|
Rubidium-82
Rubidium-82 (82Rb) is a radioactive isotope of rubidium. 82Rb is widely used in myocardial perfusion imaging. This isotope undergoes rapid uptake by myocardiocytes, which makes it a valuable tool for identifying myocardial ischemia in Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging. 82Rb is used in the pharmaceutical industry and is marketed as Rubidium-82 chloride under the trade names RUBY-FILL and CardioGen-82. History In 1953, it was discovered that rubidium carried a biological activity that was comparable to potassium. In 1959, preclinical trials showed in dogs that myocardial uptake of this radionuclide was directly proportional to myocardial blood flow. In 1979, Yano et al. compared several ion-exchange columns to be used in an automated 82Sr/82Rb generator for clinical testing. Around 1980, pre-clinical trials began using 82Rb in PET. In 1982, Selwyn et al. examined the relation between myocardial perfusion and rubidium-82 uptake during acute ischemia in six dogs after corona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rubidium-82 Chloride
Rubidium-82 chloride is a form of rubidium chloride containing a radioactive isotope of rubidium. It is marketed under the brand name Cardiogen-82 by Bracco Diagnostics for use in Myocardial perfusion imaging. It is rapidly taken up by heart muscle cells, and therefore can be used to identify regions of heart muscle that are receiving poor blood flow in a technique called PET perfusion imaging. The half-life of rubidium-82 Rubidium-82 (82Rb) is a radioactive isotope of rubidium. 82Rb is widely used in myocardial perfusion imaging. This isotope undergoes rapid uptake by myocardiocytes, which makes it a valuable tool for identifying myocardial ischemia in Positron Em ... is only 1.27 minutes; it is normally produced at the place of use by rubidium generators. References Further reading * (Note: only about 1/2 page on Rb-generator) * * Cardiac imaging Rubidium compounds Chlorides Metal halides Alkali metal chlorides Radiopharmaceuticals {{Pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than Properties of water, water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years – more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe. German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered rubidium in 1861 by the newly developed technique, Atomic emission spectroscopy#Flame emission spectroscopy, flame spectroscopy. The name comes from the Latin word , meaning deep red, the color of its emission spectrum. Rubidium's compounds have various chemical and electronic applications. Rubidium metal is easily vaporized and has a convenient spectral absorption range, making it a frequent target for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bracco Diagnostics
The Bracco Group is an Italian multinational active in the healthcare sector with more than 3,300 employees worldwide, which operates in a variety of business areas. *Diagnostic imaging, with products for X-ray imaging, including computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound and nuclear medicine. * Contrast-agent injection systems and advanced medical devices. *Prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceuticals, supplements, medical and cosmetic devices developed and distributed in Italy. *Healthcare, prevention, diagnosis and rehabilitation services through the CDI - Centro Diagnostico Italiano. Bracco has consolidated revenues of more than 1.1 billion euro, of which 75% from international sales. The Group is present in 100 countries and invests approximately 10% of its core diagnostic imaging revenues in research and innovation. In Italy Bracco is also a brand associated with a number of historic pharmaceutical products such as Cebion, Xamamina, Euclori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journal Of Nuclear Cardiology
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of personal secretive thoughts and as open book to personal therapy or used to feel connected to oneself. A record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions *Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal, a record of the traveller's experience during the course of their journey In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical **Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science **Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation *Magazine, non-academic or scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
The ''Journal of the American College of Cardiology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering all aspects of cardiovascular disease, including original clinical studies, translational investigations with clear clinical relevance, state-of-the-art papers, review articles, and editorials interpreting and commenting on the research presented, published by the American College of Cardiology. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Current Contents, EMBASE, MEDLINE, Science Citation Index, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 24.094, ranking it 4th out of 141 journals in the category "Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems". Associated journals * ''JACC: Basic to Translational Science'' (Impact Factor: 8.4) * ''JACC: CardioOncology'' (Impact Factor: 12) * '' JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging'' (Impact Factor: 12.8) * '' JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions'' (Impact Factor: 11.7) * ''JACC: Clinical Ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
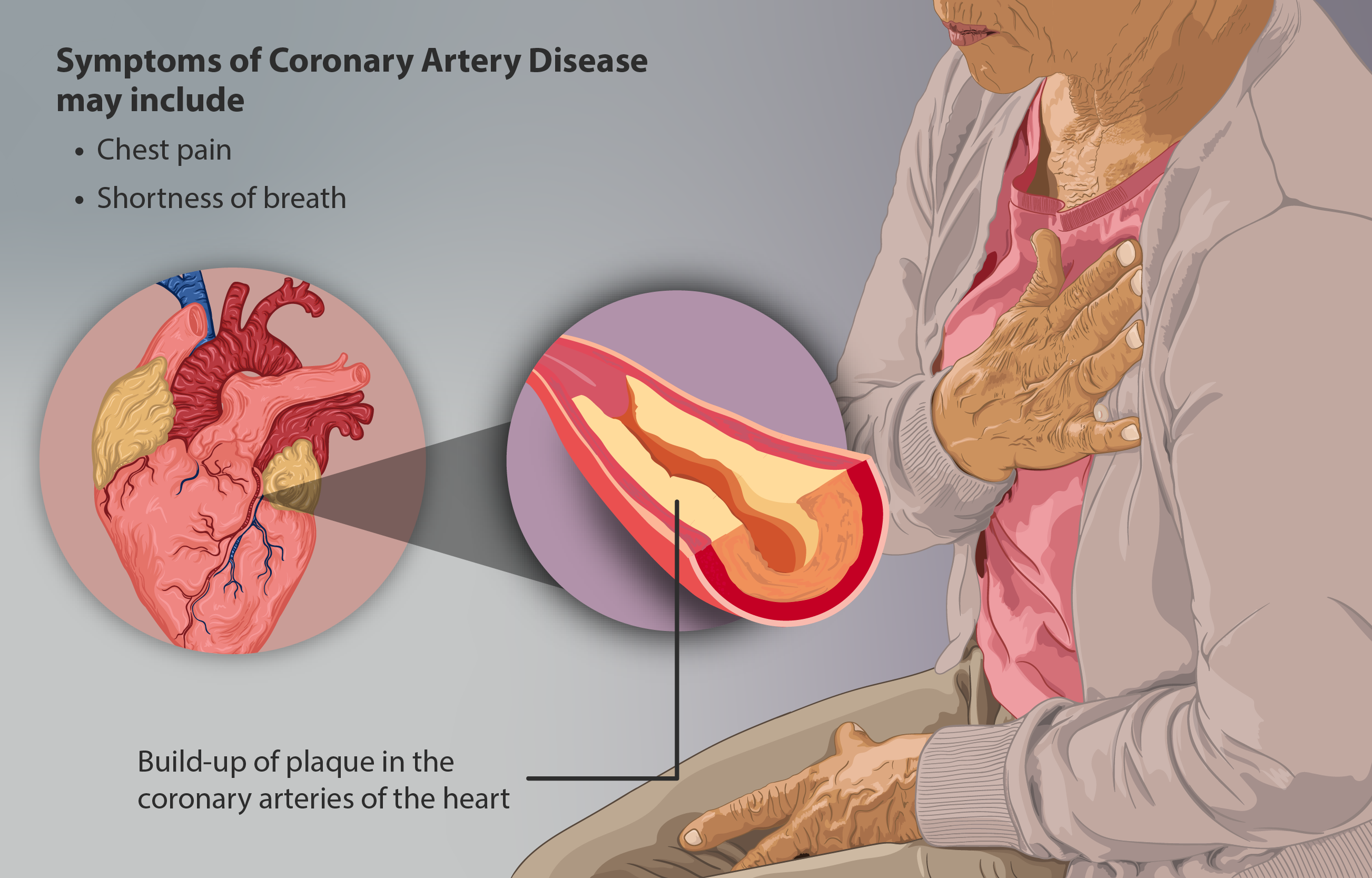
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Psychological stress, stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journal Of Cardiology
A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of personal secretive thoughts and as open book to personal therapy or used to feel connected to oneself. A record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a daily record of financial transactions *Logbook, a record of events important to the operation of a vehicle, facility, or otherwise *Transaction log, a chronological record of data processing *Travel journal, a record of the traveller's experience during the course of their journey In publishing, ''journal'' can refer to various periodicals or serial (publishing), serials: *Academic journal, an academic or scholarly periodical **Scientific journal, an academic journal focusing on science **Medical journal, an academic journal focusing on medicine **Law review, a professional journal focusing on legal interpretation *Magazine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Myocardium
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rubidium Chloride
Rubidium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula RbCl. This alkali metal halide salt is composed of rubidium and chlorine, and finds diverse uses ranging from electrochemistry to molecular biology. Structure In its gas phase, RbCl is diatomic with a bond length estimated at 2.7868 Å. This distance increases to 3.285 Å for cubic RbCl, reflecting the higher coordination number of the ions in the solid phase. Depending on conditions, solid RbCl exists in one of three arrangements or polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs as determined with holographic imaging: Sodium chloride (octahedral 6:6) The sodium chloride (NaCl) polymorph is most common. A cubic crystal system, cubic close-packed arrangement of chloride anions with rubidium cations filling the octahedral holes describes this polymorph. Both ions are six-coordinate in this arrangement. The lattice energy of this polymorph is only 3.2 kJ/mol less than the following structure's. Caesium chlorid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stannic Oxide
Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid. Structure Tin(IV) oxide crystallises with the rutile structure. As such the tin atoms are six coordinate and the oxygen atoms three coordinate. SnO2 is usually regarded as an oxygen-deficient n-type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of SnO2 have been described as stannic acid. Such materials appear to be hydrated particles of SnO2 where the composition reflects the particle size. Preparation Tin(IV) oxide occurs naturally. Synthetic tin(IV) oxide is produced by burning tin metal in air. Annual production is in the range of 10 kilotons. SnO2 is reduced industrially to the metal with carbon in a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C. Reactions The reaction from tin(IV) ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |