|
Reduit
A reduit is a fortified structure such as a citadel or a keep into which the defending troops can retreat when the outer defences are breached. The term is also used to describe an area of a country, which, through a ring of heavy fortifications or through enhancing through fortification the defences offered by natural features such as mountains, will be defended even when the rest of the country is occupied by a hostile power. . An entry for this word was first included in New English Dictionary, 1904. *1948 Times 31 Dec. 3/3 "The obsolete conception of a national reduit has been abandoned in favour of an extra-territorial base established in the Belgian Congo". *2003 Macpherson ''Amer. Intelligence War-time London'' vi. 177 "As for the Reduit (or Redoubt), this was the rumoured area for 'a last-ditch stand' in the Bavarian, Austrian and Italian Alps". National Reduit In English the term National redoubt is fairly commonly used. A redoubt is an outlying fortification, so it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redoubt
A redoubt (historically redout) is a fort or fort system usually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying on earthworks, although some are constructed of stone or brick. It is meant to protect soldiers outside the main defensive line and can be a permanent structure or a hastily constructed temporary fortification. The word means "a place of retreat". Redoubts were a component of the military strategies of most European empires during the colonial era, especially in the outer works of Vauban-style fortresses made popular during the 17th century, although the concept of redoubts has existed since medieval times. A redoubt differs from a redan in that the redan is open in the rear, whereas the redoubt was considered an enclosed work. The advent of mobile warfare in the 20th century diminished the importance of stationary defence positions and siege warfare. Historically important redoubts English Civil War During the English Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Redoubt (Belgium)
The National Redoubt (french: Réduit national, nl, Stelling van Antwerpen) was a strategic defensive belt of fortifications built in Belgium. The National redoubt was the infrastructural cornerstone of Belgian defensive strategy from 1890–1940. The following fortifications and defensive constructions were an integral part of the National redoubt: * the Fortified Position of Liège (Luik) with a number of forts * the Fortified Position of Namur (Namen) with a number of forts * Fort Eben-Emael * the K-W line: a "canal" from Koningshooikt to Wavre, to defend against tank incursions * another anti-tank canal in the Kempen, roughly aligned with the outer ring of fortifications around Antwerpen * the coastal defenses as a retreat position against invasion troops The most important part of the national redoubt was a double ring of defensive forts around the city and port of Antwerp. The National Redoubt was a -long belt of fortifications built from 1859 to 1914, as the stronge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
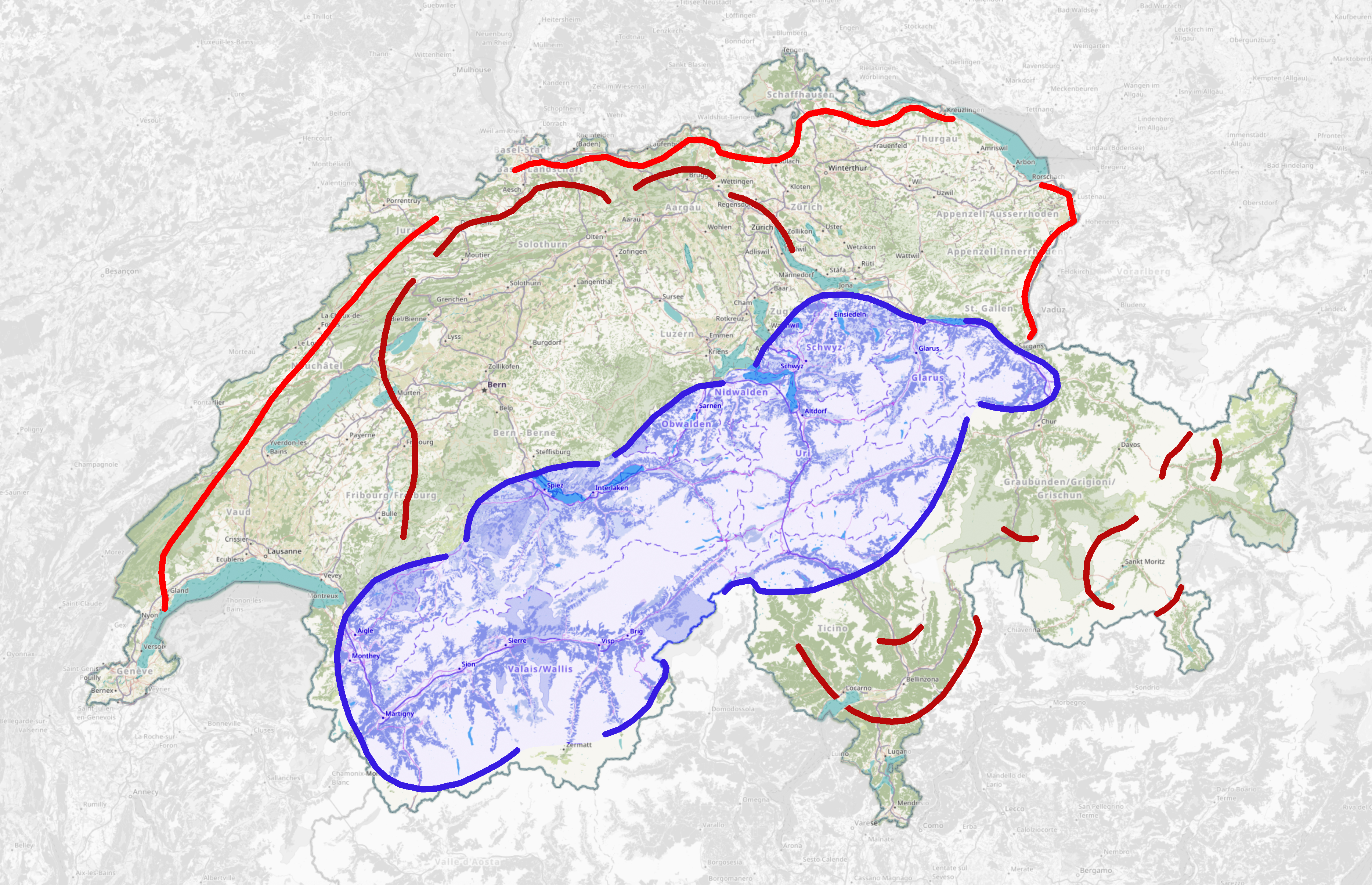
National Redoubt (Switzerland)
The Swiss National Redoubt (; ; ; ) is a defensive plan developed by the Swiss government beginning in the 1880s to respond to foreign invasion. In the opening years of the Second World War the plan was expanded and refined to deal with a potential German invasion. The term "National Redoubt" primarily refers to the fortifications begun in the 1880s that secured the mountainous central part of Switzerland, providing a defended refuge for a retreating Swiss Army. The National Redoubt encompassed a widely distributed set of fortifications on a general east-west line through the Alps, centering around the major fortress complexes of St. Maurice, St. Gotthard, and Sargans. These fortresses primarily defended the alpine crossings between Germany and Italy and were outside the industrialized and populated regions of Switzerland. These regions were defended by the "Border Line", and the "Army Position" somewhat farther back. While not intended as an impassable barrier, these lines cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all continents. The size of a peninsula can range from tiny to very large. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula. Peninsulas form due to a variety of causes. Etymology Peninsula derives , which is translated as 'peninsula'. itself was derived , or together, 'almost an island'. The word entered English in the 16th century. Definitions A peninsula is usually defined as a piece of land surrounded on most, but not all sides, but is sometimes instead defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. A peninsula may be bordered by more than one body of water, and the body of water does not have to be an ocean or a sea. A piece of land on a very tight river bend or one between two rivers is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Commune de Dunkerque (59183) INSEE It lies from the Belgian border. It has the third-largest French harbour. The population of the commune in 2019 was 86,279. Etymology and language use The name of Dunkirk derives from ' dune' or '' and 'church', thu ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
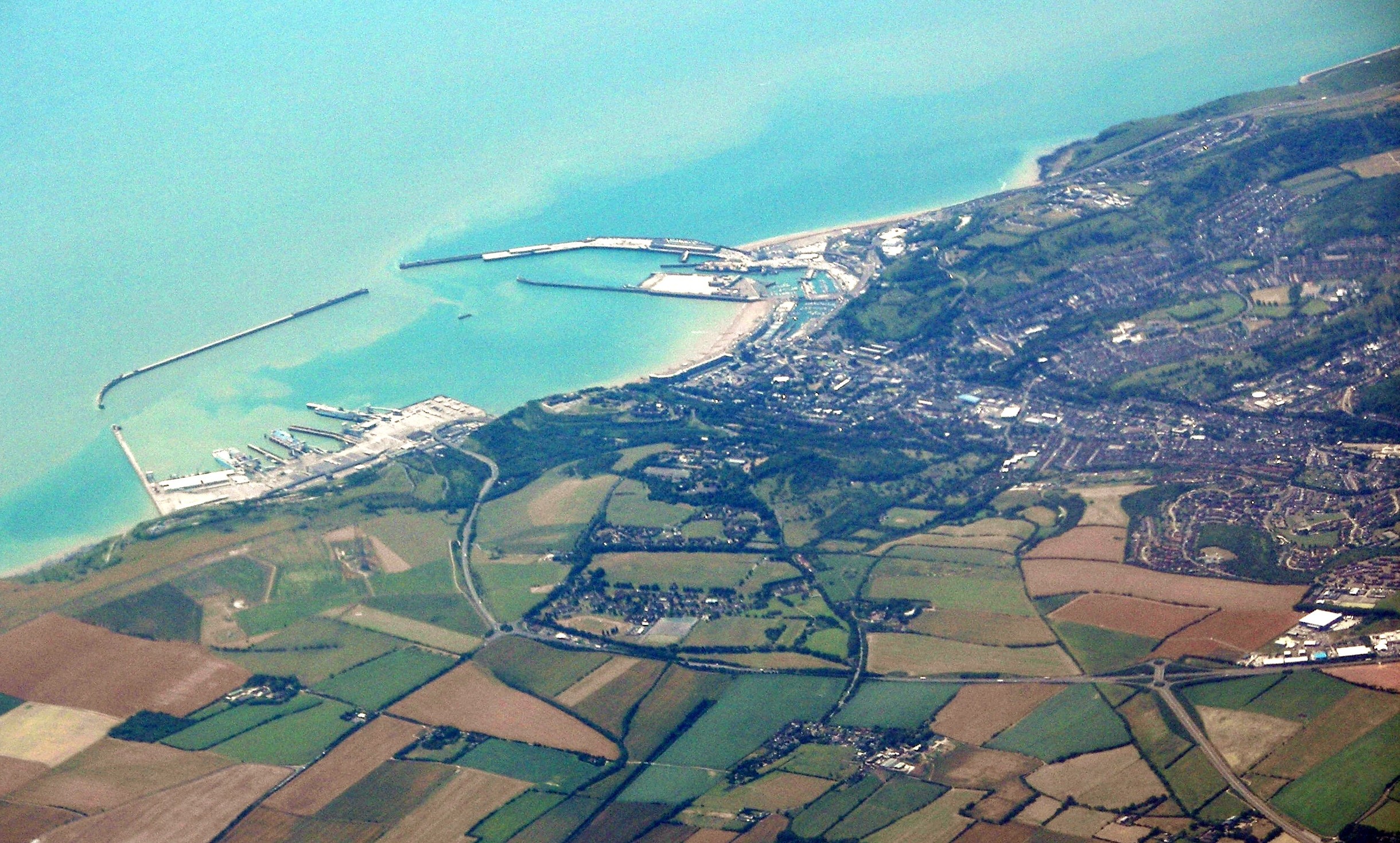
Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. The population of the city proper is 72,929; that of the urban area is 149,673 (2018).Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Calais (073), Commune de Calais (62193) INSEE Calais overlooks the Strait of Dover, the narrowest point in the |
Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the Côte d'Opale, a touristic stretch of French coast on the English Channel between Calais and Normandy, and the most visited location in the region after the Lille conurbation. Boulogne is its department's second-largest city after Calais, and the 183rd-largest in France.Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2017 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Ports
The Channel Ports are seaports in southern England and the facing continent, which allow for short crossings of the English Channel. There is no formal definition, but there is a general understanding of the term. Some ferry companies divide their routes into "short" and "long" crossings. The broadest definition might be from Plymouth east to Kent and from Roscoff to Zeebrugge although a tighter definition would exclude ports west of Newhaven and Dieppe. A historic group of such ports is the Cinque Ports of south-east England, most of which have ceased to be commercial ports. Ports England The ports vary in size and their relative importance has fluctuated during recent history. Dover has established a lead in the cross-Channel ferry routes through its geographic position and development of its facilities and hinterland. This business has been sustained despite competition from the Channel Tunnel. Other minor ports in Kent and Sussex have retained some trade but these tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France declared war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive and by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. German armies invaded Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and attempted an invasion of France. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front until the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944. In ''Fall Gelb'' ("Case Yellow"), German armoured units made a surprise push through the Ardennes and then along the Somme valley, cutting off and surrounding the Allied units that had advanced into Belgium to meet the German armies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss Plateau and the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountains, one of its three main physiographic regions. The Swiss Alps extend over both the Western Alps and the Eastern Alps, encompassing an area sometimes called Central Alps. While the northern ranges from the Bernese Alps to the Appenzell Alps are entirely in Switzerland, the southern ranges from the Mont Blanc massif to the Bernina massif are shared with other countries such as France, Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein. The Swiss Alps comprise almost all the highest mountains of the Alps, such as Dufourspitze (4,634 m), the Dom (4,545 m), the Liskamm (4,527 m), the Weisshorn (4,506 m) and the Matterhorn (4,478 m). The other following major summits can be found in this list of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
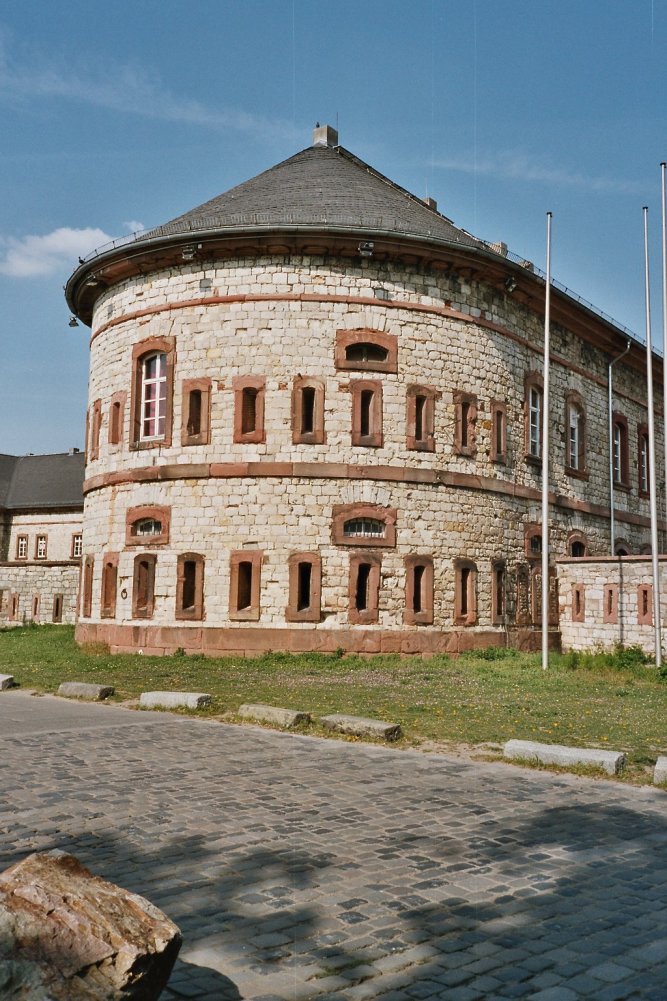
Bundesfestung Mainz Kastel
Under the terms of the 1815 Peace of Paris, France was obliged to pay for the construction of a line of fortresses to protect the German Confederation against any future aggression by France. All fortresses were located outside Austria and Prussia — the two biggest, bickering powers of the Confederation. Section C. "Defensive System of the Germanic Confederation" of the protocol drawn up at Paris on 3 November 1815, declared Mainz, Luxemburg, and Landau to be fortresses belonging to the Confederation of Germany, and stipulated that a fourth should be constructed on the Upper Rhine. In conformity with this act, a portion of the funds, which France was compelled to pay by way of indemnity for the cost of placing her on a peaceable footing, was thus appropriated: £200,000 were set aside for completing the works at Mainz; £800,000 were assigned to Prussia, to be applied upon its fortresses on the Lower Rhine; another £800,000 were reserved for constructing the new federal fortr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)