|
Silazane
A silazane is a family of compounds with Si-N bonds. Usually the Si and N have organic substituents. They are analogous to siloxanes, with -NR- (R = alkyl, aryl) replacing -O-. Examples One illustrative family of silazanes are derived from tert-butylamine, including (CH3)3SiN(H)tBu and (CH3)2Si(N(H)tBu)2. More structurally complex is H3SiN(H)tBusub>2(μ-N(H)tBu)2 with bridging amides. There are a wide variety of polysilazanes. Reactions The majority of silazanes are moisture sensitive. With water they convert to silanols or siloxanes. See also * Phosphazene * Paraformaldehyde Paraformaldehyde (PFA) is the smallest polyoxymethylene, the polymerization product of formaldehyde with a typical degree of polymerization of 8–100 units. Paraformaldehyde commonly has a slight odor of formaldehyde due to decomposition. Par ... References Nitrogen(−III) compounds Silicon compounds {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysilazane
In organosilicon chemistry, polysilazanes are polymers in which silicon and nitrogen atoms alternate to form the basic backbone (). Since each silicon atom is bound to two separate nitrogen atoms and each nitrogen atom to two silicon atoms, both chains and rings of the formula occur. R can be hydrogen atoms or organic substituents. If all substituents R are hydrogen atoms, the polymer is designated as perhydropolysilazane, polyperhydridosilazane, or inorganic polysilazane . If hydrocarbon substituents are bound to the silicon atoms, the polymers are designated as Organopolysilazanes. Molecularly, polysilazanes are isoelectronic with and close relatives to polysiloxanes (silicones). History The synthesis of polyorganosilazanes was first described in 1964 by Krüger and Rochow. By reacting ammonia with chlorosilanes (ammonolysis), trimeric or tetrameric cyclosilazanes were formed initially and further reacted at high temperatures with a catalyst to yield higher molecular weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSD CIF HMMSAZ
CSD may refer to: Finance * Central securities depository * Confederate States Dollar * Serbian dinar, by previous ISO 4217 code Organizations Education * California School for the Deaf (other), several institutions * Canyons School District, in Utah, US * Cheltenham School District, in Pennsylvania, US * Christina School District, in Delaware, US * Cleveland School District, in Mississippi, US * Cordova School District, in Alaska, US Other organizations * Canteen Stores Department (India), a chain of stores operated by the Indian Ministry of Defence at military bases * CSD Pakistan (Canteen Stores Department), a chain of stores operated by the Pakistani Ministry of Defence * Chartered Society of Designers, a British learned society for various kinds of design work * Commission on Sustainable Development (1992–2013), a former UN agency * Communication Service for the Deaf, an American non-profit company providing ASL services * Congress of Democratic Trade Unions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
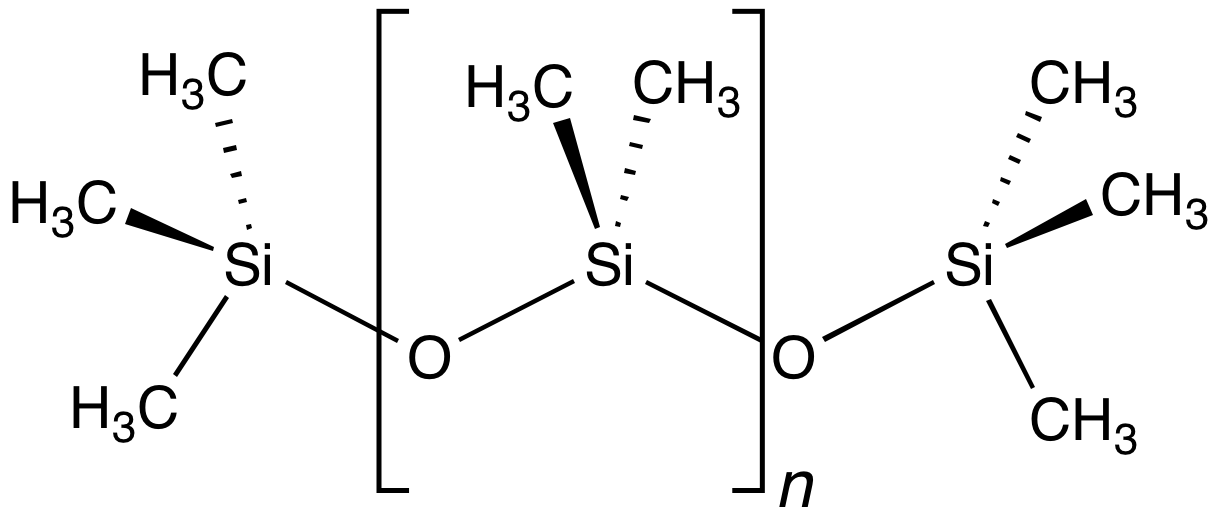
Siloxane
In organosilicon chemistry, a siloxane is an organic compound containing a functional group of two silicon atoms bound to an oxygen atom: . The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae and . Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones , the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility. Structure Siloxanes generally adopt structures expected for linked tetrahedral ("''sp''3-like") centers. The Si−O bond length is 1.64 Å (vs Si–C distance of 1.92 Å) and the Si-O-Si angle is rather open at 142.5°. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tert-butylamine
''tert''-Butylamine (also erbumine and other names) is an organic chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CNH2. It is a colorless liquid with a typical amine-like odor. ''tert''-Butylamine is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being ''n''-butylamine, ''sec''-butylamine and isobutylamine. Preparation ''tert''-Butylamine is produced commercially by direct amination of isobutylene using zeolite catalysts: :NH3 + CH2=C(CH3)2 → H2NC(CH3)3 The Ritter reaction of isobutene with hydrogen cyanide is not useful because it produces too much waste. :(CH3)2C=CH2 + HCN + H2O → (CH3)3CNHCHO :(CH3)3CNHCHO + H2O → (CH3)3CNH2 + HCO2H In the laboratory, it can be prepared by the hydrogenolysis of 2,2-dimethylethylenimine, or via ''tert''-butylphthalimide. Uses ''tert''-Butylamine is used as an intermediate in the preparation of the sulfenamides such as ''N''-''tert''-butyl-2-benzothiazylsulfenamide and ''N''-''tert''-butyl-2-benzothiazylsulfeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Moisture is defined as water in the adsorbed or absorbed phase. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some commercial products. Moisture also refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. The soil also includes moisture. Moisture control in products Control of moisture in products can be a vital part of the process of the product. There is a substantial amount of moisture in what seems to be dry matter. Ranging in products from cornflake cereals to laundry detergent, washing powders, moisture can play an important role in the final quality of the product. There are two main aspects of concern in moisture control in products: allowing too much moisture or too little of it. For example, adding some water to cornflake cereal, which is sold by weight, reduces costs and prevents it from tasting too dry, but adding too much water can affect th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silanol
A silanol is a functional group in silicon chemistry with the connectivity Si–O–H. It is related to the hydroxy functional group (C–O–H) found in all alcohols. Silanols are often invoked as intermediates in organosilicon chemistry and silicate mineralogy. If a silanol contains one or more organic residues, it is an organosilanol. Preparation From alkoxysilanes The first isolated example of a silanol was , reported in 1871 by Albert Ladenburg. He prepared the “silicol” by hydrolysis of (Et = ). From silyl halides and related compounds Silanols are generally synthesized by hydrolysis of halosilanes, alkoxysilanes, or aminosilanes. Chlorosilanes are the most common reactants: :R3Si–Cl + H2O → R3Si–OH + HCl The hydrolysis of fluorosilanes requires more forcing reagents, i.e. alkali. The alkoxysilanes ( silyl ethers) of the type are slow to hydrolyze. Compared to the silyl ethers, silyl acetates are faster to hydrolyze, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphazene
Phosphazenes refer to various classes of organophosphorus compounds featuring phosphorus(V) with a double bond between P and N. One class of phosphazenes have the formula . These phosphazenes are also known as iminophosphoranes and phosphine imides. They are superbases. BEMP and ''t''-Bu-P4 Well known phosphazene bases are BEMP (2-tert-Butylimino-2-diEthylamino-1,3-diMethylperhydro-1,3,2-diazaPhosphorine) with an acetonitrile pKa, p''K''a of the conjugate acid of 27.6 and the phosphorimidic triamide P4-t-Bu, ''t''-Bu-P4 (p''K''BH+ = 42.7) also known as P4-t-Bu, Schwesinger base. BEMP and P4-t-Bu, ''t''-Bu-P4 have attracted attention because they are nucleophilicity, low-nucleophilic, which precludes their participating in competing reactions. Being non-ionic ("charge-neutral"), they are soluble in nonpolar solvents. Protonation takes place at a doubly bonded nitrogen atom. The p''K''a's of , where R = Methyl group, Me and Pyrrolidine, pyrrolidinyl, are 42.7 and 44, respectively. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraformaldehyde
Paraformaldehyde (PFA) is the smallest polyoxymethylene, the polymerization product of formaldehyde with a typical degree of polymerization of 8–100 units. Paraformaldehyde commonly has a slight odor of formaldehyde due to decomposition. Paraformaldehyde is a poly-acetal. Synthesis Paraformaldehyde forms slowly in aqueous formaldehyde solutions as a white precipitate, especially if stored in the cold. Formalin actually contains very little monomeric formaldehyde; most of it forms short chains of polyformaldehyde. A small amount of methanol is often added as a stabilizer to limit the extent of polymerization. Reactions Paraformaldehyde can be depolymerized to formaldehyde gas by dry heating and to formaldehyde solution by water in the presence of a base, an acid or heat. The high purity formaldehyde solutions obtained in this way are used as a fixative for microscopy and histology. The resulting formaldehyde gas from dry heating paraformaldehyde is flammable. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen(−III) Compounds
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790 when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instead the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |