|
Sacral Spinal Nerve 2
The sacral spinal nerve 2 (S2) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment. Nervous System -- Groups of Nerves It originates from the from below the 2nd body of the 
Muscles S2 supplies many muscles, either directly or through nerves originating from S2. They are not innervated with S2 as single origin, but partly by S2 and partly by other spinal nerves. They are ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical vertebrae, cervical, thoracic vertebrae, thoracic, lumbar vertebrae, lumbar, sacral vertebrae, sacral and coccygeal vertebrae, coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve root axon, fibers from its Dorsal root of spinal nerve, dorsal and Ventral root of spinal nerve, ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent nerve fiber, afferent sensory root and carries sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Segment
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. In humans, the spinal cord is a continuation of the brainstem and anatomically begins at the occipital bone, passing out of the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it tapers to become the cauda equina. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmented column of vertebrae that surrounds and protects the spinal cord. The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs in a series of cartilaginous joints. The dorsal portion of the spinal column houses the spinal canal, an elongated cavity formed by the alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segment. There are around 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human spine is one of the most-studied examples, as the general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in other mammals, reptiles, and birds. The shape of the vertebral body does, however, vary somewhat b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall, it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pelvic cavity. In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincter Urethrae
The urethral sphincters are two muscles used to control the exit of urine in the urinary bladder through the urethra. The two muscles are either the male or female external urethral sphincter and the internal urethral sphincter. When either of these muscles contracts, the urethra is sealed shut. The external urethral sphincter originates at the ischiopubic ramus and inserts into the intermeshing muscle fibers from the other side. It is controlled by the deep perineal branch of the pudendal nerve. Activity in the nerve fibers constricts the urethra. * The internal sphincter muscle of urethra: located at the bladder's inferior end and the urethra's proximal end at the junction of the urethra with the urinary bladder. The internal sphincter is a continuation of the detrusor muscle and is made of smooth muscle, therefore it is under involuntary or autonomic control. This is the primary muscle for prohibiting urination. * The female or male external sphincter muscle of urethra (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteus Maximus Muscle
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes. Its large size is one of the most characteristic features of the muscular system in humans,Norman Eizenberg et al., ''General Anatomy: Principles and Applications'' (2008), p. 17. connected as it is with the power of maintaining the trunk in the erect posture. Other primates have much flatter hips and cannot sustain standing erectly. The muscle is made up of muscle fascicles lying parallel with one another, and are collected together into larger bundles separated by fibrous septa. Structure The gluteus ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the buttock, gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group. The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. Depending upon the given position of the leg, it acts either as external (lateral) rotator of the thigh or as abductor of the thigh. It is innervated by the piriformis nerve. Structure The piriformis is a flat muscle, and is pyramidal in shape. Origin The piriformis muscle originates from the Pelvic surface of sacrum, anterior (front) surface of the sacrum by three fleshy digitations attached to the Sacrum, second, third, and fourth sacral vertebra. It also arises from the superior margin of the greater sciatic notch, the gluteal surface of the Ilium (bone), ilium (near the posterior inferior iliac spine), the sacroiliac joint capsule, and (sometimes) the sacrotuberous ligament (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
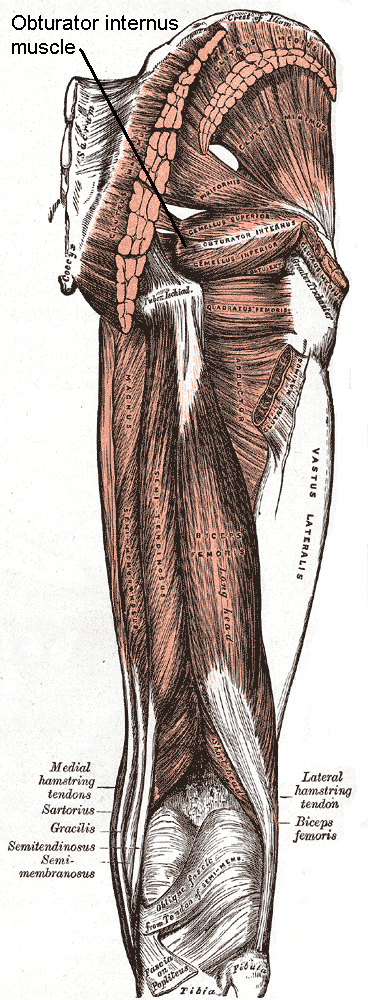
Obturator Internus Muscle
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen. The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint. It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum. Structure Origin The internal obturator muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis. It surrounds the obturator foramen. It is attached to the inferior pubic ramus and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim. It reaches from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front. It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Gemellus Muscle
The gemelli muscles are the inferior gemellus muscle and the superior gemellus muscle, two small accessory fasciculi to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle. The gemelli muscles belong to the lateral rotator group of six muscles of the hip that rotate the femur in the hip joint. Superior gemellus muscle The gemelli muscles are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the internal obturator muscle which is received into a groove between them. The superior gemellus muscle is the higher placed gemellus muscle that arises from the outer (gluteal) surface of the ischial spine, and blends with the upper part of the tendon of the internal obturator. It is smaller than the inferior gemellus. In some people, the fibres of the gemellus superior extend further than average, and are prolonged onto the medial surface of the greater trochanter of the femur. The superior and inferior gemelli are supplied by the inferior gluteal artery. Nerve supply to the superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitendinosus Muscle
The semitendinosus () is a long superficial muscle in the Posterior compartment of thigh, back of the thigh. It is so named because it has a very long tendon of insertion. It lies posteromedially in the thigh, superficial to the semimembranosus. Structure The semitendinosus, remarkable for the great length of its tendon of insertion, is situated at the posterior and medial aspect of the thigh. It arises from the lower and medial impression on the upper part of the tuberosity of the ischium, by a tendon common to it and the long head of the biceps femoris muscle, biceps femoris; it also arises from an aponeurosis which connects the adjacent surfaces of the two muscles to the extent of about 7.5 cm. from their origin. The muscle is wikt:fusiform, fusiform and ends a little below the middle of the thigh in a long round tendon which lies along the medial side of the popliteal fossa; it then curves around the Medial condyle of tibia, medial condyle of the tibia and passes over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocnemius Muscle
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It is located superficial to the soleus in the posterior (back) compartment of the leg. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, extending across a total of three joints (knee, ankle and subtalar joints). The muscle is named via Latin, from Greek γαστήρ (''gaster'') 'belly' or 'stomach' and κνήμη (''knḗmē'') 'leg', meaning 'stomach of the leg' (referring to the bulging shape of the calf). Structure Origin/proximal attachment The lateral head originates from the lateral condyle of the femur, while the medial head originates from the medial condyle of the femur. Insertion/distal attachment Its other end forms a common tendon with the soleus muscle; this tendon is known as the calcaneal tendon or Achilles tendon and inserts onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus, or heel bone. Relations The ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |