|
Rí
Rí, or commonly ríg (genitive), is an ancient Gaelic word meaning 'king'. It is used in historical texts referring to the Irish and Scottish kings, and those of similar rank. While the Modern Irish word is exactly the same, in modern Scottish Gaelic it is , apparently derived from the genitive. Cognates include Gaulish ''Rix'', Latin , Spanish , French , Sanskrit , and German . There were three grades of : a or 'overking' was a major, regional king and superior to a 'king of tribes' or a 'king of bands' either of whom, in turn, were superior to several figures known as 'king of peaks' or 'king of a tribe'. Three traditional grades The three traditional grades of in Gaelic Ireland was largely symbolic. As time went on, the real power of many lesser kings could equal or even eclipse those of higher grade. ''Rí benn'' A (king of peaks), or (king of a single tribe), was most commonly a local petty king of a single , although one might be many times the size of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
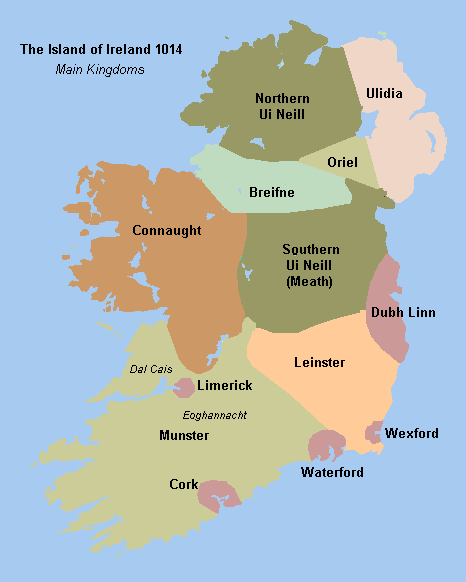
Kings Of Munster
The kings of Munster () ruled the Kingdom of Munster in Ireland from its establishment during the Irish Iron Age until the High Middle Ages. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as the ''Book of Invasions'', the earliest king of Munster was Bodb Derg of the Tuatha Dé Danann. From the Gaelic peoples, an Érainn kindred known as the Dáirine (also known as Corcu Loígde and represented today in seniority by the Ó hEidirsceoil) provided several early monarchs including Cú Roí. In a process in the ''Cath Maige Mucrama'', the Érainn lost their ascendancy in the 2nd century AD to the Deirgtine, ancestors of the Eóganachta. Munster during this period was classified as part of ''Leath Cuinn and Leath Moga, Leath Moga'', or the southern-half, while other parts of Ireland were ruled mostly by the Connachta. After losing Osraige to the east, Cashel, County Tipperary, Cashel was established as the capital of Munster by the Eóganachta. This kindred ruled wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kings Of Ulster
The King of Ulster (Old Irish: ''Rí Ulad'', Modern Irish: ''Rí Uladh'') also known as the King of Ulaid and King of the Ulaid, was any of the kings of the Irish provincial over-kingdom of Ulaid. The title rí in Chóicid, which means "king of the Fifth", was also sometimes used. Originally referring to the rulers of the Ulaid of legend and the vastly reduced territory of the historical Ulaid, the title ''rí Ulad'' ceased to exist after the Norman invasion of Ulaid in 1177 and the subsequent foundation of the Earldom of Ulster. The Mac Dúinnshléibe dynasty of Ulaid (English: Donleavy / Dunleavy) were given the title of ''rex Hibernicorum Ulidiae'', meaning "king of the Irish of Ulaid", until the extinction of their dynasty by the end of the 13th century. After the earldom's collapse in 1333, the title was resurrected and usurped after 1364 by the Ulaid's chief Gaelic rivals the Northern Uí Néill, who had overrun the ruins of the earldom and established the renamed tuath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kings Of Osraige
The kings of Osraige (alternately spelled ''Osraighe'' and Anglicised as ''Ossory'') reigned over the medieval Irish kingdom of Osraige from the first or second century AD until the late twelfth century. Osraige was a semi-provincial kingdom in south-east Ireland which disappeared following the Norman Invasion of Ireland. A number of important royal Ossorian genealogies are preserved, particularly MS Rawlinson B502, which traces the medieval Mac Giolla Phádraig dynasty back through Óengus Osrithe, who supposedly flourished in the first or second century. and one in the '' Book of Leinster'' (also known as "''Lebor na Nuachongbála''"). Recent analysis of ninth and tenth century regnal succession in Osraige has suggested that in peaceful times, kingship passed primarily from eldest to youngest brother, before crossing generations and passing to sons and nephews. Early kings of Osraige The following kings are listed in all major genealogies, but originate from an early period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and Elective monarchy, elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European languages, Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as ''rex (king), rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the natural sciences, arts, literature, and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned society and one of its leading cultural institution, cultural and academic institutions. The academy was established in 1785 and granted a royal charter by King George III in 1786. the RIA has 600 members, with regular members being Irish residents elected in recognition of their academic achievements, and honorary members similarly qualified but usually based abroad; a small number of members are also elected in recognition of non-academic contributions to the Irish society. All members are entitled to use the honorific title MRIA with their names. Until the late 19th century the Royal Irish Academy was the owner of the main national collection of Irish antiquities. It presented its collection of archaeological artefacts and similar items, which included such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kings Of Breifne
The Kingdom of Breifne or Bréifne (), anglicized as Breffny, was a medieval overkingdom in Gaelic Ireland. It comprised what is now County Leitrim, County Cavan and parts of neighbouring counties, and corresponds roughly to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kilmore. It had emerged by the 10th century, as a confederation of ' headed by an overking drawn from the Uí Briúin Bréifne. By the 11th century, Bréifne was ruled by the Ua Ruairc (O'Rourke) dynasty. The kingdom reached the height of its power in the 12th century, under Tigernán Ua Ruairc. During the latter part of his reign, Bréifne took part in campaigns against the Norman invasion of Ireland. His assassination by the Anglo-Normans in 1172 was followed by a succession dispute, and a conflict between the Ua Ruairc and Ua Raghallaigh (O'Reilly) dynasties. Following the Battle of Magh Slecht in 1256, Bréifne split into West Breifne (ruled by the Ua Ruairc) and East Breifne (ruled by the Ua Raghallaigh). Bréifn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Gaelic warfare, Warfare between List of Irish kingdoms, these territories was common. Traditionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of Irish clans, clans and, like the rest of History of Europe, Europe, was structured hierarchically according to Social class, class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly Pastoralism, pastoral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reich
( ; ) is a German word whose meaning is analogous to the English word " realm". The terms and are respectively used in German in reference to empires and kingdoms. In English usage, the term " Reich" often refers to Nazi Germany, also called "the Third Reich". The term (sometimes translated to "German Empire") continued to be used even after the collapse of the German Empire and the abolition of the monarchy in 1918. There was no emperor, but many Germans had imperialistic ambitions. According to historian Richard J. Evans: The term is used for historical empires in general, such as the Roman Empire (), Persian Empire (), and both the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire (, literally " Tsars' realm"). , the name used for Austria today, is composed of and which, literally translated, means "Eastern Realm". The name once referred to the eastern parts of the Holy Roman Empire. In the history of Germany specifically, it is used to refer to: * the early medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Táin Bó Cúailnge
(Modern ; "the driving-off of the cows of Cooley"), commonly known as ''The Táin'' or less commonly as ''The Cattle Raid of Cooley'', is an epic from Irish mythology. It is often called "the Irish ''Iliad''", although like most other early Irish literature, the ''Táin'' is written in prosimetrum, i.e. prose with periodic additions of verse composed by the characters. The ''Táin'' tells of a war against Ulster by Queen Medb of Connacht and her husband King Ailill, who intend to steal the stud bull Donn Cuailnge. Due to a curse upon the king and warriors of Ulster, the invaders are opposed only by the young demigod, Cú Chulainn. The ''Táin'' is traditionally set in the 1st century in a pagan heroic age, and is the central text of a group of tales known as the Ulster Cycle. It survives in three written versions or " recensions" in manuscripts of the 12th century and later, the first a compilation largely written in Old Irish, the second a more consistent work i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ó Flaithbertaigh
Ó, ó ( o- acute) is a letter in the Czech, Dobrujan Tatar, Emilian-Romagnol, Faroese, Hungarian, Icelandic, Kashubian, Polish, Slovak, Karakalpak, and Sorbian languages. The symbol also appears in the Afrikaans, Catalan, Dutch, Irish, Nynorsk, Bokmål, Occitan, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian and Galician languages as a variant of the letter "o". It usually represents a vowel sound longer than or slightly different from that represented by plain "o", although in some cases its sound is notably different (as in modern Polish, where it is pronounced the same as "u"). In some cases it represents the vowel "o" with a particular tone (for example, a high rising tone in Vietnamese). It is sometimes also used in English for loanwords. Usage in various languages Chinese In Chinese pinyin ó is the ''yángpíng'' tone (阳平, high-rising tone) of "o". Czech and Slovak Ó is the 24th letter of the Czech alphabet and the 28th letter of the Slovak alphabet. It represents . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kings Of Moylurg
The Kings of or Moylurg were a branch of the , and a kindred family to the Kings of Connacht. Their ancestor, , was a brother to , King of Connacht 967–973, ancestor of the O Connor family of Connacht. is said to have made a deal of some nature where, in return for abandoning any claim to the provincial kingship, he would be given . His dynasty was known as the Clan Mulrooney, and later still took the surname of MacDermot (a branch of this family were in turn called MacDermot Roe). The following is a list of their Kings, followed by the respective heads of the family up to the early modern period. ''The Kings of Moylurg'' * , fl. 956 founder of Moylurg and the Clan . * * * , fl. 1080. * , 1120–1124. * , 1124. * , 1124–1159, progenitor of the surname MacDermot. * , 1159–1187. * , 1187–1196. * , 1196–1207. * , 1207–1215. * , 1215–1218. * , 1218–1244 * , 1245–1265 * , 1256–1281. * , 1281–1287 * , 1288–1294 * , 1294–1331. * , 1331–1336. * , 1336� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kings Of Uí Maine
Uí Maine was the name of an Irish kingdom situated in south Connacht, consisting of all of County Galway east of Athenry, all of southern and central County Roscommon. In prehistory it was believed to have spanned the River Shannon, and in the 8th century even briefly extended its dominion west to Galway Bay. It existed as an independent kingdom from prehistoric times, and as a subject kingdom up to the end of the medieval era. The acknowledged senior branch of the Ó Ceallaigh (O'Kelly) Uí Maine is the O'Kelly de Gallagh and Tycooly (see Irish nobility and Chief of the Name), and are Counts of the Holy Roman Empire. Other branches include: O'Kelly of Aughrim, O'Kelly of Mullaghmore, O'Kelly of Clondoyle, O'Kelly de Galway, Ó Ceallaigh Iarthar Chláir, O'Kelly of Gurtray, O'Kelly of Screen, and O'Kelly Farrell. Semi-historic kings All dates approximate. *Maine Mór, fl. c.357–407 *Breasal mac Maine Mór, fl. c.407–c.437 *Fiachra Finn, fl. c.437–c.454 *Connall Cas Ciabha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |