|
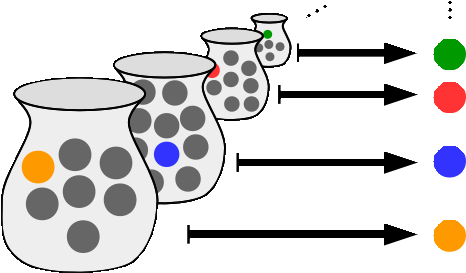
Surjective
In mathematics, a surjective function (also known as surjection, or onto function ) is a function such that, for every element of the function's codomain, there exists one element in the function's domain such that . In other words, for a function , the codomain is the image of the function's domain . It is not required that be unique; the function may map one or more elements of to the same element of . The term ''surjective'' and the related terms '' injective'' and ''bijective'' were introduced by Nicolas Bourbaki, a group of mainly French 20th-century mathematicians who, under this pseudonym, wrote a series of books presenting an exposition of modern advanced mathematics, beginning in 1935. The French word '' sur'' means ''over'' or ''above'', and relates to the fact that the image of the domain of a surjective function completely covers the function's codomain. Any function induces a surjection by restricting its codomain to the image of its domain. Every surjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injective Function
In mathematics, an injective function (also known as injection, or one-to-one function ) is a function that maps distinct elements of its domain to distinct elements of its codomain; that is, implies (equivalently by contraposition, implies ). In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element of its domain. The term must not be confused with that refers to bijective functions, which are functions such that each element in the codomain is an image of exactly one element in the domain. A homomorphism between algebraic structures is a function that is compatible with the operations of the structures. For all common algebraic structures, and, in particular for vector spaces, an is also called a . However, in the more general context of category theory, the definition of a monomorphism differs from that of an injective homomorphism. This is thus a theorem that they are equivalent for algebraic structures; see for more details. A func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Function
In mathematics, the inverse function of a function (also called the inverse of ) is a function that undoes the operation of . The inverse of exists if and only if is bijective, and if it exists, is denoted by f^ . For a function f\colon X\to Y, its inverse f^\colon Y\to X admits an explicit description: it sends each element y\in Y to the unique element x\in X such that . As an example, consider the real-valued function of a real variable given by . One can think of as the function which multiplies its input by 5 then subtracts 7 from the result. To undo this, one adds 7 to the input, then divides the result by 5. Therefore, the inverse of is the function f^\colon \R\to\R defined by f^(y) = \frac . Definitions Let be a function whose domain is the set , and whose codomain is the set . Then is ''invertible'' if there exists a function from to such that g(f(x))=x for all x\in X and f(g(y))=y for all y\in Y. If is invertible, then there is exactly one functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijective Function
In mathematics, a bijection, bijective function, or one-to-one correspondence is a function between two sets such that each element of the second set (the codomain) is the image of exactly one element of the first set (the domain). Equivalently, a bijection is a relation between two sets such that each element of either set is paired with exactly one element of the other set. A function is bijective if it is invertible; that is, a function f:X\to Y is bijective if and only if there is a function g:Y\to X, the ''inverse'' of , such that each of the two ways for composing the two functions produces an identity function: g(f(x)) = x for each x in X and f(g(y)) = y for each y in Y. For example, the ''multiplication by two'' defines a bijection from the integers to the even numbers, which has the ''division by two'' as its inverse function. A function is bijective if and only if it is both injective (or ''one-to-one'')—meaning that each element in the codomain is mapped fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set (mathematics), set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the Domain of a function, domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. History of the function concept, Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable function, differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Exponential
In mathematics, the matrix exponential is a matrix function on square matrix, square matrices analogous to the ordinary exponential function. It is used to solve systems of linear differential equations. In the theory of Lie groups, the matrix exponential gives the exponential map (Lie theory), exponential map between a matrix Lie algebra and the corresponding Lie group. Let be an real number, real or complex number, complex matrix (mathematics), matrix. The exponential of , denoted by or , is the matrix given by the power series e^X = \sum_^\infty \frac X^k where X^0 is defined to be the identity matrix I with the same dimensions as X, and . The series always converges, so the exponential of is well-defined. Equivalently, e^X = \lim_ \left(I + \frac \right)^k for integer-valued , where is the identity matrix. Equivalently, given by the solution to the differential equation \frac d e^ = X e^, \quad e^ = I When is an diagonal matrix then will be an diagonal matr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codomain2
In mathematics, a codomain, counter-domain, or set of destination of a function is a set into which all of the output of the function is constrained to fall. It is the set in the notation . The term '' range'' is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or the ''image'' of a function. A codomain is part of a function if is defined as a triple where is called the '' domain'' of , its ''codomain'', and its '' graph''. The set of all elements of the form , where ranges over the elements of the domain , is called the ''image'' of . The image of a function is a subset of its codomain so it might not coincide with it. Namely, a function that is not surjective has elements in its codomain for which the equation does not have a solution. A codomain is not part of a function if is defined as just a graph. For example in set theory it is desirable to permit the domain of a function to be a proper class , in which case there is formally no such thing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codomain
In mathematics, a codomain, counter-domain, or set of destination of a function is a set into which all of the output of the function is constrained to fall. It is the set in the notation . The term '' range'' is sometimes ambiguously used to refer to either the codomain or the ''image'' of a function. A codomain is part of a function if is defined as a triple where is called the '' domain'' of , its ''codomain'', and its '' graph''. The set of all elements of the form , where ranges over the elements of the domain , is called the ''image'' of . The image of a function is a subset of its codomain so it might not coincide with it. Namely, a function that is not surjective has elements in its codomain for which the equation does not have a solution. A codomain is not part of a function if is defined as just a graph. For example in set theory it is desirable to permit the domain of a function to be a proper class , in which case there is formally no such thin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is a Set (mathematics), set with an Binary operation, operation that combines any two elements of the set to produce a third element within the same set and the following conditions must hold: the operation is Associative property, associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element. For example, the integers with the addition, addition operation form a group. The concept of a group was elaborated for handling, in a unified way, many mathematical structures such as numbers, geometric shapes and polynomial roots. Because the concept of groups is ubiquitous in numerous areas both within and outside mathematics, some authors consider it as a central organizing principle of contemporary mathematics. In geometry, groups arise naturally in the study of symmetries and geometric transformations: The symmetries of an object form a group, called the symmetry group of the object, and the transformations of a given type form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function Composition
In mathematics, the composition operator \circ takes two function (mathematics), functions, f and g, and returns a new function h(x) := (g \circ f) (x) = g(f(x)). Thus, the function is function application, applied after applying to . (g \circ f) is pronounced "the composition of and ". Reverse composition, sometimes denoted f \mapsto g , applies the operation in the opposite order, applying f first and g second. Intuitively, reverse composition is a chaining process in which the output of function feeds the input of function . The composition of functions is a special case of the composition of relations, sometimes also denoted by \circ. As a result, all properties of composition of relations are true of composition of functions, such as #Properties, associativity. Examples * Composition of functions on a finite set (mathematics), set: If , and , then , as shown in the figure. * Composition of functions on an infinite set: If (where is the set of all real numbers) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, abbreviated AC or AoC, is an axiom of set theory. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of non-empty sets, it is possible to construct a new set by choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets (S_i as a nonempty set indexed with i), there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. The axiom of choice is equivalent to the statement that every partition has a transversal. In many cases, a set created by choosing elements can be made without invoking the axiom of choice, particularly if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available — some distinguishing property that happens to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Linear Group
In mathematics, the general linear group of degree n is the set of n\times n invertible matrices, together with the operation of ordinary matrix multiplication. This forms a group, because the product of two invertible matrices is again invertible, and the inverse of an invertible matrix is invertible, with the identity matrix as the identity element of the group. The group is so named because the columns (and also the rows) of an invertible matrix are linearly independent, hence the vectors/points they define are in general linear position, and matrices in the general linear group take points in general linear position to points in general linear position. To be more precise, it is necessary to specify what kind of objects may appear in the entries of the matrix. For example, the general linear group over \R (the set of real numbers) is the group of n\times n invertible matrices of real numbers, and is denoted by \operatorname_n(\R) or \operatorname(n,\R). More generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image (mathematics)
In mathematics, for a function f: X \to Y, the image of an input value x is the single output value produced by f when passed x. The preimage of an output value y is the set of input values that produce y. More generally, evaluating f at each Element (mathematics), element of a given subset A of its Domain of a function, domain X produces a set, called the "image of A under (or through) f". Similarly, the inverse image (or preimage) of a given subset B of the codomain Y is the set of all elements of X that map to a member of B. The image of the function f is the set of all output values it may produce, that is, the image of X. The preimage of f is the preimage of the codomain Y. Because it always equals X (the domain of f), it is rarely used. Image and inverse image may also be defined for general Binary relation#Operations, binary relations, not just functions. Definition The word "image" is used in three related ways. In these definitions, f : X \to Y is a Function (mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |