|
Ring Oscillator
A ring oscillator is a device composed of an odd number of Inverter (logic gate), NOT gates in a ring, whose output oscillation, oscillates between two voltage levels, representing ''true'' and ''false''. The NOT gates, or inverters, are attached in a chain and the output of the last inverter is fed back into the first. Details Because a single inverter computes the logical NOT of its input, it can be shown that the last output of a chain of an odd number of inverters is the logical NOT of the first input. The final output is asserted a finite amount of time after the first input is asserted and the feedback of the last output to the input causes oscillation. A circular chain composed of an even number of inverters cannot be used as a ring oscillator. The last output in this case is the same as the input. However, this configuration of inverter feedback can be used as a storage element and it is the basic building block of Static Random Access Memory, static random access m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-controlled Oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulation, modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop. VCOs are used in synthesizers to generate a waveform whose Pitch (music), pitch can be adjusted by a voltage determined by a musical keyboard or other input. A voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC) is a special type of VCO designed to be very linear in frequency control over a wide range of input control voltages. Types VCOs can be generally categorized into two groups based on the type of waveform produced. * ''Linear'' or ''harmonic oscillators'' generate a sinusoidal waveform. Harmonic oscillators in electronics usually consist of a resonator with an amplifier that re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Counter
A ring counter is a type of counter composed of flip-flops connected into a shift register, with the output of the last flip-flop fed to the input of the first, making a "circular" or "ring" structure. There are two types of ring counters: * A straight ring counter, also known as a one-hot counter, connects the output of the last shift register to the first shift register input and circulates a single one (or zero) bit around the ring. * A twisted ring counter, also called switch-tail ring counter, walking ring counter, Johnson counter, or Möbius counter, connects the complement of the output of the last shift register to the input of the first register and circulates a stream of ones followed by zeros around the ring. Four-bit ring-counter sequences Properties Ring counters are often used in hardware design (e.g. ASIC and FPGA design) to create finite-state machines. A binary counter would require an adder circuit which is substantially more complex than a ring cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Margin
In electronic amplifiers, the phase margin (PM) is the difference between the phase (waves), phase lag (< 0) and -180°, for an amplifier's output signal (relative to its input) at zero dB gain - i.e. unity gain, or that the output signal has the same amplitude as the input. :. For example, if the amplifier's open-loop gain crosses 0 dB at a frequency where the phase lag is -135°, then the phase margin of this feedback system is -135° -(-180°) = 45°. Theory Typically the Feedback#Electronic_engineering, open-loop phase lag (relative to input, < 0) varies with frequency, progressively increasing to exceed 180°, at which frequency the output signal becomes inverted, or antiphase in relation to the input. The PM will be positive but decreasing at frequencies less than the frequency at which inversion sets in (at which PM = 0), and PM is negative (PM < 0) at higher frequencies. In the presence of negative feedba ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bode Plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude (usually in decibels) of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. As originally conceived by Hendrik Wade Bode in the 1930s, the plot is an asymptotic approximation of the frequency response, using straight line segments. Overview Among his several important contributions to circuit theory and control theory, engineer Hendrik Wade Bode, while working at Bell Labs in the 1930s, devised a simple but accurate method for graphing gain and phase-shift plots. These bear his name, ''Bode gain plot'' and ''Bode phase plot''. "Bode" is often pronounced in English as , whereas in Dutch it is usually , closer to English , which is preferred by his family, but less common among researchers.Van Valkenburg, M. E. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, "In mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer Testing
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a Garnish (food), garnish on some sweet dishes. They frequently have a waffle surface pattern but may also be patterned with insignia of the food's manufacturer or may be patternless. Some chocolate bars, such as Kit Kat and Toffee Crisp, are wafers with chocolate in and around them. Communion wafers A communion wafer is a type of unleavened bread consumed as part of the Christian ritual of communion. Spa wafer Special "spa wafers" (Czech: ''lázeňské oplatky'', Slovak: ''kúpeľné oblátky'') are produced in the spa towns of the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic (e.g. Piešťany). The production of the wafers in Karlovy Vary, Karlsbad and Mariánské Lázně, Marienbad was traditional to the towns' Sudeten Germans, German-speaking population, who, after Expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia, the ethnic cleansing of the area, brought the craft to Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer (electronics)
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si, silicium), used for Semiconductor device fabrication, the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate (materials science), substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping (semiconductor), doping, ion implantation, Etching (microfabrication), etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and Photolithography, photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and Integrated circuit packaging, packaged as an integrated circuit. History In the semiconductor industry, the term wafer appeared in the 1950s to describe a thin round slice of semiconductor material, typically germanium or silicon. The round shape characteristic of these wafers comes f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hello World Program
Hello is a salutation or greeting in the English language. It is first attested in writing from 1826. Early uses ''Hello'', with that spelling, was used in publications in the U.S. as early as the 18 October 1826 edition of the '' Norwich Courier'' of Norwich, Connecticut. Another early use was an 1833 American book called ''The Sketches and Eccentricities of Col. David Crockett, of West Tennessee'', which was reprinted that same year in '' The London Literary Gazette''. The word was extensively used in literature by the 1860s. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', ''hello'' is an alteration of ''hallo'', ''hollo'', which came from Old High German "''halâ'', ''holâ'', emphatic imperative of ''halôn'', ''holôn'' to fetch, used especially in hailing a ferryman". It also connects the development of ''hello'' to the influence of an earlier form, ''holla'', whose origin is in the French ''holà'' (roughly, 'whoa there!', from French ''là'' 'there'). As in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware Random Number Generator
In computing, a hardware random number generator (HRNG), true random number generator (TRNG), non-deterministic random bit generator (NRBG), or physical random number generator is a device that generates random numbers from a physical process capable of producing entropy, unlike a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) that utilizes a deterministic algorithm and non-physical nondeterministic random bit generators that do not include hardware dedicated to generation of entropy. Many natural phenomena generate low-level, statistically random "noise" signals, including thermal and shot noise, jitter and metastability of electronic circuits, Brownian motion, and atmospheric noise. Researchers also used the photoelectric effect, involving a beam splitter, other quantum phenomena, and even the nuclear decay (due to practical considerations the latter, as well as the atmospheric noise, is not viable except for fairly restricted applications or online distribution services). Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same, thus a phase-locked loop can also track an input frequency. Furthermore, by incorporating a frequency divider, a PLL can generate a stable frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are used for clock synchronization, demodulation, frequency synthesis, clock multipliers, and signal recovery from a noisy communication channel. Since 1969, a single integrated circuit can provide a complete PLL building block, and nowadays have output frequencies from a fraction of a hertz up to many gigahertz. Thus, PLLs are widely employed in radio, telecommunications, computers (e.g. to distribute precisely timed clock signals in microprocessors), grid-tie inverters (electronic power converters used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
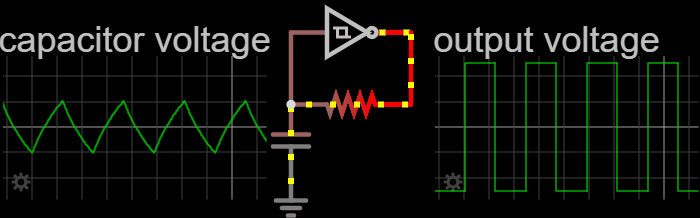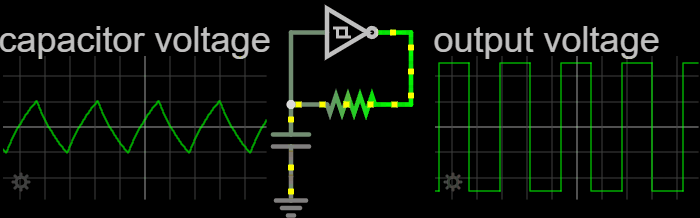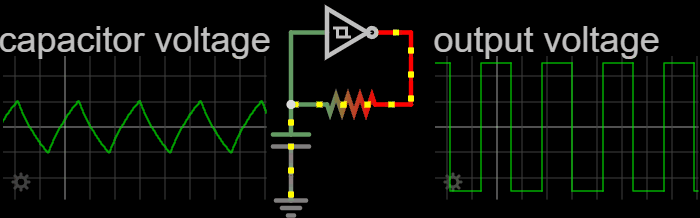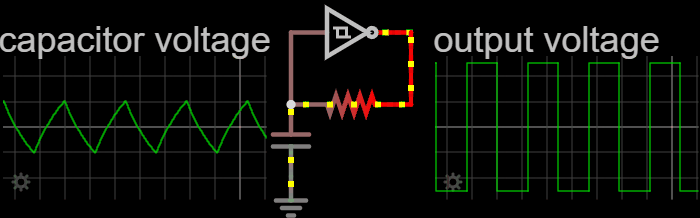
Relaxation Oscillator
In electronics, a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Oscillator (3-stage)
A ring oscillator is a circuit composed of a cascaded chain of inverters (logical NOT gates) arranged in a ring, such that the output of the inverter at the end of the chain is fed back into the first inverter, which produces an output at the output of each inverter that oscillates between two voltage levels representing ''true'' and ''false''. If the inverters used are buffered, then any odd number of inverters can be used. However, if the inverters used are unbuffered, then an odd number of at least 3 inverters must be used. (For simplicity, this article may simply say an "odd number" and ignore this caveat.) This is because a single unbuffered inverter in a loop with itself will simply have its output voltage equal its input voltage. Another formal proof of why a single unbuffered inverter won't work: the phase of the transfer function of a single unbuffered inverter doesn't cross 0° (or any integer multiple of 360°), so it fails to satisfy that necessary condition of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |