|
Stress–strain Curve
In engineering and materials science, a stress–strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain. It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation, from which the stress and strain can be determined (see tensile testing). These curves reveal many of the properties of a material, such as the Young's modulus, the yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength. Definition Generally speaking, curves that represent the relationship between stress and strain in any form of deformation can be regarded as stress–strain curves. The stress and strain can be normal, shear, or a mixture, and can also be uniaxial, biaxial, or multiaxial, and can even change with time. The form of deformation can be compression, stretching, torsion, rotation, and so on. If not mentioned otherwise, stress–strain curve typically refers to the relationship between axial normal stress and axial normal strain of materials measur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stress Strain Ductile
Stress may refer to: Science and medicine * Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition * Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase or sentence * Stress (mechanics), the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other * Oxidative stress, an imbalance of free radicals * Psychological stress, a feeling of strain and pressure ** Occupational stress, stress related to one's job * Surgical stress, systemic response to surgical injury Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and musicians * Stress (Brazilian band), a Brazilian heavy metal band * Stress (British band), a British rock band * Stress (pop rock band), an early 1980s melodic rock band from San Diego * Stress (musician) (born 1977), hip hop singer from Switzerland * Stress (record producer) (born 1979), artistic name of Can Canatan, Swedish musician and reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mechanical Properties
A material property is an intensive property of a material, i.e., a physical property or chemical property that does not depend on the amount of the material. These quantitative properties may be used as a metric by which the benefits of one material versus another can be compared, thereby aiding in materials selection. A property having a fixed value for a given material or substance is called material constant or constant of matter. (Material constants should not be confused with physical constants, that have a universal character.) A material property may also be a function of one or more independent variables, such as temperature. Materials properties often vary to some degree according to the direction in the material in which they are measured, a condition referred to as anisotropy. Materials properties that relate to different physical phenomena often behave linearly (or approximately so) in a given operating range . Modeling them as linear functions can significantly si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ultimate Tensile Stress
Ultimate tensile strength (also called UTS, tensile strength, TS, ultimate strength or F_\text in notation) is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In brittle materials, the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials, the ultimate tensile strength can be higher. The ultimate tensile strength is usually found by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain. The highest point of the stress–strain curve is the ultimate tensile strength and has units of stress. The equivalent point for the case of compression, instead of tension, is called the compressive strength. Tensile strengths are rarely of any consequence in the design of ductile members, but they are important with brittle members. They are tabulated for common materials such as alloys, composite materials, ceramics, plastics, and wood. Definition The ultimate tensile strength of a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cottrell Atmosphere
In materials science, the concept of the Cottrell atmosphere was introduced by A. H. Cottrell and B. A. Bilby in 1949 to explain how dislocations are pinned in some metals by boron, carbon, or nitrogen interstitials. Cottrell atmospheres occur in body-centered cubic (BCC) and face-centered cubic (FCC) materials, such as iron or nickel, with small impurity atoms, such as boron, carbon, or nitrogen. As these interstitial atoms distort the lattice slightly, there will be an associated residual stress field surrounding the interstitial. This stress field can be relaxed by the interstitial atom diffusing towards a dislocation, which contains a small gap at its core (as it is a more open structure), see Figure 1. Once the atom has diffused into the dislocation core the atom will stay. Typically only one interstitial atom is required per lattice plane of the dislocation. The collection of solute atoms around the dislocation core due to this process is the Cottrell atmosphere. Infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
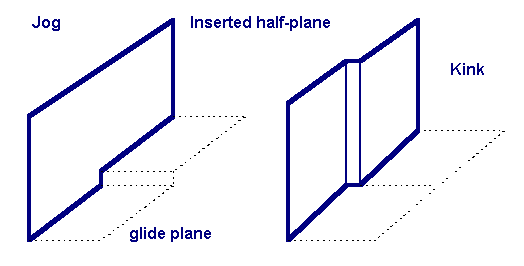
Dislocations
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or Slip (materials science), slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plasticity (physics), Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Modulus Of Elasticity
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it. Definition The elastic modulus of an object is defined as the slope of its stress–strain curve in the elastic deformation region: A stiffer material will have a higher elastic modulus. An elastic modulus has the form: :\delta \ \stackrel\ \frac where stress is the force causing the deformation divided by the area to which the force is applied and strain is the ratio of the change in some parameter caused by the deformation to the original value of the parameter. Since strain is a dimensionless quantity, the units of \delta will be the same as the units of stress. Elastic constants and moduli Elastic constants are specific parameters that quantify the stiffness of a material in response to applied stresses and are fundamental in defining the elastic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversible upon removing the stress. Ductility is a critical mechanical performance indicator, particularly in applications that require materials to bend, stretch, or deform in other ways without breaking. The extent of ductility can be quantitatively assessed using the percent elongation at break, given by the equation: \% \mathrm= \left ( \frac \right )\times100 where l_ is the length of the material after fracture and l_0 is the original length before testing. This formula helps in quantifying how much a material can stretch under tensile stress before failure, providing key insights into its ductile behavior. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing. It defines a material's suitability for certain manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stress Strain Comparison Brittle Ductile
Stress may refer to: Science and medicine * Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition * Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase or sentence * Stress (mechanics), the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other * Oxidative stress, an imbalance of free radicals * Psychological stress, a feeling of strain and pressure ** Occupational stress, stress related to one's job * Surgical stress, systemic response to surgical injury Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and musicians * Stress (Brazilian band), a Brazilian heavy metal band * Stress (British band), a British rock band * Stress (pop rock band), an early 1980s melodic rock band from San Diego * Stress (musician) (born 1977), hip hop singer from Switzerland * Stress (record producer) (born 1979), artistic name of Can Canatan, Swedish musician and recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Necking (engineering)
In engineering and materials science, necking is a mode of tensile Deformation (engineering), deformation where relatively large amounts of Deformation (mechanics), strain localize disproportionately in a small region of the material. The resulting prominent decrease in local cross-sectional area provides the basis for the name "neck". Because the local strains in the neck are large, necking is often closely associated with Yield (engineering), yielding, a form of Plasticity (physics), plastic deformation associated with ductile materials, often metals or polymers. Once necking has begun, the neck becomes the exclusive location of yielding in the material, as the reduced area gives the neck the largest local Stress (mechanics), stress. Formation Necking results from an instability during tensile deformation when the cross-sectional area of the sample decreases by a greater proportion than the material Strain hardening, strain hardens. :fr:Armand Consid%C3%A8re, Armand Considè ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Critical Resolved Shear Stress
In materials science, critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) is the shear stress that is necessary to initiate Slip (materials science), slip on a particular slip system in a Crystallite, grain. Resolved shear stress (RSS) is the shear component of an applied tensile or compressive stress resolved in the slip direction on a slip plane that is neither perpendicular nor parallel to the stress axis. The RSS is related to the applied stress by a geometrical factor, , typically called the Schmid Factor, Schmid factor: :\tau_\text = \sigma_\text m = \sigma_\text (\cos \phi \cos \lambda) where \sigma_\mathrm is the magnitude of the applied tensile stress, \phi is the angle between the normal of the slip plane and the direction of the applied force, and \lambda is the angle between the slip direction and the direction of the applied force. The Schmid factor is most applicable to Face centered cubic, FCC single-crystal metals, but for polycrystal metals the G. I. Taylor, Taylor factor has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or Slip (materials science), slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plasticity (physics), Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lüders Band
Lüders bands are a type of plastic bands, slip band or stretcher-strain mark which are formed due to localized bands of plastic deformation in metals experiencing tensile stresses, common to low-carbon steels and certain Al-Mg alloys. First reported by Guillaume Piobert, and later by W. Lüders, the mechanism that stimulates their appearance is known as dynamic strain aging, or the inhibition of dislocation In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ... motion by interstitial atoms (in steels, typically carbon and nitrogen), around which "Cottrell atmosphere, atmospheres" or "zones" naturally congregate. As internal stresses tend to be highest at the shoulders of tensile test specimens, band formation is favored in those areas. However, the formation of Lüders bands depends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |