|
Signal Beam
A signal beam or object beam is one of at least two laser A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ... beams used to write holograms. The signal beam is the beam that carries the information to be stored in the hologram. In the case of a holographic picture, this beam is reflected off the object being recorded, into the media. In the case of holographic data storage, the beam has some kind information encoded into it (for instance, it can be sent through a transparency or a spatial light modulator). The other beam necessary to write a hologram is the reference beam. Holography Laser applications {{Tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hologram
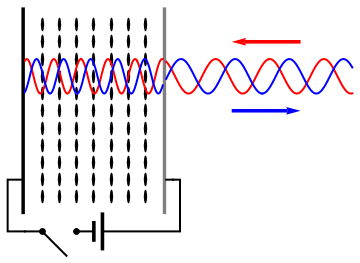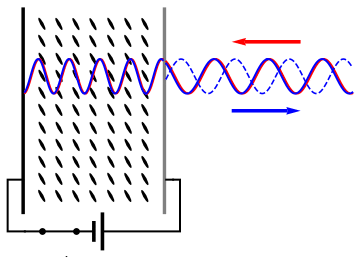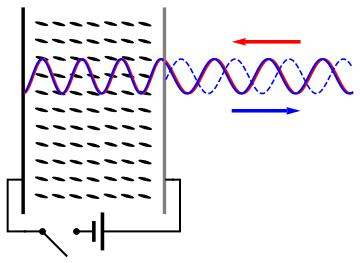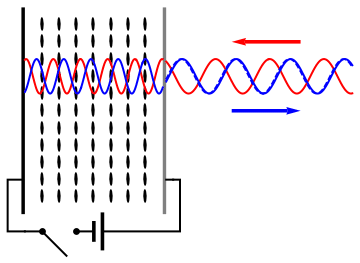
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave. A hologram is a recording of an interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. When s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (optics)
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable light scattering by particles, scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material (with or without scattering of light). It allows light to pass through but the light does not necessarily follow Snell's law on the macroscopic scale; the photons may be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in the index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Light Modulator
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the intensity, phase, or polarization of light in a spatially varying manner. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. SLMs are primarily marketed for image projection, displays devices, and maskless lithography. SLMs are also used in optical computing and holographic optical tweezers. Usually, an SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. It is also possible to produce devices that modulate the polarization of the beam, and modulate the polarization, phase, and intensity simultaneously. SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to the way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Beam
A reference beam is a laser beam used to read and write holograms. It is one of two laser beams used to create a hologram. In order to read a hologram out, some aspects of the reference beam (namely its angle of incidence, beam profile and wavelength) must be reproduced exactly as when it was used to write the hologram. As a result, usually reference beams are Gaussian beam In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or ...s or spherical wave beams (beams that radiate from a single point) which are fairly easy to reproduce. The other beam used to write a hologram is the signal beam or object beam. References Works cited * Holography {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of Holography#Non-optical holography, wave. A hologram is a recording of an Wave interference, interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |