|
Right Coronary Artery
In the coronary circulation, blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the Aortic sinus, right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux cordis, crux of the heart. It gives off many branches, including the sinoatrial nodal artery, Right marginal branch of right coronary artery, right marginal artery, posterior interventricular artery, conus artery, and atrioventricular nodal branch. It contributes the right side of the heart, and parts of the interventricular septum. Structure The right coronary artery originates above the Aortic sinus, right aortic sinus above the aortic valve. It passes along the right coronary sulcus, coronary sulcus (right atrioventricular groove) towards the Crux cordis, crux of the heart. Segments * Proximal: starting at RCA origin, spanning half the distance to the Right border of heart, acute margin * Middle: from proxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Circulation
Coronary circulation is the Circulatory system#Coronary vessels, circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the cardiac muscle, heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. #Cardiac veins, Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by hypoxia (medical), oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventricular Septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The interventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior interventricular sulcus, anterior and Posterior interventricular sulcus, posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous. During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker. Structure The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the Ventricle (heart), ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomosis
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale in a fetus' heart) or abnormal (such as the patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Greek ἀναστόμωσις, anastomosis, "outlet, opening", Greek ana- "up, on, upon", stoma "mouth" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
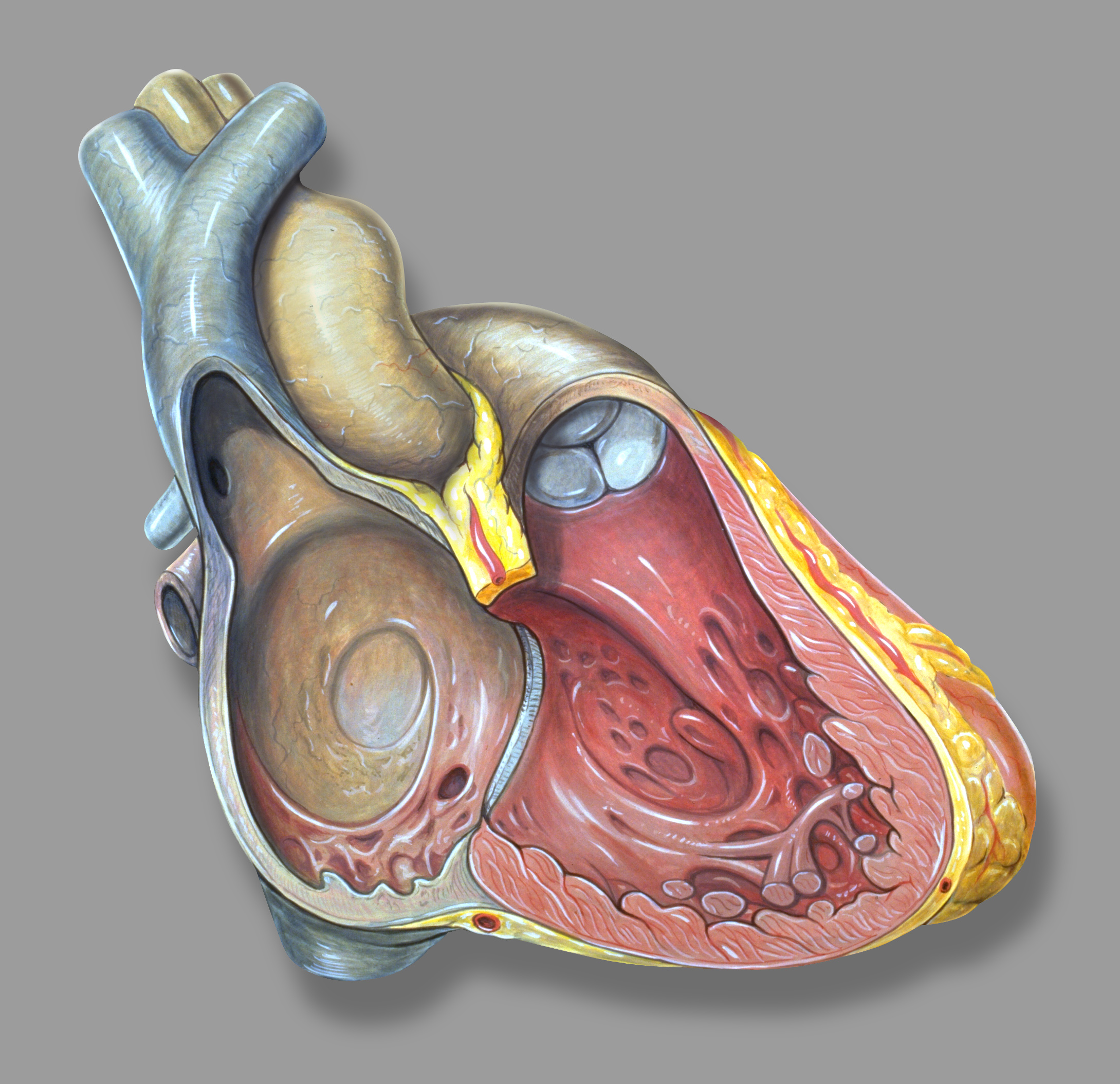
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrium (heart)
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two Heart#Chambers, upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the Ventricle (heart), heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valve, atrioventricular mitral valve, mitral and tricuspid valve, tricuspid heart valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle, the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA Nodal Artery
The sinoatrial nodal artery, sinoatrial nodal artery or sinoatrial artery is an artery of the heart which supplies the sinoatrial node, the natural pacemaker center of the heart. It is usually a branch of the right coronary artery. It passes between the right atrium, and the opening of the superior vena cava. Anatomy Origin It arises from the right coronary artery in around 60% of individuals, from the left circumflex coronary artery in about 40% of individuals, and in less than 1% of humans, the artery has an anomalous origin directly from the coronary sinus, descending aorta, or distal right coronary artery. The origin of the sinoatrial node artery is not related to coronary artery dominance, which means the side (right or left) that provides the circulation to the back of the heart. In contrast, the atrioventricular nodal branch, that is the artery that brings blood to the atrioventricular node, depends on coronary artery dominance. Course In more than 50% of human he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papillary Muscle
The papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (also known as the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or prolapse of these valves on systole (or ventricular contraction). Structure There are five total papillary muscles in the heart; three in the right ventricle and two in the left ventricle. The anterior, posterior, and septal papillary muscles of the right ventricle each attach via chordae tendineae to the tricuspid valve. The anterolateral and posteromedial papillary muscles of the left ventricle attach via chordae tendineae to the mitral valve. Blood supply to the left ventricle The mitral valve papillary muscles in the left ventricle are called the anterolateral and posteromedial muscles. * Anterolateral muscle blood supply: left anterior descending artery - diagonal branch (LAD) and left circumflex artery - obtuse marginal bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The interventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous. During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker. Structure The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Wall
{{disambiguation ...
Inferior may refer to: * Inferiority complex * An anatomical term of location * Inferior angle of the scapula, in the human skeleton * ''Inferior'' (book), by Angela Saini * ''The Inferior'', a 2007 novel by Peadar Ó Guilín * Inferior good: economics term for goods that consumers buy less of as they become wealthier (vs "normal goods" where they buy more) See also *Junior (other) Junior or Juniors may refer to: Aircraft * Ekolot JK-05L Junior, a Polish ultralight aircraft * PZL-112 Junior, a Polish training aircraft * SZD-51 Junior, a Polish-made training and club glider Arts and entertainment Characters * Bowser Jr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Circumflex Artery
The circumflex branch of left coronary artery (also known as the left circumflex artery or circumflex artery) is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove (coronary sulcus). It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle. In a minority of individuals, the left circumflex artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, in which cases such a heart is deemed left dominant. Anatomy The left circumflex artery follows the left part of the coronary sulcus, running first to the left and then to the right, reaching nearly as far as the posterior longitudinal sulcus. There have been multiple anomalies described, for example the left circumflex having an aberrant course from the right coronary artery. Branches The circumflex artery curves to the left around the heart within the coronary sulcus, giving rise to one or more left marginal arteries (also called obtuse marginal branches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Descending Artery
In the coronary circulation, the posterior descending artery (PDA), also called the posterior interventricular artery (PIV, PIA, or PIVA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets with the left anterior descending artery also known as the anterior interventricular artery. The PDA supplies the posterior third of the interventricular septum. The remaining anterior two-thirds is supplied by the left anterior descending artery, which is a branch of left coronary artery. It is typically a branch of the right coronary artery (70%, known as right dominance). Alternately, the PDA can be a branch of the circumflex coronary artery (10%, known as left dominance) which itself is a branch of the left coronary artery. It can also be supplied by an anastomosis An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Groove
The coronary sulcus (also called coronary groove, auriculoventricular groove, atrioventricular groove, AV groove) is a groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the atria from the ventricles. The structure contains the trunks of the nutrient vessels of the heart, and is deficient in front, where it is crossed by the root of the pulmonary trunk. On the posterior surface of the heart, the coronary sulcus contains the coronary sinus. The right coronary artery, circumflex branch of left coronary artery, and small cardiac vein all travel along parts of the coronary sulcus. Structure In relation to the rib cage, the coronary sulcus spans from the medial side of the 3rd left costal cartilage, to the middle of the right 6th costal cartilage. Epicardial fat tends to be concentrated along the coronary sulcus. There are two coronary sulci in the heart, including left and right coronary sulci. Left coronary sulcus The left coronary sulcus originates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |