|
Strong Electrolyte
In chemistry, a strong electrolyte is a solute that completely, or almost completely, ionizes or dissociates in a solution. These ions are good conductors of electric current in the solution. Originally, a "strong electrolyte" was defined as a chemical compound that, when in aqueous solution, is a good conductor of electricity. With a greater understanding of the properties of ions in solution, its definition was replaced by the present one. A concentrated solution of this strong electrolyte has a lower vapor pressure than that of pure water at the same temperature. Strong acids, strong bases and soluble ionic salts that are not weak acids or weak bases are strong electrolytes. Writing reactions For strong electrolytes, a single reaction arrow shows that the reaction occurs completely in one direction, in contrast to the dissociation of weak electrolytes, which both ionize and re-bond in significant quantities.Brown, Theodore L. ''Chemistry: The Central Science'', 9th editio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydriodic Acid
Hydroiodic acid (or hydriodic acid) is a colorless liquid. It is an aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula . It is a strong acid, in which hydrogen iodide is ionized completely in an aqueous solution. Concentrated aqueous solutions of hydrogen iodide are usually 48% to 57% HI by mass. Preparation Reactions Hydroiodic acid reacts with oxygen in air to give iodine: : Like hydrogen halides, hydroiodic acid adds to alkenes to give alkyl iodides. It can also be used as a reducing agent, for example in the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to anilines. Cativa process The Cativa process is a major end use of hydroiodic acid, which serves as a co-catalyst for the production of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol. Illicit uses Hydroiodic acid is listed as a U.S. Federal DEA List I Chemical, owing to its use as a reducing agent related to the production of methamphetamine from ephedrine Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Triflic Acid
Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents. Synthesis Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is produced industrially by electrochemical fluorination (ECF) of methanesulfonic acid CH3SO3H + 4 HF ->CF3SO2F + H2O + 3 H2 The resulting CF3SO2F is hydrolyzed, and the resulting triflate salt is reprotonated. Alternatively, trifluoromethanesulfonic acid arises by oxidation of trifluoromethylsulfenyl chloride: CF3SCl + 2 Cl2 + 3 H2O -> CF3SO3H + 5 HCl Triflic acid is purified by distillation from triflic anhydride. Historical Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid was first synthesized in 1954 by Robert Haszeldine and Kidd by the following reaction: : Reactions As an acid In the laboratory, trif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
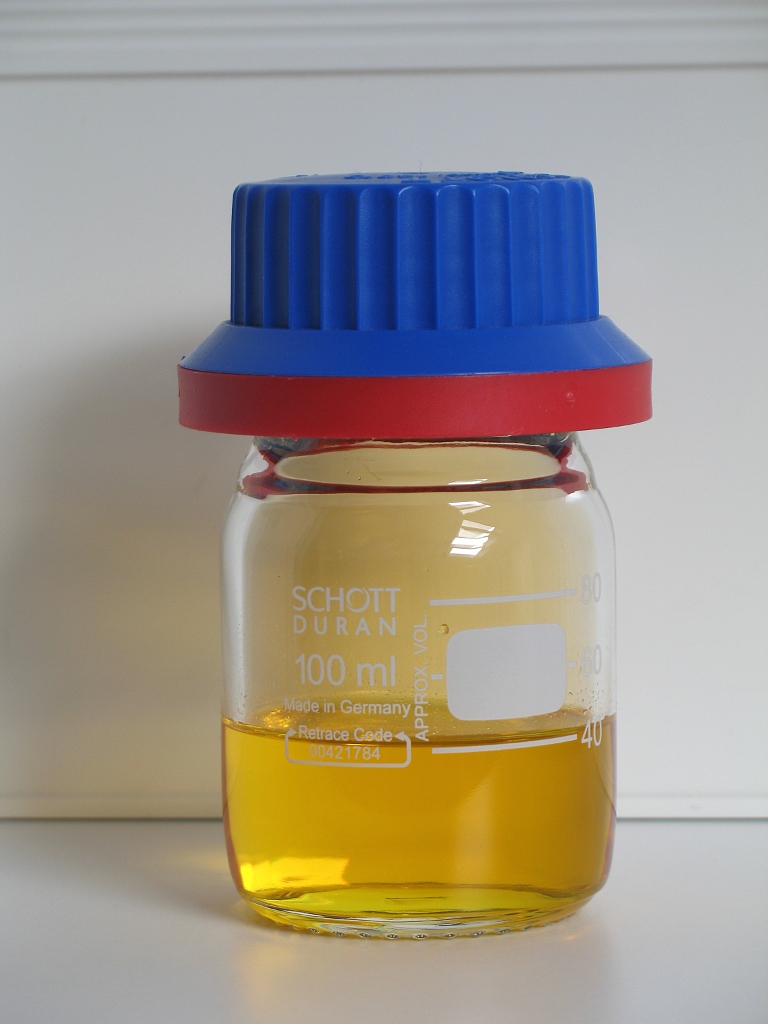
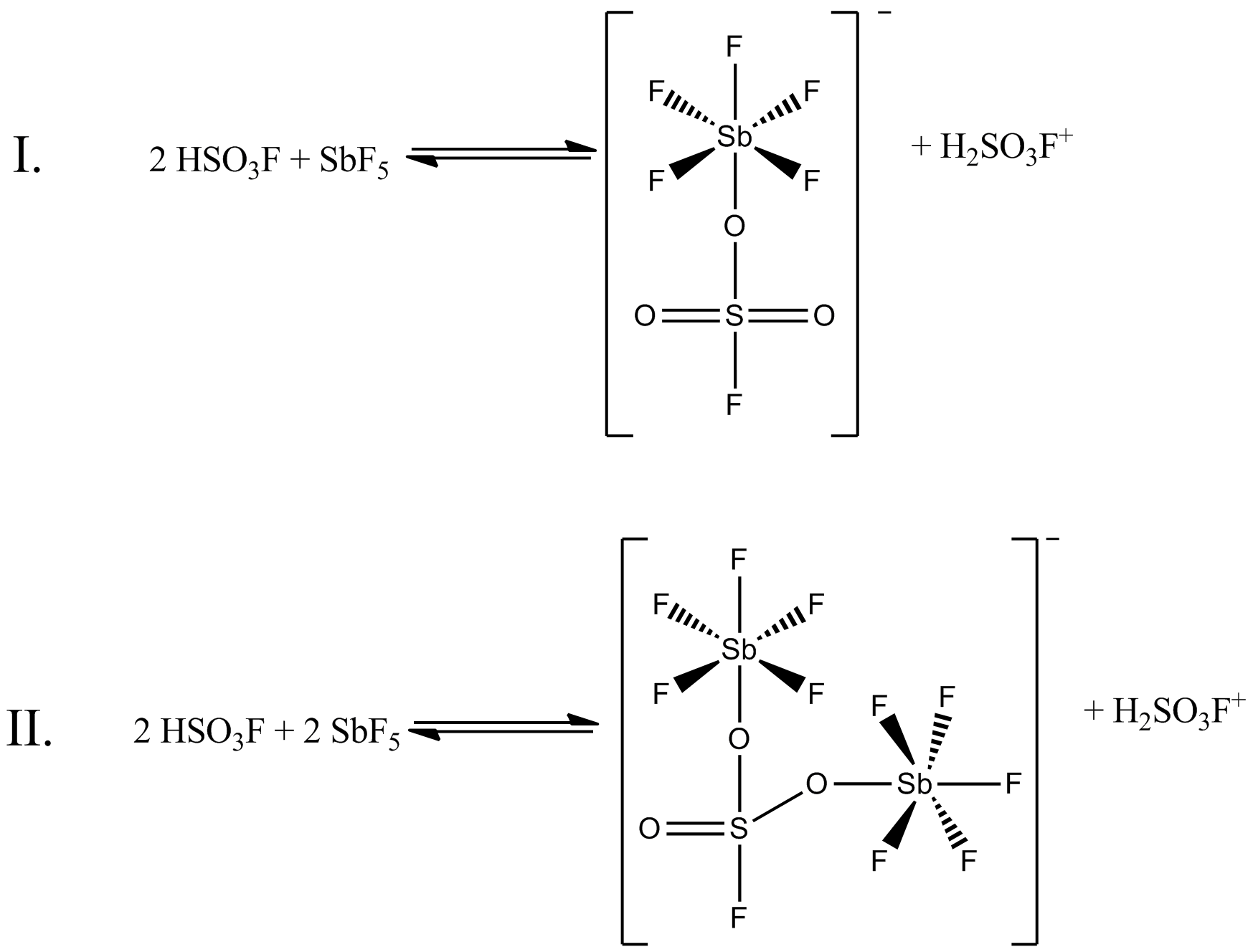
Fluorosulfuric Acid
Fluorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurofluoridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is one of the strongest acids commercially available. It is a tetrahedral molecule and is closely related to sulfuric acid, , substituting a fluorine atom for one of the hydroxyl groups. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples are often yellow.Erhardt Tabel, Eberhard Zirngiebl, Joachim Maas "Fluorosulfuric Acid" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Properties Fluorosulfuric acid is a free-flowing colorless liquid. It is soluble in polar organic solvents (e.g. nitrobenzene, acetic acid, and ethyl acetate), but poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents such as alkanes. is one of the strongest known simple Brønsted acids. It has an ''H''0 value of −15.1 compared to −12 for sulfuric acid. The combination of and the Lewis acid antimony pentafluoride produces "Magic acid", which is a far stronger protonating ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carborane Superacid
Carborane acids (X, Y, Z = H, Alk, F, Cl, Br, CF3) are a class of superacids, some of which are estimated to be at least one million times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid in terms of their Hammett acidity function values (''H''0 ≤ −18) and possess computed p''K''a values well below −20, establishing them as some of the strongest known Brønsted acids. The best-studied example is the highly chlorinated derivative . The acidity of was found to vastly exceed that of triflic acid, , and bistriflimide, , compounds previously regarded as the strongest isolable acids. Their high acidities stem from the extensive delocalization of their conjugate bases, carboranate anions (CXB11Y5Z6−), which are usually further stabilized by electronegative groups like Cl, F, and CF3. Due to the lack of oxidizing properties and the exceptionally low nucleophilicity and high stability of their conjugate bases, they are the only superacids known to protonate C60 fullerene without decomposin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Magic Acid
Magic acid () is a superacid consisting of a mixture, most commonly in a 1:1 molar ratio, of fluorosulfuric acid () and antimony pentafluoride (). This conjugate Brønsted acid, Brønsted–Lewis acid, Lewis superacid system was developed in the 1960s by Ronald Gillespie and his team at McMaster University, and has been used by George Olah to stabilise carbocations and hypercoordination, hypercoordinated carbonium ions in liquid media. Magic acid and other superacids are also used to catalyze isomerization of saturated hydrocarbons, and have been shown to protonation, protonate even weak bases, including methane, xenon, halogens, and molecular hydrogen. History The term "superacid" was first used in 1927 when James Bryant Conant found that perchloric acid could protonate ketones and aldehydes to form salts in nonaqueous solution. The term itself was coined by R. J. Gillespie, after Conant combined sulfuric acid with fluorosulfuric acid, and found the solution to be several million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fluoroantimonic Acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions (the simplest being and ). This mixture is a superacid stronger than pure sulfuric acid, by many orders of magnitude, according to its Hammett acidity function. It even protonates some hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations ( carbonium ions). Like its precursor hydrogen fluoride, it attacks glass, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon) or PFA. Chemical composition Fluoroantimonic acid is formed by combining hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride: :SbF5 + 2 HF + H2F+ The speciation (i.e., the inventory of components) of fluoroantimonic acid is complex. Spectroscopic measurements show that fluoroantimonic acid consists of a mixture of HF-solvated protons, – (such as ). Thus, the formula "" is a convenient but oversimplified approximation of the true composition. Nevertheless, the extreme acidity of this mixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Periodic Acid
Periodic acid ( ) is an oxoacid of iodine. It can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula , and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula . Periodic acids are colourless crystals. Periodic acid features iodine in the highest oxidation state of +7. Periodic acid was discovered by Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller in 1833. Synthesis Modern industrial scale production involves the oxidation of a solution of sodium iodate under Alkali, alkaline conditions, either electrochemically on a Lead dioxide, anode, or by treatment with chlorine: : (counter ions omitted for clarity) Standard electrode potential, ''E''° = −1.6 V : A standard laboratory preparation involves treating a mixture of tribarium dihydrogen orthoperiodate with nitric acid. Upon concentrating the mixture, the barium nitrate, which is less soluble, is separated from periodic acid: : Properties Orthoperiodic acid has a number of acid dissociation constants. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perbromic Acid
Perbromic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . Perbromic acid is characterized as a colorless liquid which has no characteristic scent. It is an oxoacid of bromine, with an oxidation state of +7. Perbromic acid is a strong acid and strongly oxidizing, though dilute perbromic acid solutions are slow oxidizing agents. It is the most unstable of the halogen(VII) oxoacids. It decomposes rapidly on standing to bromic acid and oxygen, which releases toxic brown bromine vapors. It can be used in the synthesis of perbromate salts, by reacting with a base. Perbromic acid is unstable and cannot be formed by displacement of chlorine from perchloric acid, as periodic acid is prepared; it can only be made by protonation of the perbromate ion. Perbromic acid is stable in aqueous solutions no greater than 6M. Perbromic acid solutions greater than 6M are unstable in air, where an autocatalytic decomposition of the compound will occur. Metals such as and can also catalyze the compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bromic Acid
Bromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromate, is an oxoacid with the molecular formula HBrO3. It only exists in aqueous solution.''The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals''. 14th Edition. 2006.''Van Nostrand's Scientific Encyclopedia''. Glenn D. Considine. Ninth Edition. Volume 1. p 554 It is a colorless solution that turns yellow at room temperature as it decomposes to bromine.Recipes for Belousov–Zhabotinsky reagents. ''J. Chem. Educ.'', 1991, 68 (4), 320. doi:10.1021/ed068p320 Bromic acid and bromates are powerful oxidizing agents and are common ingredients in Belousov–Zhabotinsky reactions.The Source of the Carbon Monoxide in the Classical Belousov–Zhabotinsky Reaction. ''J. Phys. Chem. A.'', 2007, 111 (32), 7805–12 doi:10.1021/jp073512+ Belousov-Zhabotinsky reactions are a classic example of non-equilibrium thermodynamics Non-equilibrium thermodynamics is a branch of thermodynamics that deals with physical systems that are not in ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chloric Acid
Chloric acid, H Cl O3, is an oxoacid of chlorine, and the formal precursor of chlorate salts. It is a strong acid ( p''K''a ≈ −2.7) and an oxidizing agent. Properties Chloric acid is thermodynamically unstable with respect to disproportionation. Chloric acid is stable in cold aqueous solution up to a concentration of approximately 30%, and solution of up to 40% can be prepared by careful evaporation under reduced pressure. Above these concentrations, chloric acid solutions decompose to give a variety of products, for example: : : Hazards Chloric acid is a powerful oxidizing agent. Most organics and flammables will deflagrate on contact. Production It may be produced from barium chlorate through its reaction with sulfuric acid, which results in a solution of chloric acid and insoluble barium sulfate precipitate: : The chlorate must be dissolved in boiling water and the acid should be somewhat diluted in water and heated before mixing. Another method which can be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |