|
Ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins. Structures Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating interaction with the negatively charged nucleic acid chains. The Protein tertiary structure, tertiary structures and biological functions of many nucleoproteins are understood.Graeme K. Hunter G. K. (2000): Vital Forces. The discovery of the molecular basis of life. Academic Press, London 2000, . Important techniques for determining the structures of nucleoproteins include X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance and cryo-electron microscopy. Viruses Virus genomes (either DNA virus, DNA or RNA virus, RNA) are extremely tightly packed into the Capsid, viral capsid. Many viruses are therefore little more than an organised collection of nucleoproteins with their binding sites pointing inwards. Structurally characterised viral nucleoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rabies Virus
Rabies virus (''Lyssavirus rabies'') is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in animals, including humans. It can cause violence, hydrophobia, and fever. Rabies transmission can also occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. Rabies virus, like many Rhabdoviridae, rhabdoviruses, has an extremely wide host range. In the wild it has been found infecting many mammalian species, while in the laboratory it has been found that birds can be infected, as well as cell cultures from mammals, birds, reptiles and insects. Rabies is reported in more than 150 countries and on all continents except Antarctica. The main burden of disease is reported in Asia and Africa, but some cases have been reported also in Europe in the past 10 years, especially in returning travellers. Rabies virus has a cylindrical morphology and is a member of the ''Lyssavirus'' genus of the ''Rhabdoviridae'' family. These viruses are Viral envelope, enveloped and have a Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as causing seasonal flu in humans. Mammals in which different strains of IAV circulate with sustained transmission are bats, pigs, horses and dogs; other mammals can occasionally become infected. IAV is an enveloped negative-sense RNA virus, with a segmented genome. Through a combination of mutation and genetic reassortment the virus can evolve to acquire new characteristics, enabling it to evade host immunity and occasionally to jump from one species of host to another. Subtypes of IAV are defined by the combination of the antigenic H and N proteins in the viral envelope; for example, "H1N1" designates an IAV subtype that has a type-1 hemagglutinin (H) protein and a type-1 neuraminidase (N) protein. Almost all possible combinations of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bunyamwera Virus
Bunyamwera virus (BUNV) is a negative-sense, single-stranded enveloped RNA virus. It is assigned to the '' Orthobunyavirus'' genus, in the ''Peribunyaviridae'' family. Bunyamwera virus can infect both humans and ''Aedes aegypti'' (yellow fever mosquito). It is named for Bunyamwera, a town in western Uganda, where it was isolated in 1943. Reassortant viruses derived from Bunyamwera virus, such as Ngari virus, have been associated with large outbreaks of viral haemorrhagic fever in Kenya and Somalia. Molecular biology The genetic structure of Bunyamwera virus is typical for viruses in '' Bunyaviricetes'', which are a class of enveloped negative-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a genome split into three parts—Small (S), Middle (M), and Large (L). The L RNA segment encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L protein), the M RNA segment encodes two surface glycoproteins (Gc and Gn) and a nonstructural protein (NSm), while the S RNA segment encodes a nucleocapsid pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Schmallenberg Virus
Schmallenberg virus, abbreviated SBV, is a virus that causes congenital malformations and stillbirths in cattle, sheep, goats, and possibly alpaca. It appears to be transmitted by midges (''Culicoides'' spp.), which are likely to have been most active in causing the infection in the Northern Hemisphere summer and autumn of 2011, with animals subsequently giving birth from late 2011. Schmallenberg virus falls in the Simbu Serotype, serogroup of orthobunyaviruses. It is considered to be most closely related to the Sathuperi virus, Sathuperi and Douglas virus, Douglas viruses. The virus is named after Schmallenberg, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, from where the first definitive sample was derived. It was first reported in October 2011. After Germany, it has also been detected in the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Luxembourg, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, Ireland, Finland, Denmark, Sweden, Austria, Norway, Poland and Estonia. The virus has been recognised by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Viral Nucleoprotein
Viral nucleoproteins (NPs) are essential RNA-binding protein, RNA-binding proteins encoded by many Virus, viruses, especially Negative-strand RNA virus, negative-sense single-stranded RNA (–ssRNA) viruses. They play crucial roles in Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis, encapsulating viral RNA, facilitating Viral replication, genome replication and Transcription (biology), transcription, organizing viral Nucleoprotein, ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) complexes, and Immune system, evading host immunity. Structure and function Key functions of viral NPs include: * RNA Encapsulation: NPs coat the viral genome in a sequence-independent manner, protecting it from Nuclease, nucleases and Pattern recognition receptor, host pattern recognition receptors such as RIG-I and MDA5. * RNP Assembly: NP-RNA complexes serve as templates for viral RNA synthesis by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). * Regulation of Replication: NP levels help determine the balance between Transcription (biology), tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lassa Virus
Lassa virus (LASV) is an Arenaviridae, arenavirus that causes Lassa hemorrhagic fever, a type of viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF), in humans and other primates. Lassa virus is an Emerging infectious disease, emerging virus and a select agent, requiring Biosafety level#Biosafety level 4, Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment. It is endemic in West African countries, especially Sierra Leone, the Republic of Guinea, Nigeria, and Liberia, where the annual incidence of infection is between 300,000 and 500,000 cases, resulting in 5,000 deaths per year. As of 2012 discoveries within the Mano River region of west Africa have expanded the endemic zone between the two known Lassa endemic regions, indicating that LASV is more widely distributed throughout the tropical wooded savannah ecozone in west Africa. There are no approved vaccines against Lassa fever for use in humans. Discovery In 1969, missionary nurse Laura Wine fell ill with a mysterious disease she contracted from an obstetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hazara Virus
In 1954 the Hazara virus, one of the 34 tick-borne viruses of the genus '' Orthonairovirus'', was discovered in Pakistan in the ''Ixodes'' tick native to that region. Today this virus is studied in mice in an attempt to develop treatments for the highly pathogenic Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus. Characteristics Hazara virus is part of the genus ''Orthonairovirus'' of the '' Nairoviridae'' family of viruses, which are a family of enveloped negative-stranded RNA viruses with a genome split into three parts—Small (S), Middle (M) and Large (L). The L RNA segment encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L protein), the M RNA segment encodes two surface glycoproteins (Gc and Gn), and the S RNA segment encodes a nucleocapsid protein (N). The three genomic RNA segments are encapsidated by copies of the N protein in the form of ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes. The N protein is the most abundant viral protein in ''Bunyaviridae'' virus particles and infected cells and, therefore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
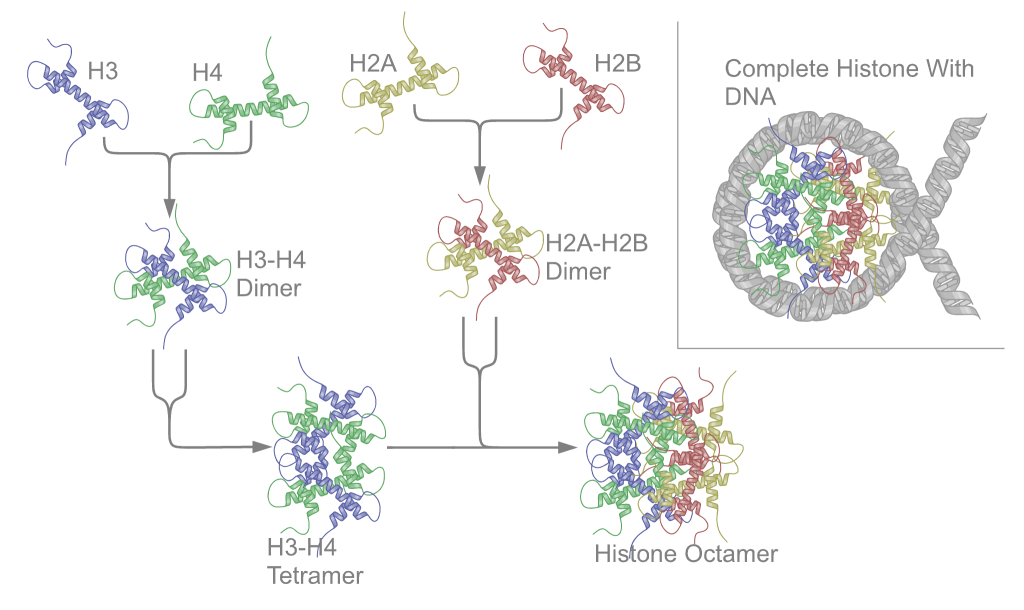
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA repair#DNA damage, DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30 nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |