|
Simply Connected Space
In topology, a topological space is called simply connected (or 1-connected, or 1-simply connected) if it is path-connected and every path between two points can be continuously transformed into any other such path while preserving the two endpoints in question. Intuitively, this corresponds to a space that has no disjoint parts and no holes that go completely through it, because two paths going around different sides of such a hole cannot be continuously transformed into each other. The fundamental group of a topological space is an indicator of the failure for the space to be simply connected: a path-connected topological space is simply connected if and only if its fundamental group is trivial. Definition and equivalent formulations A topological space X is called if it is path-connected and any loop in X defined by f : S^1 \to X can be contracted to a point: there exists a continuous map F : D^2 \to X such that F restricted to S^1 is f. Here, S^1 and D^2 denotes the unit c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Torsion (mechanics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a Set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of List of continuity-related mathematical topics, continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and Homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klein Bottle
In mathematics, the Klein bottle () is an example of a Orientability, non-orientable Surface (topology), surface; that is, informally, a one-sided surface which, if traveled upon, could be followed back to the point of origin while flipping the traveler upside down. More formally, the Klein bottle is a two-dimensional manifold on which one cannot define a normal vector at each point that varies continuous function, continuously over the whole manifold. Other related non-orientable surfaces include the Möbius strip and the real projective plane. While a Möbius strip is a surface with a Boundary (topology), boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary. For comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary. The Klein bottle was first described in 1882 by the mathematician Felix Klein. Construction The following square is a fundamental polygon of the Klein bottle. The idea is to 'glue' together the corresponding red and blue edges with the arrows matching, as in the diagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Plane
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane (geometry), plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect at a single point, but there are some pairs of lines (namely, parallel lines) that do not intersect. A projective plane can be thought of as an ordinary plane equipped with additional "points at infinity" where parallel lines intersect. Thus ''any'' two distinct lines in a projective plane intersect at exactly one point. Renaissance artists, in developing the techniques of drawing in Perspective (graphical)#Renaissance, perspective, laid the groundwork for this mathematical topic. The archetypical example is the real projective plane, also known as the extended Euclidean plane. This example, in slightly different guises, is important in algebraic geometry, topology and projective geometry where it may be denoted variously by , RP2, or P2(R), among other notations. There are many other projective planes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Möbius Strip
In mathematics, a Möbius strip, Möbius band, or Möbius loop is a Surface (topology), surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist. As a mathematical object, it was discovered by Johann Benedict Listing and August Ferdinand Möbius in 1858, but it had already appeared in Ancient Rome, Roman mosaics from the third century Common Era, CE. The Möbius strip is a orientability, non-orientable surface, meaning that within it one cannot consistently distinguish clockwise from counterclockwise turns. Every non-orientable surface contains a Möbius strip. As an abstract topological space, the Möbius strip can be embedded into three-dimensional Euclidean space in many different ways: a clockwise half-twist is different from a counterclockwise half-twist, and it can also be embedded with odd numbers of twists greater than one, or with a Knot (mathematics), knotted centerline. Any two embeddings with the same knot for the centerline and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in a solid ball versus sphere surface)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term "cylinder" could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the '' right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George A. Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
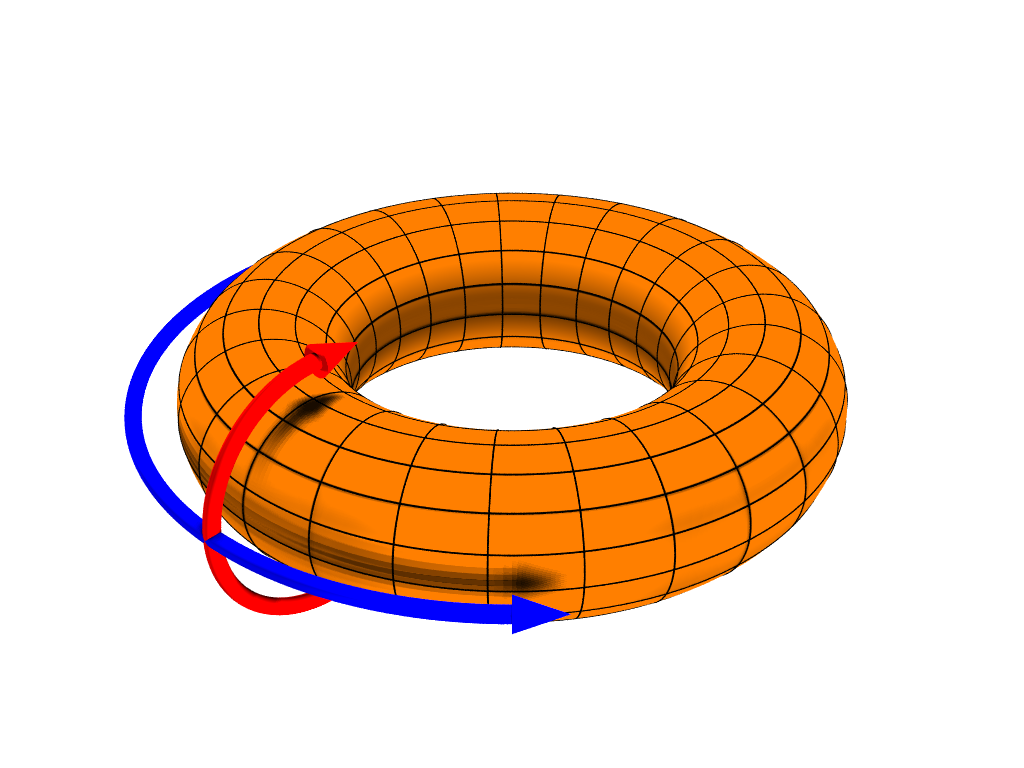
Torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a Lemon (geometry), spindle torus (or ''self-crossing torus'' or ''self-intersecting torus''). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Subset
In geometry, a set of points is convex if it contains every line segment between two points in the set. For example, a solid cube (geometry), cube is a convex set, but anything that is hollow or has an indent, for example, a crescent shape, is not convex. The boundary (topology), boundary of a convex set in the plane is always a convex curve. The intersection of all the convex sets that contain a given subset of Euclidean space is called the convex hull of . It is the smallest convex set containing . A convex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval (mathematics), interval with the property that its epigraph (mathematics), epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of a function, graph of the function) is a convex set. Convex minimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization, optimization that studies the problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets. The branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex sets and convex f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-sphere
In mathematics, an -sphere or hypersphere is an - dimensional generalization of the -dimensional circle and -dimensional sphere to any non-negative integer . The circle is considered 1-dimensional and the sphere 2-dimensional because a point within them has one and two degrees of freedom respectively. However, the typical embedding of the 1-dimensional circle is in 2-dimensional space, the 2-dimensional sphere is usually depicted embedded in 3-dimensional space, and a general -sphere is embedded in an -dimensional space. The term ''hyper''sphere is commonly used to distinguish spheres of dimension which are thus embedded in a space of dimension , which means that they cannot be easily visualized. The -sphere is the setting for -dimensional spherical geometry. Considered extrinsically, as a hypersurface embedded in -dimensional Euclidean space, an -sphere is the locus of points at equal distance (the ''radius'') from a given '' center'' point. Its interior, consisting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus Cycles
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a spindle torus (or ''self-crossing torus'' or ''self-intersecting torus''). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a '' toroid'', as in a square toroid. Real-world objects that ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wormhole
A wormhole is a hypothetical structure that connects disparate points in spacetime. It can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are based on a special Solutions of the Einstein field equations, solution of the Einstein field equations. More precisely they are a transcendental bijection of the spacetime continuum, an Asymptote, asymptotic projection of the Calabi–Yau manifold manifesting itself in anti-de Sitter space. Wormholes are consistent with the General relativity, general theory of relativity, but whether they actually exist is unknown. Many physicists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a Four-dimensional space, fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |