|
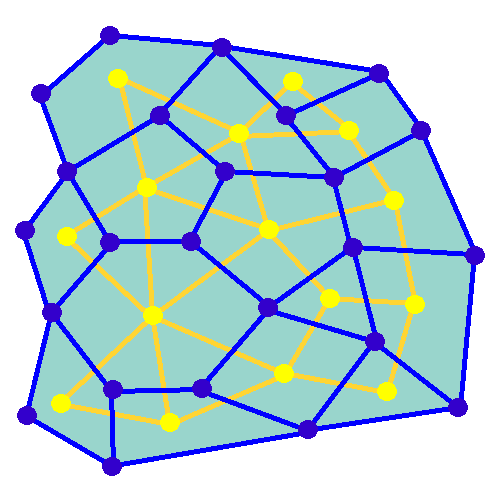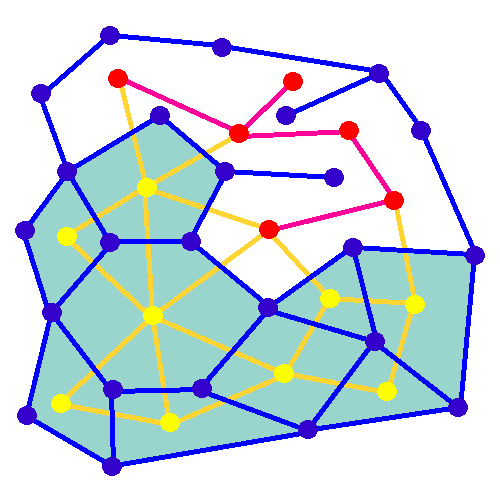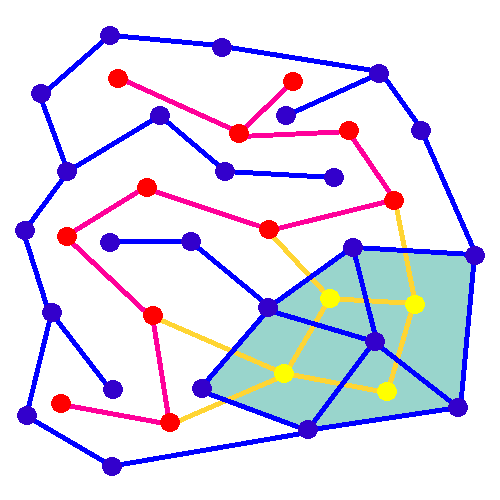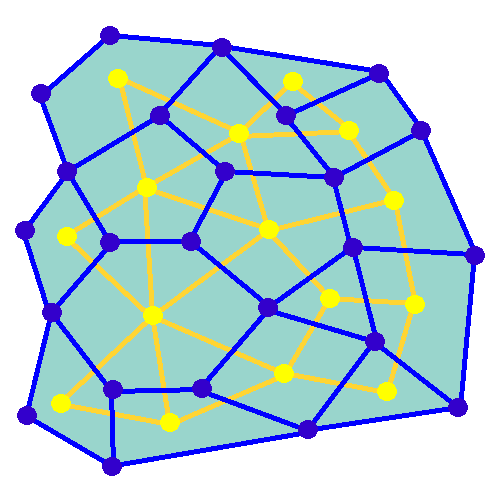
Random Minimum Spanning Tree
In mathematics, a random minimum spanning tree may be formed by assigning independent random weights from some distribution to the edges of an undirected graph, and then constructing the minimum spanning tree of the graph. When the given graph is a complete graph on vertices, and the edge weights have a continuous distribution function whose derivative at zero is , then the expected weight of its random minimum spanning trees is bounded by a constant, rather than growing as a function of . More precisely, this constant tends in the limit (as goes to infinity) to , where is the Riemann zeta function and is Apéry's constant. For instance, for edge weights that are uniformly distributed on the unit interval, the derivative is , and the limit is just . For other graphs, the expected weight of the random minimum spanning tree can be calculated as an integral involving the Tutte polynomial of the graph. In contrast to uniformly random spanning trees of complete graphs, for which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Independence (probability Theory)
Independence is a fundamental notion in probability theory, as in statistics and the theory of stochastic processes. Two event (probability theory), events are independent, statistically independent, or stochastically independent if, informally speaking, the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other or, equivalently, does not affect the odds. Similarly, two random variables are independent if the realization of one does not affect the probability distribution of the other. When dealing with collections of more than two events, two notions of independence need to be distinguished. The events are called Pairwise independence, pairwise independent if any two events in the collection are independent of each other, while mutual independence (or collective independence) of events means, informally speaking, that each event is independent of any combination of other events in the collection. A similar notion exists for collections of random variables. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Uniform Spanning Tree
A uniform is a variety of costume worn by members of an organization while usually participating in that organization's activity. Modern uniforms are most often worn by armed forces and paramilitary organizations such as police, emergency services, security guards, in some workplaces and schools, and by inmates in prisons. In some countries, some other officials also wear uniforms in their duties; such is the case of the Commissioned Corps of the United States Public Health Service or the French prefects. For some organizations, such as police, it may be illegal for non-members to wear the uniform. Etymology From the Latin ''unus'' (meaning one), and ''forma'' (meaning form). Variants Corporate and work uniforms Workers sometimes wear uniforms or corporate clothing of one nature or another. Workers required to wear a uniform may include retail workers, bank and post-office workers, public-security and health-care workers, blue-collar employees, personal trainers in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discrete Applied Mathematics
''Discrete Applied Mathematics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering algorithmic and applied areas of discrete mathematics. It is published by Elsevier and the editor-in-chief is Endre Boros (Rutgers University). The journal was split off from another Elsevier journal, ''Discrete Mathematics'', in 1979, with that journal's founder Peter Ladislaw Hammer as its founding editor-in-chief. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexing in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.139. References External links *{{official website, http://www.journals.elsevier.com/discrete-applied-mathematics/ Discrete mathematics journals Academic journals established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Annals Of Probability
''Annals of Probability'' is a leading peer-reviewed probability journal published by the Institute of Mathematical Statistics, which is the main international society for researchers in the areas probability and statistics. The journal was started in 1973 as a continuation in part of the ''Annals of Mathematical Statistics'', which was split into the '' Annals of Statistics'' and this journal. In July 2021, the journal was ranked 7th in the field Probability & Statistics with Applications according to Google Scholar. It had an impact factor of 1.470 (), according to the ''Journal Citation Reports''. The impact factor for 2018 is 2.085. Its CiteScore is 4.3, and SCImago Journal Rank The SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) indicator is a measure of the prestige of scholarly journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the prestige of the journals where the citations come from. Etymology SCImago ... is 3.184, both from 2020. Editors-in-chief: past a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maze Generation
Maze generation algorithms are algorithm, automated methods for the creation of mazes. Graph theory based methods A maze can be generated by starting with a predetermined arrangement of cells (most commonly a rectangular grid but other arrangements are possible) with wall sites between them. This predetermined arrangement can be considered as a connected graph with the edges representing possible wall sites and the nodes representing cells. The purpose of the maze generation algorithm can then be considered to be making a subgraph in which it is challenging to find a route between two particular nodes. If the subgraph is not connected graph, connected, then there are regions of the graph that are wasted because they do not contribute to the search space. If the graph contains loops, then there may be multiple paths between the chosen nodes. Because of this, maze generation is often approached as generating a random spanning tree (mathematics), spanning tree. Loops, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Invasion Percolation
Invasion percolation is a mathematical model of realistic fluid distributions for slow immiscible fluid invasion in porous media, in percolation theory. It "explicitly takes into account the transport process taking place". A wetting fluid such as water takes over from a non-wetting fluid such as oil, and capillary forces are taken into account. It was introduced by Wilkinson and Willemsen (1983). Invasion percolation proceeds in avalanches or bursts, and thus exhibits a form of intermittency. This avalanche behavior has been likened to self-organized criticality Self-organized criticality (SOC) is a property of dynamical systems that have a critical point as an attractor. Their macroscopic behavior thus displays the spatial or temporal scale-invariance characteristic of the critical point of a phas ....D. Sornette, A. Johansen, I. Dornic, J. Phys. I (France) 5, 325 (1995) References Percolation theory Fluid dynamics {{fluiddynamics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Grid Graph
In graph theory, a lattice graph, mesh graph, or grid graph is a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph whose graph drawing, drawing, Embedding, embedded in some Euclidean space , forms a regular tiling. This implies that the group (mathematics), group of Bijection, bijective transformations that send the graph to itself is a lattice (group), lattice in the group-theoretical sense. Typically, no clear distinction is made between such a graph in the more abstract sense of graph theory, and its drawing in space (often the plane or 3D space). This type of graph may more shortly be called just a lattice, mesh, or grid. Moreover, these terms are also commonly used for a finite section of the infinite graph, as in "an 8 × 8 square grid". The term lattice graph has also been given in the literature to various other kinds of graphs with some regular structure, such as the Cartesian product of graphs, Cartesian product of a number of complete graphs. Square grid graph A comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diameter (graph Theory)
In graph theory, the diameter of a connected undirected graph is the farthest distance between any two of its vertices. That is, it is the diameter of a set for the set of vertices of the graph, and for the shortest-path distance in the graph. Diameter may be considered either for weighted or for unweighted graphs. Researchers have studied the problem of computing the diameter, both in arbitrary graphs and in special classes of graphs. The diameter of a disconnected graph may be defined to be infinite, or undefined. Graphs of low diameter The degree diameter problem seeks tight relations between the diameter, number of vertices, and degree of a graph. One way of formulating it is to ask for the largest graph with given bounds on its degree and diameter. For any fixed degree, this maximum size is exponential in diameter, with the base of the exponent depending on the degree. The girth of a graph, the length of its shortest cycle, can be at most 2k+1 for a graph of diameter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tutte Polynomial
The Tutte polynomial, also called the dichromate or the Tutte–Whitney polynomial, is a graph polynomial. It is a polynomial in two variables which plays an important role in graph theory. It is defined for every undirected graph G and contains information about how the graph is connected. It is denoted by T_G. The importance of this polynomial stems from the information it contains about G. Though originally studied in algebraic graph theory as a generalization of counting problems related to graph coloring and nowhere-zero flow, it contains several famous other specializations from other sciences such as the Jones polynomial from knot theory and the partition functions of the Potts model from statistical physics. It is also the source of several central computational problems in theoretical computer science. The Tutte polynomial has several equivalent definitions. It is essentially equivalent to Whitney’s rank polynomial, Tutte’s own dichromatic polynomial and Fortuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Undirected Graph
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', then this graph is directed, because owing money is not necessarily reciprocated. Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unit Interval
In mathematics, the unit interval is the closed interval , that is, the set of all real numbers that are greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1. It is often denoted ' (capital letter ). In addition to its role in real analysis, the unit interval is used to study homotopy theory in the field of topology. In the literature, the term "unit interval" is sometimes applied to the other shapes that an interval from 0 to 1 could take: , , and . However, the notation ' is most commonly reserved for the closed interval . Properties The unit interval is a complete metric space, homeomorphic to the extended real number line. As a topological space, it is compact, contractible, path connected and locally path connected. The Hilbert cube is obtained by taking a topological product of countably many copies of the unit interval. In mathematical analysis, the unit interval is a one-dimensional analytical manifold whose boundary consists of the two points 0 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apéry's Constant
In mathematics, Apéry's constant is the infinite sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers, cubed. That is, it is defined as the number : \begin \zeta(3) &= \sum_^\infty \frac \\ &= \lim_ \left(\frac + \frac + \cdots + \frac\right), \end where is the Riemann zeta function. It has an approximate value of : . It is named after Roger Apéry, who proved that it is an irrational number. Uses Apéry's constant arises naturally in a number of physical problems, including in the second- and third-order terms of the electron's gyromagnetic ratio using quantum electrodynamics. It also arises in the analysis of random minimum spanning trees and in conjunction with the gamma function when solving certain integrals involving exponential functions in a quotient, which appear occasionally in physics, for instance, when evaluating the two-dimensional case of the Debye model and the Stefan–Boltzmann law. The reciprocal of (0.8319073725807... ) is the probabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |