|
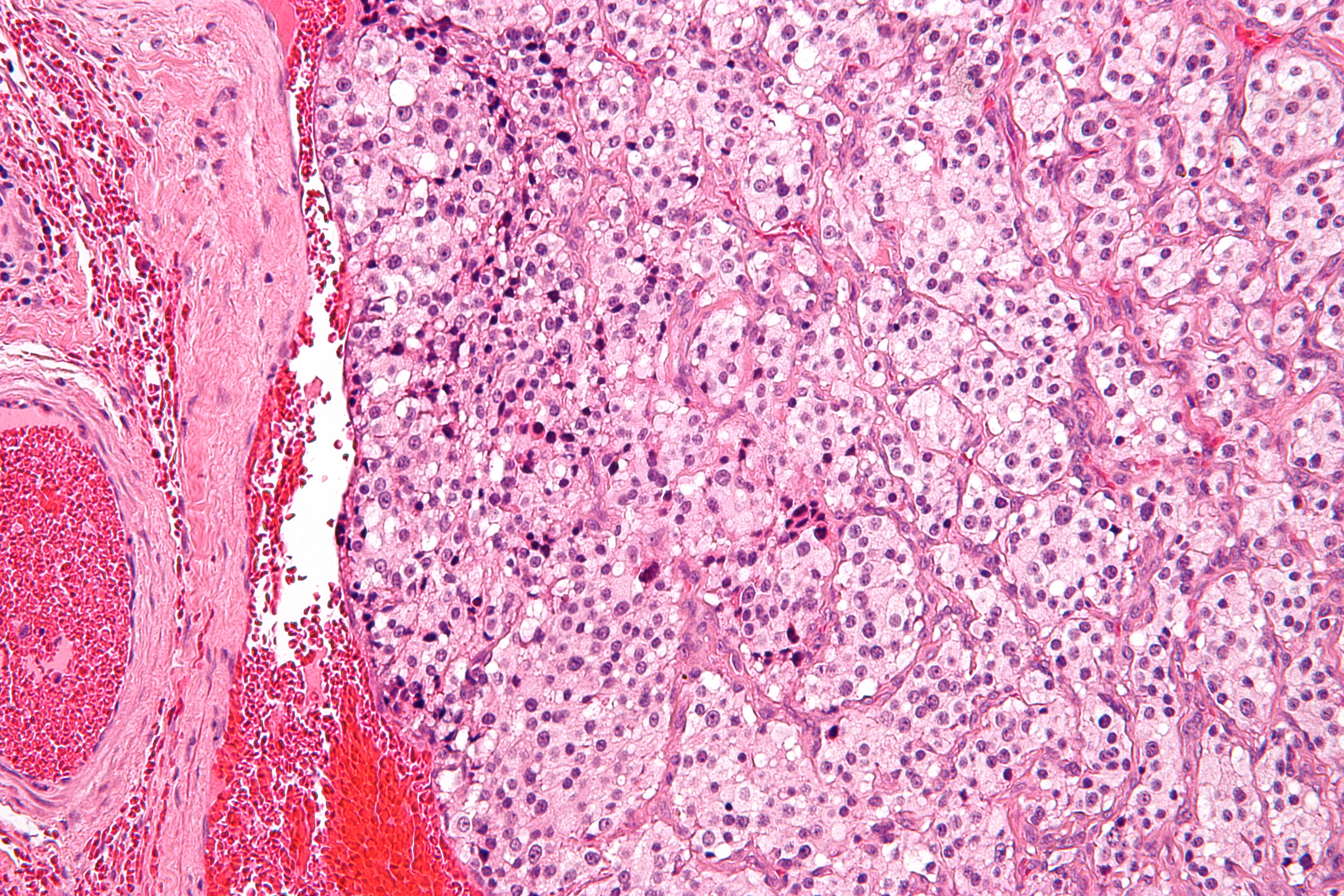
Superior Cervical Ganglion
The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck. Structure The superior cervical ganglion is reddish-gray color, and usually shaped like a spindle with tapering ends. It measures about 3 cm in length. Sometimes the SCG is broad and flattened, and occasionally constricted at intervals. It formed by the coalescence of four ganglia, corresponding to the four upper-most cervical nerves C1–C4. The bodies of its preganglionic sympathetic afferent neurons are located in the lateral horn of the spinal cord. Their axons enter the SCG to synapse with postganglionic neurons whose axons then exit the rostral end of the SCG and proceed to innervate their targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Ganglia
The cervical ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Preganglionic nerves from the thoracic spinal cord enter into the cervical ganglions and synapse with its postganglionic fibers or nerves. The cervical ganglion has three paravertebral ganglia: * superior cervical ganglion (largest) – adjacent to C2 & C3; postganglionic axon projects to target: (heart, head, neck) via "hitchhiking" on the carotid arteries * middle cervical ganglion (smallest) – adjacent to C6; target: heart, neck * inferior cervical ganglion The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia (i.e. of the cervical portion of the sympathetic trunk). It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the .... The inferior ganglion may be fused with the first thoracic ganglion to form a single structure, the stellate ganglion. – adjacent to C7; target: heart, lower neck, arm, posterior crani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pupillary Dilatation
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs. It may also be of unknown cause. Normally, as part of the pupillary light reflex, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day. A ''mydriatic'' pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment. The excitation of the radial fibres of the iris which increases the pupillary aperture is referred to as a mydriasis. More generally, mydriasis also refers to the natural dilation of pupils, for instance in low light conditions or under sympathetic stimulation. Mydriasis is frequently induced by drugs for certain ophthalmic examinations and procedures, particularly those requiring visual access to the retina. Fixed, unilateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (is Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). Circadian rhythms are regulated by a circadian clock whose primary function is to rhythmically co-ordinate biological processes so they occur at the correct time to maximize the fitness of an individual. Circadian rhythms have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria and there is evidence that they evolved independently in each of these kingdoms of life. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ', meaning "around", and ', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose. Anatomists divide the gland into two sections, a palpebral lobe, or portion, and an orbital lobe or portion. The smaller ''palpebral lobe'' lies close to the eye, along the inner surface of the eyelid; if the upper eyelid is everted, the palpebral portion can be seen. The orbital lobe of the gland, contains fine interlobular ducts that connect the orbital lobe and the palpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Plexus
The internal carotid plexus is a nerve plexus situated upon the lateral side of the internal carotid artery. It is composed of post-ganglionic sympathetic fibres which have synapsed at (i.e. have their nerve cell bodies at) the superior cervical ganglion. The plexus gives rise to the deep petrosal nerve. Anatomy Postganglionic sympathetic fibres ascend from the superior cervical ganglion, along the walls of the internal carotid artery, to enter the internal carotid plexus. These fibres are then distributed to deep structures, including the superior tarsal muscle and pupillary dilator muscle. It includes fibres destined for the pupillary dilator muscle as part of a neural circuit regulating pupillary dilatation component of the pupillary reflex. Some fibres of the plexus converge to form the deep petrosal nerve.Richard L. Drake, Wayne Vogel & Adam W M Mitchell, "Gray's Anatomy for Students", Elsevier inc., 2005 The internal carotid plexus communicates with the trigeminal gangli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salivary Glands
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of Duct (anatomy), ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (Parotid gland, parotid, Submandibular gland, submandibular, and sublingual gland, sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as Serous gland, serous, Mucous gland, mucous, or seromucous gland, seromucous (mixed). In Serous fluid, serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in Mucus, mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by Parasympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1, muscarinic receptors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Body
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is situated on the posterior aspect of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles, it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle, there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two cerebral hemisphere, hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. It is one of the neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine Circumventricular organs, secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly Vascular permeability, permeable to solutes in the blood. The pineal gland is present in almost all vertebrates, but is absent in Protochordata, protochordates in which there is a simple pineal homologue. The hagfish, archaic vertebrates, lack a pineal gland. In some species of amphibians and reptiles, the gland is linked to a light-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropeptide Y
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36 amino-acid neuropeptide that is involved in various physiological and homeostatic processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It is secreted alongside other neurotransmitters such as GABA and glutamate. In the autonomic system it is produced mainly by neurons of the sympathetic nervous system and serves as a strong vasoconstrictor and also causes growth of fat tissue. In the brain, it is produced in various locations including the hypothalamus, and is thought to have several functions, including: increasing food intake and storage of energy as fat, reducing anxiety and stress, reducing pain perception, affecting the circadian rhythm, reducing voluntary alcohol intake, lowering blood pressure, and controlling epileptic seizures. Function Neuropeptide Y has been identified as being synthesized in GABAergic neurons and to act as a neurotransmitter during cellular communication. Neuropeptide Y is expressed in interneurons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |