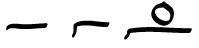|
Section Sign
The section sign (§) is a typographical character for referencing individually numbered sections of a document; it is frequently used when citing sections of a legal code. It is also known as the section symbol, section mark, double-s, or silcrow. In other languages it may be called the "paragraph symbol" (for example, ). The section sign typically appears akin to a letter S stacked on top of another S. Use The section sign is often used when referring to a specific section of a legal code. For example, in Bluebook style, "Title 16 of the United States Code Section 580p" becomes "16 U.S.C. §580p". The section sign is frequently used along with the ''pilcrow'' (or ''paragraph sign''), , to reference a specific paragraph within a section of a document. While is usually read in spoken English as the word "section", many other languages use the word "paragraph" exclusively to refer to a section of a document (especially of legal text), and use other words to describe a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typographical
Typography is the art and technique of arranging type to make written language legible, readable and appealing when displayed. The arrangement of type involves selecting typefaces, point sizes, line lengths, line spacing, letter spacing, and spaces between pairs of letters. The term ''typography'' is also applied to the style, arrangement, and appearance of the letters, numbers, and symbols created by the process. Type design is a closely related craft, sometimes considered part of typography; most typographers do not design typefaces, and some type designers do not consider themselves typographers. Typography also may be used as an ornamental and decorative device, unrelated to the communication of information. Typography is also the work of graphic designers, art directors, manga artists, comic book artists, and, now, anyone who arranges words, letters, numbers, and symbols for publication, display, or distribution, from clerical workers and newsletter writers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO-8859-1
ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, ''Information technology—8-bit computing, 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character (computing), character sets—Part 1: Latin alphabet No. 1'', is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. ISO/IEC 8859-1 encodes what it refers to as "Latin alphabet no. 1", consisting of 191 character (computing), characters from the Latin script. This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa. It is the basis for some popular 8-bit character sets and the first two blocks of characters in Unicode. , 1.1% of all website, web sites use . It is the most declared single-byte character encoding, but as Web browsers and the HTML5 standard interpret them as the superset Windows-1252, these documents may include characters from that set. Some countries or languages show a higher usage than the global average, in 2025 Brazil according to web ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punctuation Marks
Punctuation marks are marks indicating how a piece of written text should be read (silently or aloud) and, consequently, understood. The oldest known examples of punctuation marks were found in the Mesha Stele from the 9th century BC, consisting of points between the words and horizontal strokes between sections. The alphabet-based writing began with no spaces, no capitalization, no vowels (see abjad), and with only a few punctuation marks, as it was mostly aimed at recording business transactions. Only with the Greek playwrights (such as Euripides and Aristophanes) did the ends of sentences begin to be marked to help actors know when to make a pause during performances. Punctuation includes space between words and both obsolete and modern signs. By the 19th century, the punctuation marks were used hierarchically, according to their weight. Six marks, proposed in 1966 by the French author Hervé Bazin, could be seen as predecessors of emoticons and emojis. In rare cases, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bell & Sons
George Bell & Sons was an English book publishing house. It was based in London and existed from 1839 to 1986. History George Bell & Sons was founded by George Bell as an educational bookseller, with the intention of selling the output of London university presses; but became best known as an independent publisher of classics and children's books. One of Bell's first investments in publishing was a series of ''Railway Companions''; that is, booklets of timetables and tourist guides. Within a year Bell's publishing business had outstripped his retail business, and he elected to move from his original offices into Fleet Street. There G. Bell & Sons branched into the publication of books on art, architecture, and archaeology, in addition to the classics for which the company was already known. Bell's reputation was only improved by his association with Henry Cole. In the mid-1850s, Bell expanded again, printing the children's books of Margaret Gatty (''Parables from Nature' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, Application software, software applications, music, audiovisual, and print materials. The Archive also advocates a Information wants to be free, free and open Internet. Its mission is committing to provide "universal access to all knowledge". The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of billions of web captures. The Archive also oversees numerous Internet Archive#Book collections, book digitization projects, collectively one of the world's largest book digitization efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paragraphos
A paragraphos (, , from , 'beside', and , 'to write') was a mark in ancient Greek punctuation, marking a division in a text (as between speakers in a dialogue or drama) or drawing the reader's attention to another division mark, such as the two dot punctuation mark (used as an obelism). There are many variants of this symbol, sometimes supposed to have developed from Greek gamma (), the first letter of the word . It was usually placed at the beginning of a line and trailing a little way under or over the text. It was referenced by Aristotle, who was dismissive of its use. Unicode encodes multiple versions: * * * * See also * Obelus and Obelism, Greek marginal notes * Coronis, the Greek paragraph mark * Pilcrow In typography, the pilcrow (¶) is a glyph used to identify a paragraph. In editorial production the ''pilcrow'' typographic character is also known as the paragraph mark, the paragraph sign, the paragraph symbol, the paraph, and the blind ... (¶), the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Language
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic or Homeric period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, though its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek, and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek, and Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harper & Brothers
Harper is an American publishing house, the flagship Imprint (trade name), imprint of global publisher HarperCollins, based in New York City. Founded in New York in 1817 by James Harper (publisher), James Harper and his brother John, the company operated as J. & J. Harper until 1833, when it changed its name to Harper & Brothers, reflecting the inclusion of Joseph and Fletcher Harper. Harper began publishing ''Harper's Magazine'', ''Harper's Weekly'', and other periodicals beginning in the 1850s. From 1962 to 1990, the company was known as Harper & Row after its merger with Row, Peterson & Company. Harper & Row was purchased in 1987 by News Corporation and combined with William Collins, Sons, its United Kingdom counterpart, in 1990 to form HarperCollins, although the Harper name has been used in its place since 2007. History J. & J. Harper (1817–1833) James Harper (publisher), James Harper and his brother John, printers by training, started their book publishing business, J. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotype Imaging
Monotype Imaging Holdings Inc., founded as Lanston Monotype Machine Company in 1887 in Philadelphia by Tolbert Lanston, is an American (historically Anglo-American) company that specializes in digital typesetting and typeface design for use with consumer electronics devices. Based in Woburn, Massachusetts, the company has been responsible for many developments in printing technology—in particular the Monotype machine, which was a fully mechanical hot metal typesetter, that produced texts automatically, all single type. Monotype was involved in the design and production of many typefaces in the 20th century. Monotype developed many of the most widely used typeface designs, including Times New Roman, Gill Sans, and Arial. Via acquisitions including Linotype GmbH, International Typeface Corporation, Bitstream, FontShop, URW, Hoefler & Co., Fontsmith, and Colophon Foundry, the company has gained the rights to major font families including Helvetica, ITC Franklin Gothi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En:signum
Signum is Latin for "sign" and may refer to: Brands and companies * Integra Signum, a (defunct) Swiss railroad signaling company ** Integra-Signum, a train protection system * Opel Signum, an Opel car model * Signum Biosciences, a company based in New Jersey * Signum (typeface), a 1955 typeface designed by Georg Trump for the Weber Typefoundry Media * ''Signum'' (magazine), a German literary magazine * Signum (musical group), a trance music group * Signum (''Nanoha''), a character from the ''Magical Girl Lyrical Nanoha'' series * Signum Quartet, a string quartet based in Cologne, Germany * Signum Records, a classical music record label in the UK Other uses * Signum, part of Roman naming conventions * Signum, an alternative name for some Roman Republic army units * Signum (anatomy), a part of the female Lepidoptera genitalia * Signum function In mathematics, the sign function or signum function (from '' signum'', Latin for "sign") is a function that has the value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |