|
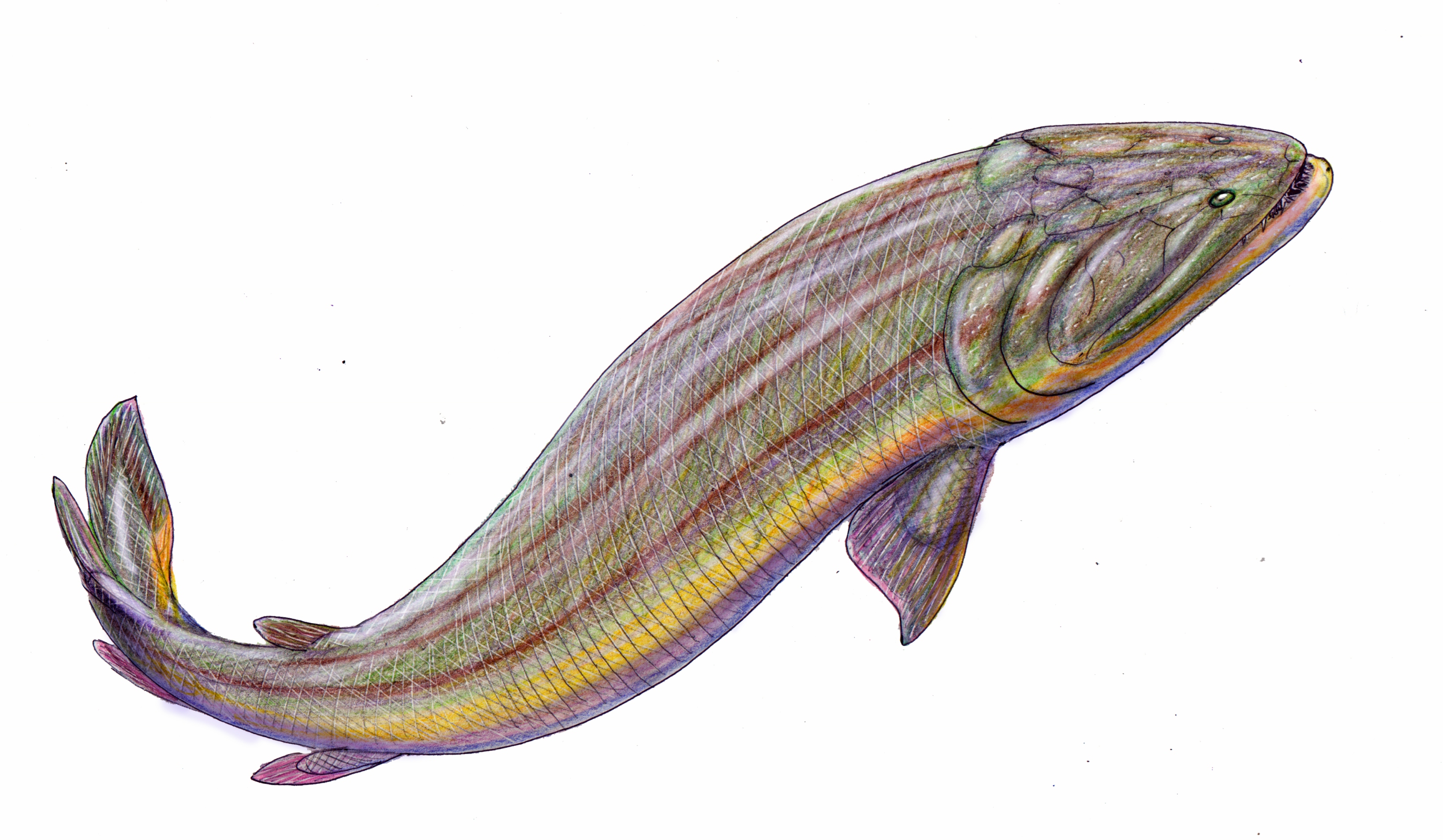
Sarcopterygians
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines supporting the fins. The tetrapods, a mostly terrestrial clade of vertebrates, are now recognized as having evolved from sarcopterygian ancestors and are most closely related to lungfishes. Their paired pectoral and pelvic fins evolved into limbs, and their foregut diverticulum eventually evolved into air-breathing lungs. Cladistically, this would make the tetrapods a subgroup within Sarcopterygii and thus sarcopterygians themselves. As a result, the phrase "lobe-finned fish" normally refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
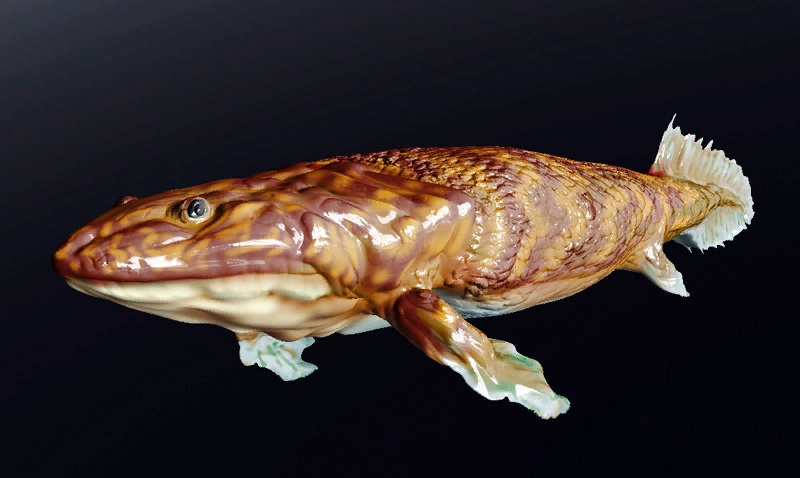
Panderichthys
''Panderichthys'' is a genus of extinction, extinct Sarcopterygii, sarcopterygian (lobe-finned fish) from the late Devonian period, about 380 Myr, Mya. ''Panderichthys'', which was recovered from Frasnian (early Late Devonian) deposits in Latvia, is represented by two species. ''P. stolbovi'' is known only from some snout fragments and an incomplete lower jaw. ''P. rhombolepis'' is known from several more complete specimens. Although it probably belongs to a sister group of the earliest tetrapods, ''Panderichthys'' exhibits a range of features transitional between Tristichopteridae, tristichopterid lobe-fin fishes (e.g., ''Eusthenopteron'') and early tetrapods. It is named after the German-Baltic paleontologist Christian Heinrich Pander. Possible tetrapod tracks dating back to before the appearance of ''Panderichthys'' in the fossil record were reported in 2010, which suggests that ''Panderichthys'' is not a direct ancestor of tetrapods, but nonetheless shows the traits that evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiyu Oneiros
''Guiyu oneiros'' is one of the earliest articulated Osteichthyes, bony fish discovered. Fossils of ''Guiyu'' have been found in what is now Qujing, Yunnan, China, in late Silurian marine strata, about 425 million years old. ''Guiyu'' is part of the Xiaoxiang fauna which is rich in fossils representing a marine ecosystem. Found in the late Silurian#Ludlow, Ludlow-aged Kuanti Formation, the remains were dated using conodonts as index fossils. The Xiaoxiang fauna also includes galeaspids, placoderms and acanthodians. Discovery and naming ''Guiyu'' was described by Chinese palaeontologist Zhu Min (:zh:朱敏 (古生物学家), 朱敏) and others in 2009, based on a near-complete articulated specimen. The generic name ''Guiyu'' is a transliteration of the Mandarin 鬼魚 ''guǐyú'' "Ghosts in Chinese culture, ghost fish" and the specific name ''oneiros'' is from Greek ὄνειρος "dream". Description The holotype specimen is about in length and about in depth. The caudal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinistia
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus '' Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was described from specimens fished off the coast of South Africa from 1938 onward; they are now also known to inhabit the seas around the Comoro Islands off the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorpha
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as '' Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodomorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Characteristics Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onychodontiformes
Onychodontiformes (also known as Onychodontida and Struniiformes) is an order of prehistoric sarcopterygian fish that lived during the Devonian period. The onychodontiforms are generally regarded as early-diverging members of the coelacanth lineage. Phylogeny The following cladogram is adapted from Mondéjar-Fernández (2020). The study recovered Onychodontiformes as a paraphyletic Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ... group, which is shown in green: References External links Onychodontiformes at Palaeos Prehistoric lobe-finned fish Prehistoric fish orders Devonian bony fish Early Devonian first appearances Famennian extinctions Paraphyletic groups {{paleo-lobefinned-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psarolepis
''Psarolepis'' (; ''psārolepis'', from Greek ψαρός 'speckled' and λεπίς 'scale') is a genus of extinct bony fish which lived around 397 to 418 million years ago ( Pridoli to Lochkovian stages). Fossils of ''Psarolepis'' have been found mainly in South China and described by paleontologist Xiaobo Yu in 1998. It is not known certainly in which group ''Psarolepis'' belongs, but paleontologists agree that it probably is a basal genus and seems to be close to the common ancestor of lobe-finned and ray-finned fishes.Benton, M. J. (2005): ''Vertebrate Palaeontology'', page 65. In 2001, paleontologist John A. Long compared ''Psarolepis'' with onychodontiform fishes and refer to their relationships. Description ''Psarolepis'' had a pair of 'parasymphysical tooth whorls', teeth which extend up at the front of the lower jaw. The head was made of several thick dermal plates and covered with deep pock-marks and large pores. Another trait is a large pectoral spine, just in fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bony Fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) and the extinct placoderms and acanthodians, which have endoskeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of extant taxon, extant fish are members of Osteichthyes, being an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 order (biology), orders, over 435 family (biology), families and 28,000 species. The group is divided into two main clades, the ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii, which makes up the vast majority of extant fish) and the lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii, which gave rise to all land vertebrates, i.e. tetrapods). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 425 million years old from the late Silurian, which are also transitional fossils showing a dentition, tooth pattern th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapodomorph
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced forms transitional between fish and the early labyrinthodonts, such as '' Tiktaalik'', have been referred to as "fishapods" by their discoverers, being half-fish, half-tetrapods, in appearance and limb morphology. The Tetrapodomorpha contains the crown group tetrapods (the last common ancestor of living tetrapods and all of its descendants) and several groups of early stem tetrapods, which includes several groups of related lobe-finned fishes, collectively known as the osteolepiforms. The Tetrapodomorpha minus the crown group Tetrapoda are the stem Tetrapoda, a paraphyletic unit encompassing the fish to tetrapod transition. Characteristics Among the characteristics defining tetrapodomorphs are modifications to the fins, notably a hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidotrichia
In a zoological context, spines are hard, needle-like anatomical structures found in both vertebrate and invertebrate species. The spines of most spiny mammals are modified hairs, with a spongy center covered in a thick, hard layer of keratin and a sharp, sometimes barbed tip. Occurrence Mammals Spines in mammals include the prickles of hedgehogs, and among rodents, the quills of porcupines (of both the New World and the Old), as well as the prickly fur of spiny mice, spiny pocket mice, and of species of spiny rat. They are also found on afrotherian tenrecs of the family Tenrecinae (hedgehog and streaked tenrecs), marsupial spiny bandicoots, and on echidnas (a monotreme). An ancient synapsid, ''Dimetrodon'', had extremely long spines on its backbone that were joined together with a web of skin that formed a sail-like structure. Many mammalian species, like cats and fossas, also have penile spines. The Mesozoic eutriconodont mammal '' Spinolestes'' already displayed sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fish fin, fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spine (zoology), spines called ''lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister taxon, sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation (anatomy), articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |