|
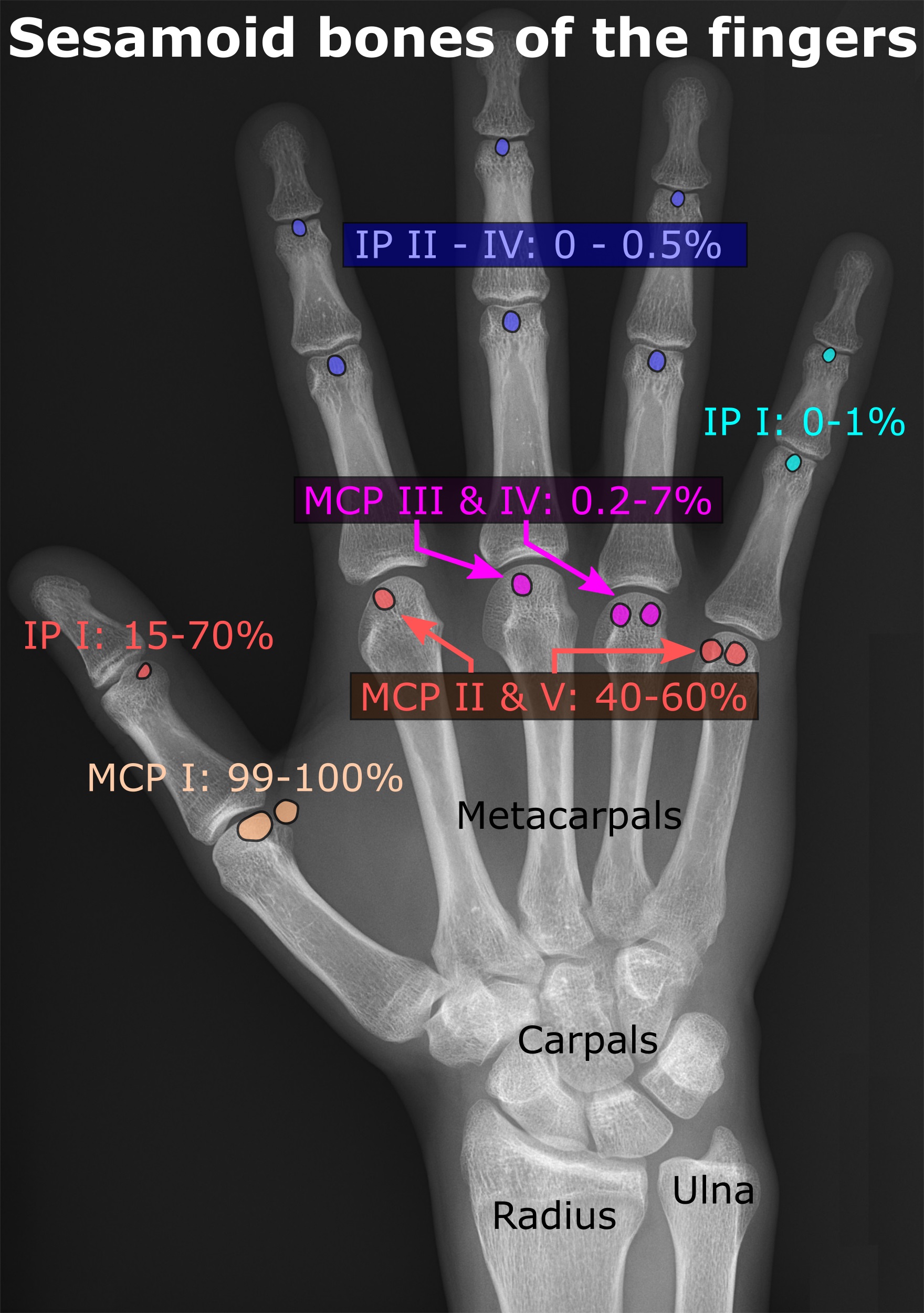
Sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the human body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone and fifth metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
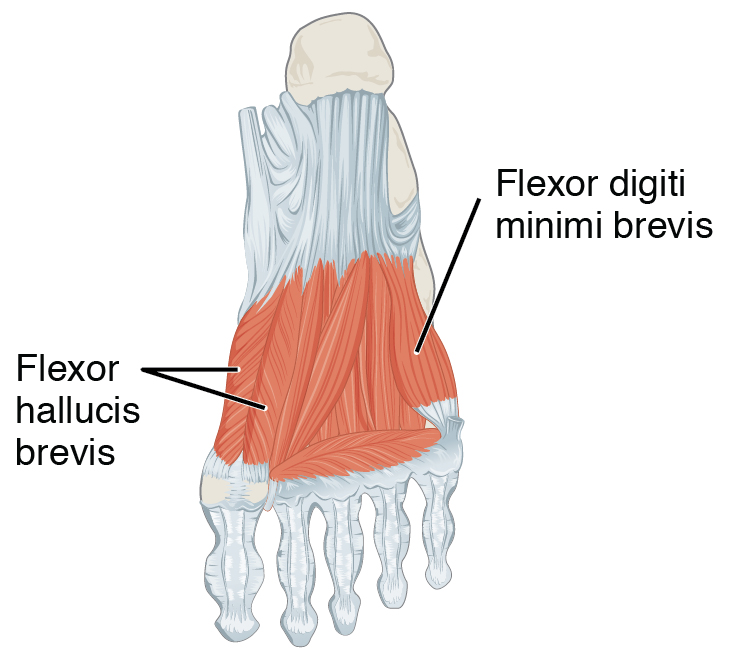
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe. Structure Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Innervation The med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Metatarsal Bone
The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them. Like the four other metatarsals, it can be divided into three parts: base, body and head. The base is the part closest to the ankle and the head is closest to the big toe. The narrowed part in the middle is referred to as the body of the bone. The bone is somewhat flattened, giving it two sides: the plantar (towards the sole of the foot) and the dorsal side (the area facing upwards while standing). The base presents, as a rule, no articular facets (joint surfaces) on its sides, but occasionally on the lateral side there is an oval facet, by which it articulates with the second metatarsal. On the lateral part of the plantar surface there is a rough oval prominence, or tuberosity, for the insertion of the tendon of the fibularis longus. The first metatarsal articulates (forms joints) with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisiformis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist ( carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi uln ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patella
The patella (: patellae or patellas), also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds, and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles. In humans, the patella is the largest sesamoid bone (i.e., embedded within a tendon or a muscle) in the body. Babies are born with a patella of soft cartilage which begins to ossify into bone at about four years of age. Structure The patella is a sesamoid bone roughly triangular in shape, with the apex of the patella facing downwards. The apex is the most inferior (lowest) part of the patella. It is pointed in shape, and gives attachment to the patellar ligament. The front and back surfaces are joined by a thin margin and towards centre by a thicker margin. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle attaches to the base of the patella., with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabella
The fabella is a small sesamoid bone found in some mammals embedded in the tendon of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle behind the lateral condyle of the femur. It is an accessory bone, an anatomical variation present in 39% of humans. Rarely, there are two or three of these bones (fabella bi- or tripartita). It can be mistaken for a loose body or osteophyte. The word ''fabella'' is a Latin diminutive of ''faba'' 'bean'. In humans, it is more common in men than women, older individuals compared to younger, and there is high regional variation, with fabellae being most common in people living in Asia and Oceania and least common in people living in North America and Africa. Bilateral cases (one per knee) are more common than unilateral ones (one per individual), and within individual cases, fabellae are equally likely to be present in right or left knees. Taken together, these data suggest the ability to form a fabella may be genetically controlled, but fabella ossific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialised connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralisation of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Variation
An anatomical variation, anatomical variant, or anatomical variability is a presentation of body structure with Morphology (biology), morphological features different from those that are typically described in the majority of individuals. Anatomical variations are categorized into three types including morphometric (size or shape), consistency (present or absent), and spatial (proximal/distal or right/left). Variations are seen as normal in the sense that they are found consistently among different individuals, are mostly without symptoms, and are termed anatomical variations rather than abnormalities. Anatomical variations are mainly caused by genetics and may vary considerably between different populations. The rate of variation considerably differs between single organ (anatomy), organs, particularly in muscles. Knowledge of anatomical variations is important in order to distinguish them from pathological conditions. A very early paper published in 1898, presented anatomic var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsophalangeal Joint
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints) are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are analogous to the knuckles of the hand, and are consequently known as toe knuckles in common speech. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges). The region of skin directly below the joints forms the Ball (foot), ball of the foot. The ligaments are the plantar and two collateral. Movements The movements permitted in the metatarsophalangeal joints are flexion, Extension (kinesiology), extension, List of abductors of the human body, abduction, List of adductors of the human body, adduction and Circumduction (anatomy), circumduction. File:The feet of C. H. Unthan, the armless fiddler Wellcome L0034227.jpg, Left: toes adducted (pulled towards the center) and spread (abducted); right, both feet clenched (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory And Sesamoid Bones Of The Foot - Dorsoplantar Projection
Accessory may refer to: * Accessory (legal term), a person who assists a criminal In anatomy * Accessory bone * Accessory breast * Accessory kidney * Accessory muscle * Accessory nucleus, in anatomy, a cranial nerve nucleus * Accessory nerve * Accessory spleen In arts and entertainment * Accessory (band), with members Dirk Steyer and Ivo Lottig * Video game accessory, a piece of hardware used in conjunction with a video game console for playing video games * ''Accessories'' (album), a compilation album from Dutch alternative rock band The Gathering * Accessory, a type of rulebook in ''Dungeons & Dragons'' and other role-playing games Other uses * Fashion accessory, an item used to complement a fashion or style * Accessory suite, a secondary dwelling on a parcel of land * Rental accessories and attachments, accessories used in the rental industry * Cable accessories for connecting and terminating cables * Accessory fruit, in which some of the flesh is derived from ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal Bone
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head (distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |