|
Sasine
Sasine in Scots law is the delivery of feudal property, typically land. Feudal property means immovable property, and includes everything that naturally goes with the property. For land, that would include such things as buildings, trees, and underground minerals. A superior (e.g., a heritor) might authorise his agent or factor to give possession of his property to someone else through a document known as a "precept of sasine". One of the earliest records in Scotland is from 1248 when Sir Malcolm, son of the then Earl of Lennox, ‘conferred full Sasine’ of certain lands at Strathblane to Sir David Graham. Over time, sasine came to be used in common speech as a reference to the deed or document recording the transfer, rather than to the transfer itself. Hence phrases such as "to give sasines", "to deliver sasines", "to receive sasines", "to take sasines". Alternative spellings include: ''seizin'', ''seisin'', ''sasin'', ''seasin'', ''sasing'', ''seasing'', ''sesin'', ''seasin' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registers Of Scotland
Registers of Scotland (RoS) is the non-ministerial department of the Scottish Government responsible for compiling and maintaining records relating to property and other legal documents. They currently maintain 20 public registers. The official responsible with maintaining the Registers of Scotland is the Keeper of the Registers of Scotland (known simply as the Keeper). By ex officio, the Keeper of the Registers of Scotland is also the Deputy Keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland. The Keeper of the Registers of Scotland should not be confused with the Keeper of the Records of Scotland. History of Public Records & Registration The first official tasked with the care and administration of the public registers was first recorded in the role of ''Clericus Rotulorum'' (Clerk of the Rolls) in the Kingdom of Scotland in 1286. Registers, rolls and records were kept in Edinburgh Castle from about the 13th century. The role of the Clerk of the Rolls eventually became known as the Lor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register Of Sasines
, type = Non-ministerial government department , seal = , logo = Registers of Scotland logo.svg , logo_width = , logo_caption = , formed = , jurisdiction = Scotland , headquarters = Meadowbank House, 153 London Road, Edinburgh EH8 7AU , employees = ~ 1,300 , budget = , minister1_name = Ben Macpherson (politician) , minister1_pfo = Cabinet Secretary for Finance , chief1_name = Jennifer Henderson , chief1_position = Keeper of the Registers of Scotland , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , chief3_name = , chief3_position = , chief4_name = , chief4_position = , chief5_name = , chief5_position = , chief6_name = , chief6_position = , chief7_name = , chief7_position = , chief8_name = , chief8_position = , chief9_name = , chief9_position = , parent_department = , website = Registers of Scotland (RoS) is the non-ministerial department of the Scottish Government responsible for compiling and maintaining records relating to property a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seisin
Seisin (or seizin) denotes the legal possession of a feudal fiefdom or fee, that is to say an estate in land. It was used in the form of "the son and heir of X has obtained seisin of his inheritance", and thus is effectively a term concerned with conveyancing in the feudal era. The person holding such estate is said to be "seized of it", a phrase which commonly appears in inquisitions ''post mortem'' (i.e. "The jurors find that X died seized of the manor of ..."). The monarch alone "held" all the land of England by his allodial right and all his subjects were merely his tenants under various contracts of feudal tenure. Etymology Seisin comes from Middle English ''saysen'', ''seysen'', in the legal sense of to put in possession of, or to take possession of, hence, to grasp, to seize. The Old French variations ''seisir'', ''saisir'', are from Low Latin ''sacire'', generally referred to the same source as Gothic ''satjan'', Old English ''settan'', to put in place, set. Tenures sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seisin
Seisin (or seizin) denotes the legal possession of a feudal fiefdom or fee, that is to say an estate in land. It was used in the form of "the son and heir of X has obtained seisin of his inheritance", and thus is effectively a term concerned with conveyancing in the feudal era. The person holding such estate is said to be "seized of it", a phrase which commonly appears in inquisitions ''post mortem'' (i.e. "The jurors find that X died seized of the manor of ..."). The monarch alone "held" all the land of England by his allodial right and all his subjects were merely his tenants under various contracts of feudal tenure. Etymology Seisin comes from Middle English ''saysen'', ''seysen'', in the legal sense of to put in possession of, or to take possession of, hence, to grasp, to seize. The Old French variations ''seisir'', ''saisir'', are from Low Latin ''sacire'', generally referred to the same source as Gothic ''satjan'', Old English ''settan'', to put in place, set. Tenures sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moot Hill
A moot hill or ''mons placiti'' (statute hill) is a hill or mound historically used as an assembly or meeting place, as a moot hall is a meeting or assembly building, also traditionally to decide local issues. In early medieval Britain, such hills were used for "moots", meetings of local people to settle local business. Among other things, proclamations might be read; decisions might be taken; court cases might be settled at a moot. Although some moot hills were naturally occurring features or had been created long before as burial mounds, others were purpose-built. Etymology Although the word ''moot'' or ''mote'' is of Old English origin, deriving from the verb ''to meet'', it has come to have a wider meaning throughout the United Kingdom; initially referring to any popular gathering. In England, the word '' folkmoot'' in time came to mean a more specific local assembly with recognised legal rights. In Scotland the term is used in the literature for want of any other single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livery Of Seisin
Livery of seisin () is an archaic legal conveyancing ceremony, formerly practised in feudal England and in other countries following English common law, used to convey holdings in property. The term ''livery'' is closely related to if not synonymous with ''delivery'' used in some jurisdictions in contract law or the related law of deeds. The oldest forms of common law provided that a valid conveyance of a feudal tenure in land required physical transfer by the transferor to the transferee in the presence of witnesses of a piece of the ground itself, in the literal sense of a hand-to-hand passing of an amount of soil, a twig, key to a building on that land, or other token. Varieties Livery of seisin could refer to either: * ''Livery in deed'', whereby the parties met together on the land and the transferor symbolically delivered possession of the land by handing over a twig or a clump of earth to the recipient. * ''Livery in law'', whereby the parties went within sight of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livery Of Seisin
Livery of seisin () is an archaic legal conveyancing ceremony, formerly practised in feudal England and in other countries following English common law, used to convey holdings in property. The term ''livery'' is closely related to if not synonymous with ''delivery'' used in some jurisdictions in contract law or the related law of deeds. The oldest forms of common law provided that a valid conveyance of a feudal tenure in land required physical transfer by the transferor to the transferee in the presence of witnesses of a piece of the ground itself, in the literal sense of a hand-to-hand passing of an amount of soil, a twig, key to a building on that land, or other token. Varieties Livery of seisin could refer to either: * ''Livery in deed'', whereby the parties met together on the land and the transferor symbolically delivered possession of the land by handing over a twig or a clump of earth to the recipient. * ''Livery in law'', whereby the parties went within sight of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Law
Scots law () is the legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different historical sources. Together with English law and Northern Ireland law, it is one of the three legal systems of the United Kingdom.Stair, General Legal Concepts (Reissue), para. 4 (Online) Retrieved 2011-11-29 Early Scots law before the 12th century consisted of the different legal traditions of the various cultural groups who inhabited the country at the time, the Gaels in most of the country, with the Britons and Anglo-Saxons in some districts south of the Forth and with the Norse in the islands and north of the River Oykel. The introduction of feudalism from the 12th century and the expansion of the Kingdom of Scotland established the modern roots of Scots law, which was gradually influenced by other, especially Anglo-Norman and continental legal traditions. Although there was some indirect Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Use
Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as settlements and semi-natural habitats such as arable fields, pastures, and managed woods. Land use by humans has a long history, first emerging more than 10,000 years ago. It has been defined as "the purposes and activities through which people interact with land and terrestrial ecosystems" and as "the total of arrangements, activities, and inputs that people undertake in a certain land type." Land use is one of the most important drivers of global environmental change. History Human tribes since prehistory have segregated land into territories to control the use of land. Today, the total arable land is 10.7% of the land surface, with 1.3% being permanent cropland. Regulation Land use practices vary considerably across the world. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization Water Development Division explains that "Land use concerns the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Property Law
Scots property law governs the rules relating to property found in the legal jurisdiction of Scotland. As a hybrid legal system with both common law and civil law heritage, Scots property law is similar, but not identical, to property law in South Africa and the American state of Louisiana. The term 'property' is wide-ranging but in this article, as in Scots law and many other jurisdictions, it does not solely describe land. Instead, in Scots law, the term 'a person's property' is used when describing objects or 'things' (in Latin ''res'') that an individual holds a right of ownership in. It is the rights that an individual holds in a 'thing' that are the subject matter of Scots property law. The terms objects or 'things' is also a wide-ranging definition, and is based on Roman law principles. Objects (or things) can be physical (such as land, a house, a car, a statue or a keyring) or they can also be unseen but still capable of being owned, (e.g. a person can have a right to payme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Law Legal Terminology
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: * Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland * Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland * Scoti, a Latin name for the Gaels * SCOTS, abbreviation for Royal Regiment of Scotland * Scottish Corpus of Texts and Speech (SCOTS), a linguistic resource See also * Southern Culture on the Skids (SCOTS), an American rock band * Scot's Lo-Cost, a grocery store owned by Weis Markets * Scotch (other) * Scots Church (other) * Scots College (other) * Scott's (other) * Scottish (other) * Scotts (other) * Pound Scots The pound (Modern and Middle Scots: ''Pund'') was the currency of Scotland prior to the 1707 Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. It was introduced by Da ..., historical currency * Scots pine, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
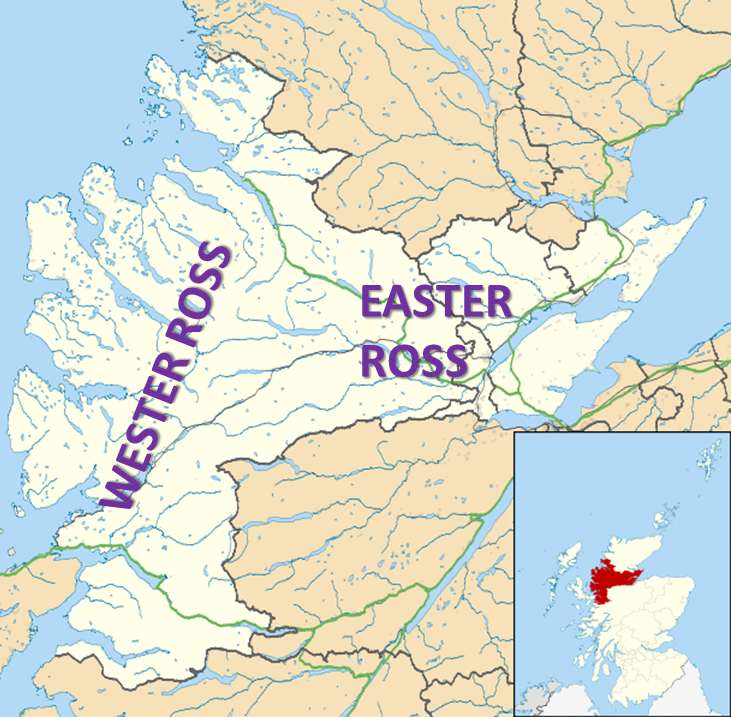
Easter Ross
Easter Ross ( gd, Ros an Ear) is a loosely defined area in the east of Ross, Highland, Scotland. The name is used in the constituency name Caithness, Sutherland and Easter Ross, which is the name of both a British House of Commons constituency and a Scottish Parliament constituency. The two constituencies have however different boundaries. Settlements Places in Easter Ross include: * Alness * Dingwall (included in some contexts in the term ''Easter Ross'', though in some contexts it refers to the area to the north-east of Dingwall) * Evanton * Invergordon * Kildary * Milntown of Tarbat (Milton) * Portmahomack * The Seaboard villages: ** Balintore ** Hilton of Cadboll ** Shandwick * Tain Easter Ross is well known for Black Isle and its towns: Avoch, Rosemarkie, Fortrose, and Cromarty. See also * Black Isle * Ross and Cromarty * Ross-shire * Wester Ross Wester Ross () is an area of the Northwest Highlands of Scotland in the council area of Highland. The area is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |