|
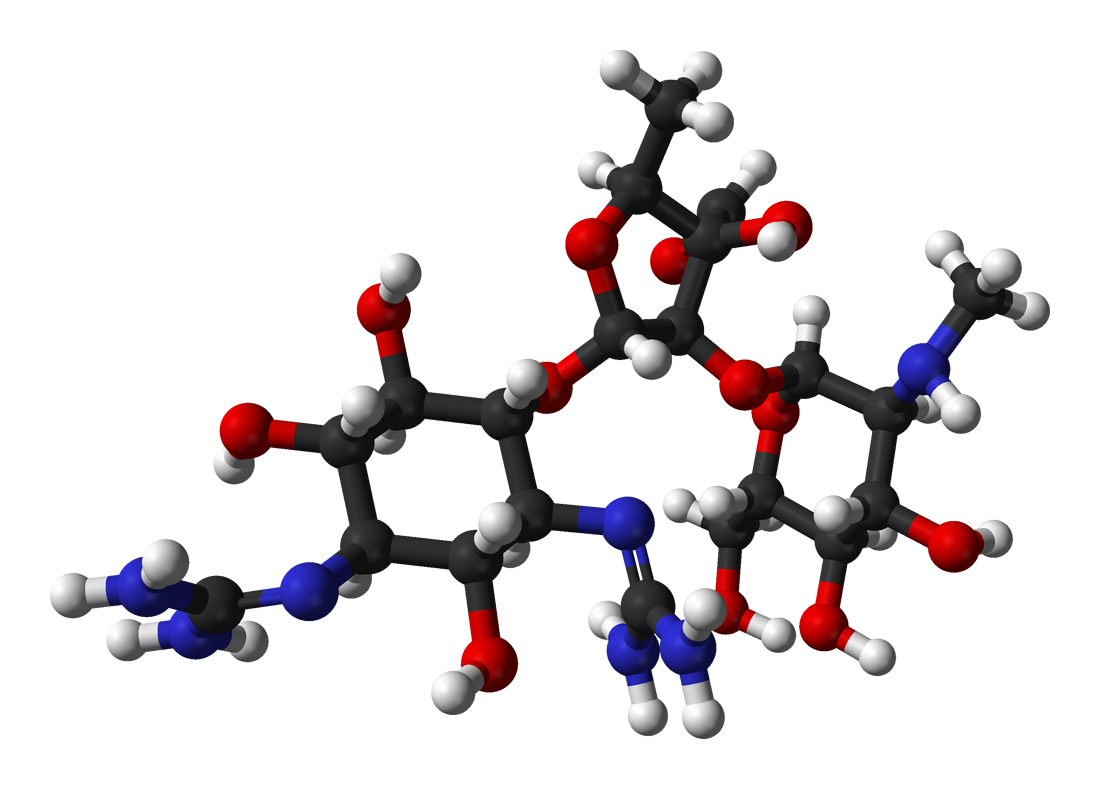
Sulopenem Etzadroxil Probenecid
Sulopenem (CP-70,429) is a thiopenem antibiotic derivative from the penem family, which unlike most related drugs is orally active. It was developed in Japan in the 1990s, and has been approved to treat uncomplicated urinary tract infections in combination with probenecid (Brand name: Orlynvah). It has reached Phase III clinical trials on several occasions and continues to be the subject of ongoing research into potential applications, especially in the treatment of multiple drug resistant urinary tract infections. In October 2024, the US Food and Drug Administration approved sulopenem etzadroxil with probenecid combination for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by ''Escherichia coli'', ''Klebsiella pneumoniae'', or ''Proteus mirabilis'' in adult women with limited alternative oral antibiotic options. The combination was developed by Iterum Therapeutics under the trade name ORLYNVAH™. See also * Imipenem Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is a synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penem
A penem is a type of β-lactam with an unsaturated five-member heterocycle containing a sulfur atom in a pentacyclic ring fused to the β-lactam ring. Penems do not occur naturally; all are synthetic. Related to penems are carbapenems, which have a carbon atom in place of the sulfur atom. An example is faropenem. Structure Penem molecules do not occur naturally, and production of penems is an entirely synthetic process. Five main penem subgroups — thiopenems, oxypenems, aminopenems, alkylpenems, and arylpenems — have been produced and are distinguished by the side chain (at position 2) of the unsaturated five-membered ring. One structurally distinct penem is BRL 42715. This molecule has no substitution at the above position, but has a bulky group attached to the β-lactam ring, and it displays effective inhibition of class C β-lactamase Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide Multiple drug resistance, multi-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Drug Resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasites (resistant to multiple antifungal, antiviral, and antiparasitic drugs of a wide chemical variety). Recognizing different degrees of MDR in bacteria, the terms ''extensively drug-resistant'' (''XDR'') and ''pandrug-resistant'' (''PDR'') have been introduced. ''Extensively drug-resistant (XDR)'' is the non-susceptibility of one bacteria species to all antimicrobial agents except in two or less antimicrobial categories. Within XDR, ''pandrug-resistant (PDR)'' is the non-susceptibility of bacteria to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or Abdominal pain, flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear Hematuria, bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes mellitus, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probenecid
Probenecid, also sold under the brand name Probalan, is a medication that increases uric acid excretion in the urine. It is primarily used in treating gout and hyperuricemia. Probenecid was developed as an alternative to caronamide to competitively inhibit renal excretion of some drugs, thereby increasing their plasma concentration and prolonging their effects. Medical uses Probenecid is primarily used to treat gout and hyperuricemia. Probenecid is sometimes used to increase the concentration of some antibiotics and to protect the kidneys when given with cidofovir. Specifically, a small amount of evidence supports the use of intravenous cefazolin once rather than three times a day when it is combined with probenecid. It has also found use as a masking agent, potentially helping athletes using performance-enhancing substances to avoid detection by drug tests. Adverse effects Mild symptoms such as nausea, loss of appetite, dizziness, vomiting, headache, sore gums, or frequent uri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose- fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar. Although found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines, it can cause destructive changes to human and animal lungs if aspirated, specifically to the alveoli, resulting in bloody, brownish or yellow colored jelly-like sputum. In the clinical setting, it is the most significant member of the genus ''Klebsiella'' of the Enterobacteriaceae. ''K. oxytoca'' and ''K. rhinoscleromatis'' have also been demonstrated in human clinical specimens. In recent years, ''Klebsiella'' species have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections. It naturally occurs in the soil, and about 30% of strains can fix nitrogen in anaerobic conditions. As a free-living diazotroph, its nitrogen-fixation system has been much-studied, and is of agricultural interest, as ''K. pneumoniae'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with Urinary tract infection, infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imipenem
Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is a synthetic beta-lactam, β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the carbapenems chemical class. developed by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus playing a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics. It is usually administered through intravenous injection. Imipenem was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1985. It was developed via a lengthy trial-and-error search for a more stable version of the natural product thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium ''Streptomyces cattleya''. Thienamycin has antibacterial activity, but is unstable in aqueous solution, thus it is practically of no medicinal use. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against Aerobic organism, aerobic and Anaerobic organism, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tebipenem
Tebipenem (brand name Orapenem) is a broad-spectrum orally-administered antibiotic, from the carbapenem subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics. It was developed as a replacement drug to combat bacteria that had acquired antibiotic resistance to commonly used antibiotics. Tebipenem is formulated as the ester tebipenem pivoxil due to the better absorption and improved bioavailability of this form. It has performed well in clinical trials for ear infection and looks likely to be further developed in future. It is only marketed in Japan. Tebipenem is the first carbapenem whose prodrug A prodrug is a pharmacologically inactive medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be ... form, the pivalyl ester, is orally available. References Carbapenem antibiotics Prodrugs Thiazolines Formals {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |