae superioris and inser ... (eye) See also * ''Tarsalia'' (bee), a genus of bees {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)