|
Spinal Plexus
A nerve plexus is a plexus (branching network) of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including: * Spinal plexuses **Cervical plexusserves the head, neck and shoulders **Brachial plexusserves the chest, shoulders, arms and hands **Lumbosacral plexus ***Lumbar plexusserves the back, abdomen, groin, thighs, knees, and calves **** Subsartorial plexusbelow the sartorius muscle of thigh ***Sacral plexusserves the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plexus
In anatomy, a plexus (from the Latin term for 'braid') is a branching network of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, or nerves. The nerves are typically axons outside the central nervous system. The standard plural form in English is plexuses. Alternatively, the Latin plural plexūs may be used. Types Nerve plexuses The four primary nerve plexuses are the cervical plexus, brachial plexus, lumbar plexus, and the sacral plexus. Cardiac plexus Celiac plexus Renal plexus Venous plexus Choroid plexus The choroid plexus is a part of the central nervous system in the brain and consists of capillaries, brain ventricles, and ependymal cells. Invertebrates The plexus is the characteristic form of nervous system in the coelenterates and persists with modifications in the flatworms. The nerves of the radially symmetric echinoderms also take this form, where a plexus underlies the ectoderm of these animals and deeper in the body other nerve cells form plexuses of limited extent. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissner's Plexus
The submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of parasympathetic nerves around the superior mesenteric artery. Branches from the myenteric plexus perforate the circular muscle fibers to form the submucosal plexus. Ganglia from the plexus extend into the muscularis mucosae and also extend into the mucous membrane A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It .... They contain Dogiel cells. The nerve bundles of the submucosal plexus are finer than those of the myenteric plexus. Its function is to innervate cells in the epithelial layer and the smooth muscle of the muscularis mucosae. 14% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C6-C7 (lateral cord) and C8 and T1 (medial cord). The median nerve is the only nerve that passes through the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the disability that results from the median nerve being pressed in the carpal tunnel. Structure The median nerve arises from the branches from lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, courses through the anterior part of arm, forearm, and hand, and terminates by supplying the muscles of the hand. Arm After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
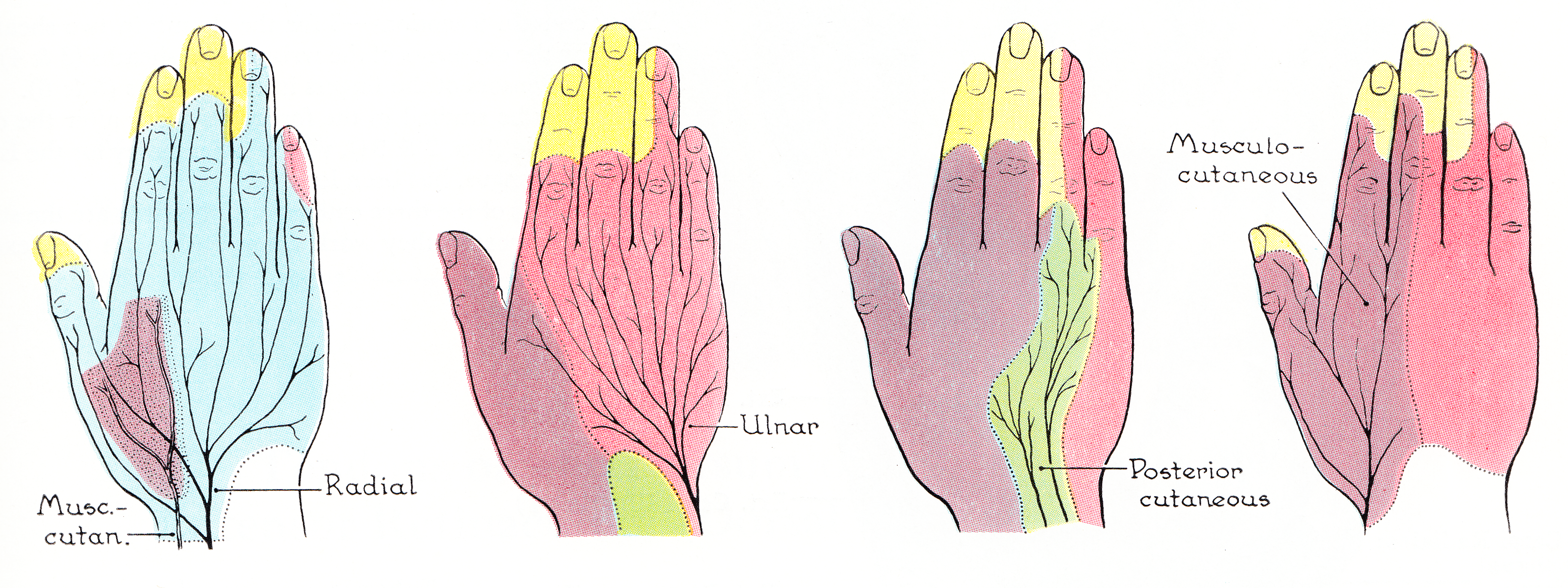
Radial Nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the posterior roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. The radial nerve and its branches provide Motor neuron, motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous Nerve supply to the skin, sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
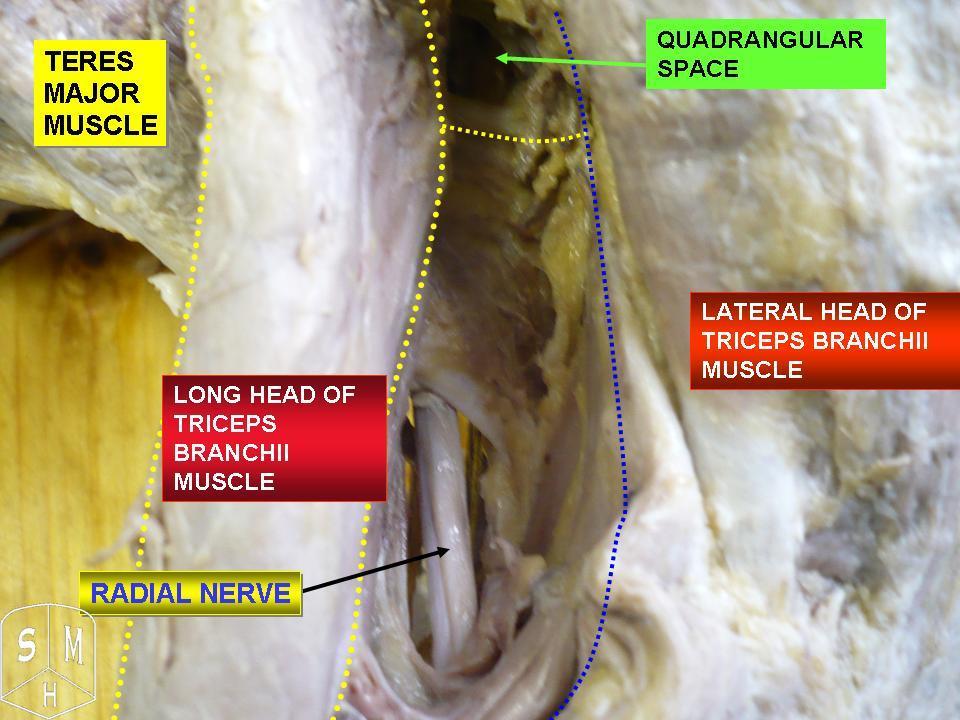
Axillary Nerve
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus ( upper trunk, posterior division, posterior cord) at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor. Structure The nerve lies at first behind the axillary artery, and in front of the subscapularis, and passes downward to the lower border of that muscle. It then winds from anterior to posterior around the neck of the humerus, in company with the posterior humeral circumflex artery, through the quadrangular space (bounded above by the teres minor, below by the teres major, medially by the long head of the triceps brachii, and laterally by the surgical neck of the humerus), and divides into an anterior, a posterior, and a collateral branch to the long head of the triceps brachii bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musculocutaneous Nerve
The musculocutaneous nerve is a Mixed nerve, mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis minor. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the Coracobrachialis muscle, coracobrachialis, Biceps brachi, biceps brachii, and Brachialis muscle, brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm (via its Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm, terminal branch). It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of Biceps brachi, biceps brachii it is becomes known as the Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm, lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. Structure Course Musculocutaneous nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus with root value of C5 to C7 of the spinal cord. It follows the course of the third part of the axillary artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the C3–C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerve roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic nerve or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Nerves
The supraclavicular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the third and fourth cervical (spinal) nerves. It emerges from beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then split into multiple branches. Together, these innervate the skin over the shoulder. The supraclavicular nerve can be blocked during shoulder surgery. Anatomy Origin The supraclavicular nerve is a branch of the cervical plexus that arises from cervical (spinal) nerves C3-C4 with the predominant contribution from C4. Course It emerges at the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle alongside the other three cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus, then promptly divides into several branches. The nerves descend in the posterior triangle of the neck beneath the platysma muscle and the deep cervical fascia. Near the clavicle, the supraclavicular nerves perforate the fascia and the platysma muscle to become cutaneous. They are arranged, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
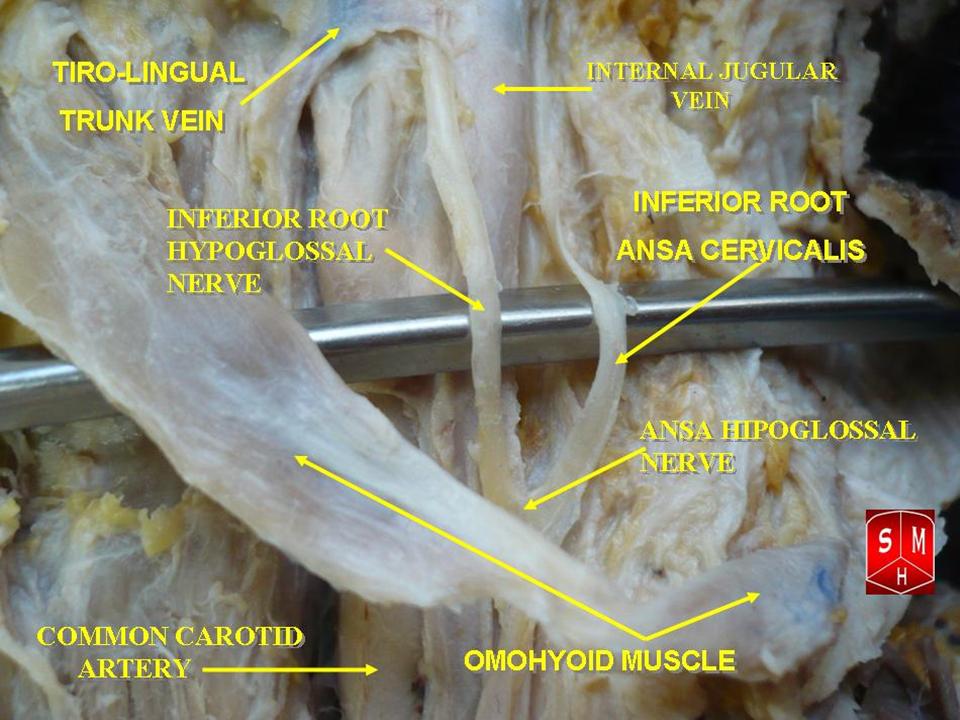
Ansa Cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (or ansa hypoglossi in older literature) is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root (formed by branch of C1) and an inferior root (formed by union of branches of C2 and C3) - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated anterior to the carotid sheath. Branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate three of the four infrahyoid muscles: the sternothyroid, sternohyoid, and omohyoid muscles (note that the thyrohyoid muscle is the one infrahyoid muscle not innervated by the ansa cervicalis - it is instead innervated by cervical spinal nerve 1 via a separate thyrohyoid branch). Its name means "handle of the neck" in Latin. Anatomy The ansa cervicalis is typically embedded within the anterior wall of the carotid sheath anterior to the internal jugular vein. Superior root The superior root of the ansa cervicalis (formerly known as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Cervical Nerve
The transverse cervical nerve (superficial cervical or cutaneous cervical) is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the cervical plexus that arises from the second and third cervical spinal nerves (C2-C3). It curves around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle, then pierces the fascia of the neck before dividing into two branches. It provides sensory innervation to the front of the neck. Anatomy Course and relations It curves around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus muscle about its middle, and, passing obliquely forward beneath the external jugular vein to the anterior border of the muscle, it perforates the deep cervical fascia before dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch beneath the platysma. The ascending branch communicates with the cervical branch of the facial nerve The cervical branch of the facial nerve is a nerve in the neck. It is a branch of the facial nerve (VII). It supplies the platysma muscle, among other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Auricular Nerve
The great auricular nerve is a Cutaneous nerve, cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third spinal nerve, cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over the parotid gland and the Mastoid part of the temporal bone, mastoid process, parts of the outer ear, and to the parotid gland and its parotid fascia, fascia. Pain resulting from parotitis is caused by an impingement on the great auricular nerve. Structure The great auricular nerve is the largest of the ascending branches of the cervical plexus. Origin It arises from the second and third cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3), with the predominant contribution coming from C2. Course and relations The great auricular nerve is a large trunk that ascends almost vertically over the sternocleidomastoid. It winds around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, then perforates the deep fascia before ascending alongside the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Occipital Nerve
The lesser occipital nerve (or small occipital nerve) is a cutaneous spinal nerve of the cervical plexus. It arises from second cervical (spinal) nerve (C2) (along with the greater occipital nerve). It innervates the skin of the back of the upper neck and of the scalp posterior to the ear. Structure Origin It arises from the (lateral branch of the ventral ramus) of cervical spinal nerve C2; it (sources differ) receives or may also receive fibres from cervical spinal nerve C3. It originates between the atlas, and axis. The lesser occipital nerve is one of the four cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus. Course and relations It curves around the accessory nerve (CN XI) to come to course anterior to it. It then curves around and ascends along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle; rarely, it may pierce the muscle. Near the cranium, it perforates the deep cervical fascia. It is continued upwards along the scalp posterior to the auricle. It divides in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |