|
Southern Pembrokeshire
Little England beyond Wales is a name that has been applied to an area of southern Pembrokeshire and southwestern Carmarthenshire in Wales, which has been English rather than Welsh in language and culture for many centuries despite its remoteness from England. Its origins may lie in the Irish, Norse, Norman, Flemish and Saxon settlement that took place in this area more than in other areas of South West Wales. Its northern boundary is known as the Landsker Line. A number of writers and scholars, ancient and modern, have discussed how and when this difference came about, and why it should persist, with no clear explanation coming to the fore. Etymology The language boundary between this region and the area to the north where Welsh is more commonly spoken, sometimes known as the Landsker Line, is noted for its sharpness and resilience. Although it is probably much older, the first known approximation of "Little England beyond Wales" was in the 16th century, when William Camden cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes a part of northern Finland). In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and cultural similarities. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
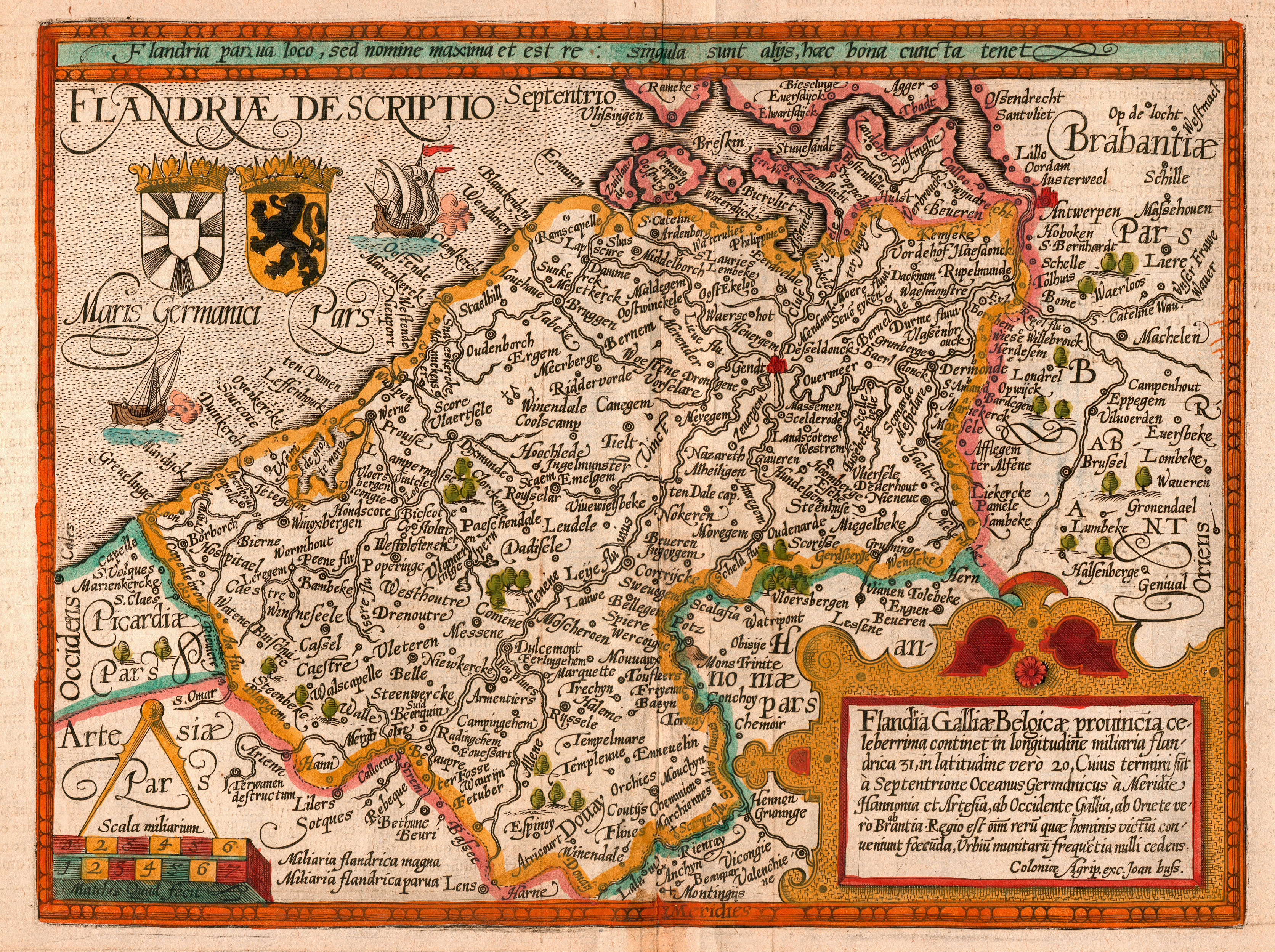
Belgian Refugees
Following the creation of Belgium as a nation state, Belgian people have sought refuge abroad on several occasions. From the early days of independence and the threat of The Netherlands or France, to two World Wars and the Independence of Congo, Belgians have been on the run themselves, for various reasons, as refugees. Before 1914 Little England beyond Wales (12th c.) Both Henry I and Henry II systematically plantied of Flemish settlers in the part of south Pembrokeshire that became referred to as Little England beyond Wales. As well as securing a part of Wales this was also driven by the desire to have the warmongering Flemish (the "Flemish wolves") out of England. As an increasing number of "foreigners" settled, the original inhabitants were driven away in a "process of ethnical cleansing". The Normans and the Flemish built the Landsker Line, a line of castles from Newgale on the west coast to Amroth on the south east coast, a line which remains as a regional divide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish People
Flemish people or Flemings ( ) are a Germanic peoples, Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%. ''Flemish'' was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders in modern-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings" irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval Duchy of Brabant and the medieval County of Loon, where the modern national identity and Flemish culture, culture gradually formed. History The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shire
Shire () is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries. It is generally synonymous with county (such as Cheshire and Worcestershire). British counties are among the oldest extant national divisions in the world. It was first used in Wessex from the beginning of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlement, and spread to most of the rest of England in the 10th century. Today, 23 counties bear the "-shire" suffix in England, 23 in Scotland, and 10 in Wales. In some rural parts of Australia, a shire is a local government area; however, in Australia, it is not synonymous with a "county", which is a lands administrative divisions of Australia, lands administrative division. Etymology The word ''shire'' derives from the Old English language, Old English , from the Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic (), denoting an 'official charge' a 'district under a governor', and a 'care'. In the UK, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcher Lord
A marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales. A marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in France) before the introduction of the title of "marquess" in Britain; no marcher lord ever bore the rank of marquess. In this context, the word ''march'' means a border region or frontier, and is cognate with the verb "to march", both ultimately derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*mereg-'', "edge" or "boundary". The greatest marcher lords included the earls of Chester, Gloucester, Hereford, Pembroke and Shrewsbury (see also English earls of March). County palatine Some strong earldoms along the Welsh border were granted the privileged status of county palatine shortly after the Norman Conquest, but only that based on Chester survived for a long period. The term particularly applies to Anglo-Norman lords in Wales, who had complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I Of England
Henry I ( – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in 1087, Henry's elder brothers Robert Curthose and William Rufus inherited Duchy of Normandy, Normandy and England, respectively; Henry was left landless. He purchased the County of Cotentin in western Normandy from Robert, but his brothers deposed him in 1091. He gradually rebuilt his power base in the Cotentin and allied himself with William Rufus against Robert. Present in England with his brother William when William died in a hunting accident, Henry seized the English throne, promising at his coronation to correct many of William's less popular policies. He married Matilda of Scotland and they had two surviving children, Empress Matilda and William Adelin; he also had many illegitimate children by his numerous mistresses. Robert, who invaded from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Pembroke
Earl of Pembroke is a title in the Peerage of England that was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title, which is associated with Pembroke, Pembrokeshire in West Wales, has been recreated ten times from its original inception. Due to the number of creations of the Earldom, the original seat of Pembroke Castle is no longer attached to the title. , the current holder of the earldom is William Herbert, 18th Earl of Pembroke, which is the 10th creation of the title. For the past 400 years, his family's seat has been Wilton House, Wiltshire. The Earls of Pembroke also hold the title Earl of Montgomery, created for the Philip Herbert, 4th Earl of Pembroke, younger son of Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke before he succeeded as the 4th Earl in 1630. The current Earls of Pembroke also carry the subsidiary titles: Baron Herbert of Cardiff, of Cardiff in the County of Glamorgan (1551), Baron Herbert of Shurland, of Shurland in the Isle of Sheppey in the Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnulf De Montgomery
Arnulf de Montgomery (born 1066; died 1118/1122) was an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman magnate. He was a younger son of Roger de Montgomerie, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury, Roger de Montgomery and Mabel de Bellême. Arnulf's father was a leading magnate in Duchy of Normandy, Normandy and Anglo-Norman England, England, and played an active part in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Wales in the late eleventh century. Following the Montgomerys' successes against the Welsh, Arnulf established himself at Pembroke, Pembrokeshire, Pembroke, where an earth and timber castle was erected, and was probably rewarded with the title Earl of Pembroke. At the turn of the twelfth century Arnulf reached height, with his lordship including much of the former Welsh Kingdom of Deheubarth as well as various lands in Yorkshire. Not long after reaching this apex of his career, Arnulf assisted his eldest surviving brother, Robert of Bellême, 3rd Earl of Shrewsbury, Robert de Bellême, in a rebellion against Henry I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Trevisa
350px, John Trevisa (or John of Trevisa; ; fl. 1342–1402 AD) was a Cornish writer and professional translator. Trevisa was born at Trevessa in the parish of St Enoder in mid-Cornwall, in Britain and was a native Cornish speaker. He was educated at Exeter College, Oxford, and became Vicar of Berkeley, Gloucestershire, chaplain to the 5th Lord Berkeley, and Canon of Westbury on Trym. He translated into English for his patron the Latin '' Polychronicon'' of Ranulf Higden, adding remarks of his own, and prefacing it with a '' Dialogue on Translation between a Lord and a Clerk''. He likewise made various other translations, including Bartholomaeus Anglicus' ''On the Properties of Things'' ''(De Proprietatibus Rerum)'', a medieval forerunner of the encyclopedia. It seems likely that he was the translator of the Bible into Cornish, a language, which until recently, was thought not to have possessed a bible translation. A fellow of The Queen's College, Oxford, from 1372 to 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic peoples, Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Although the details of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, their early settlement and History of Anglo-Saxon England, political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St David's
St Davids or St David's (, , "Saint David, David's Welsh toponymy, house”) is a St David's Cathedral, cathedral City status in the United Kingdom, city in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It lies on the River Alun, Pembrokeshire, River Alun and is part of the community (Wales), community of St Davids and the Cathedral Close. It is the resting place of Saint David, Wales's patron saint, and named after him. St Davids is the United Kingdom's List of smallest cities in the United Kingdom, smallest city by population (number of residents within the wider community was 1,751 in 2021) and Urban area#United Kingdom, urban area, however it is not the smallest city by Local government#United Kingdom, local authority boundary area (which is the City of London). St Davids was given City status in the United Kingdom, city status in the 12th century. This does not derive automatically, but in England and Wales was traditionally given to cathedral towns under practices laid down in the early 154 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |