|
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose group with high morphological and ecological diversity. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved global distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Rhynchocephalians are distinguished from squamates by a number of traits, including the retention of rib-like gastralia bones in the belly, as well as most rhynchocephalians having acrodont teeth that are fused to the crests of the jaws (the latter also found among a small number of modern lizard grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
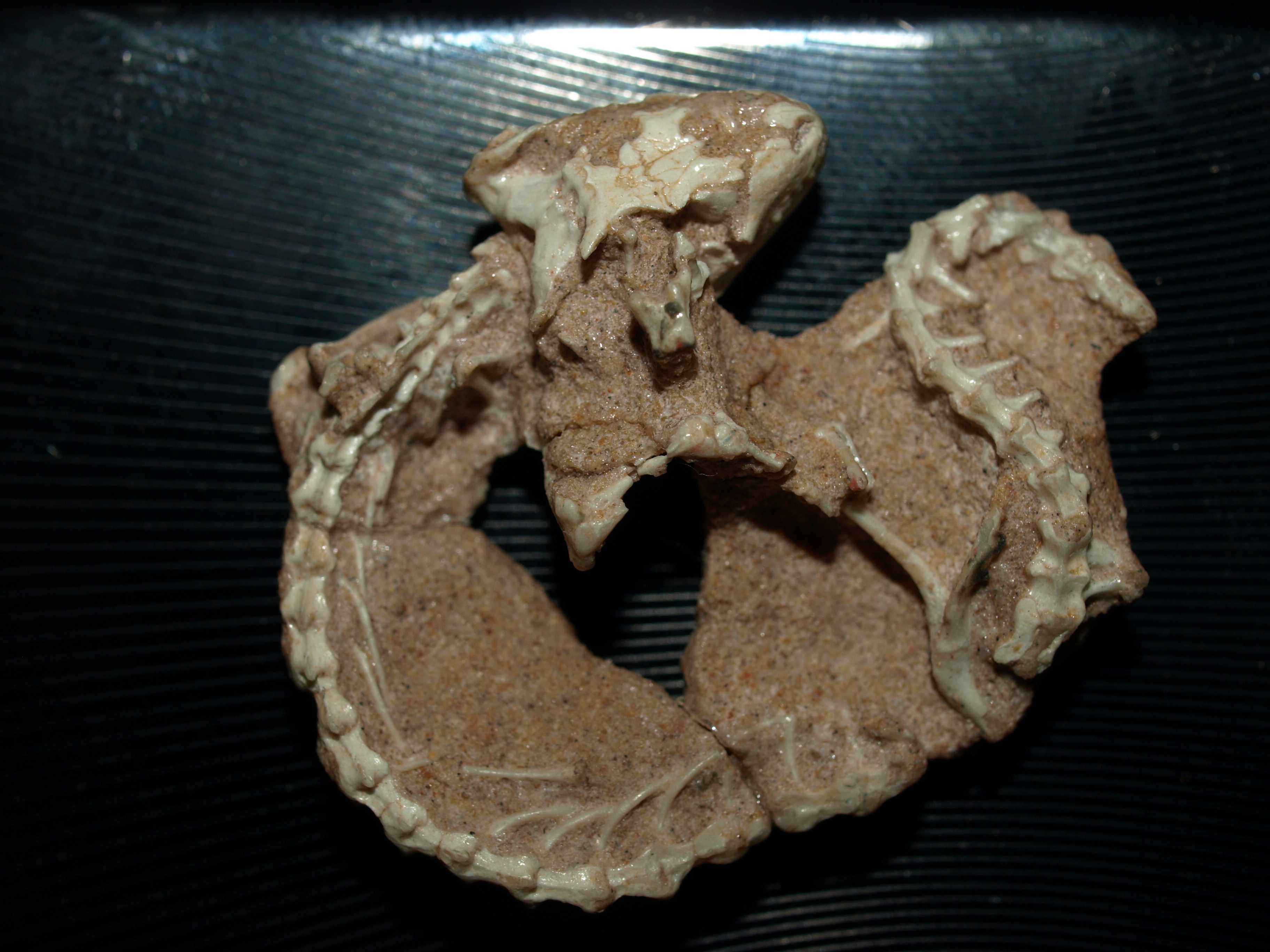
Sapheosaurs
Sapheosaurs are an extinct group of rhynchocephalian reptiles from the Late Jurassic period. "Sapheosaurs" is an informal name for a group of rhynchocephalians closely related to the genus '' Sapheosaurus''. It was first recognized as a group containing multiple genera by Hoffstetter in 1955. The group has sometimes been given a formal taxonomic name as the family Sapheosauridae, although in some analyses this group belongs to the family Sphenodontidae (which also contains the tuatara, the only living rhynchocephalian) and thus cannot be assigned its own family. They were fairly advanced rhynchocephalians which may have had semiaquatic habits. Classification The most well-known members of the group are ''Sapheosaurus'' and '' Kallimodon'', and most phylogenetic analyses on rhynchocephalians only study these two genera as representatives of sapheosaurs. Although a few early phylogenies in the 1990s did not find that these two formed a natural clade, the relation between these tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
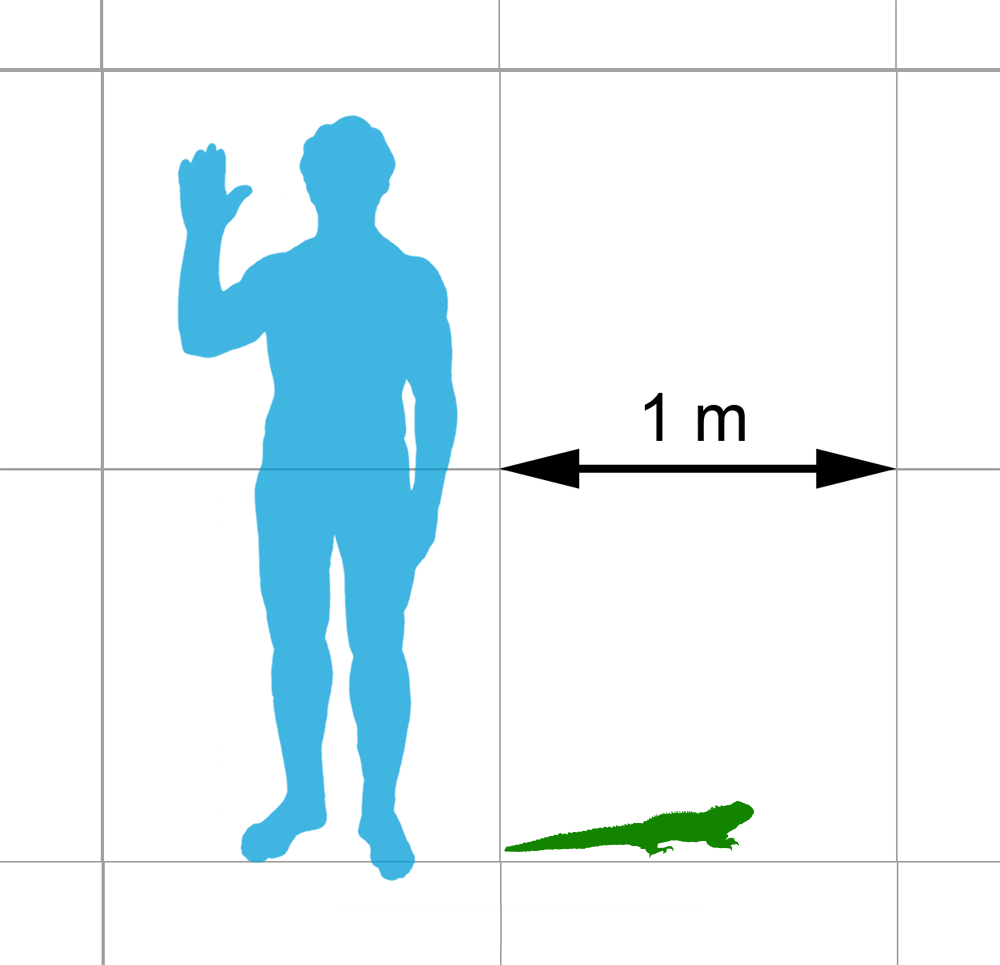
Tuatara
The tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') is a species of reptile endemic to New Zealand. Despite its close resemblance to lizards, it is actually the only extant member of a distinct lineage, the previously highly diverse order Rhynchocephalia. The name is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order, which was highly diverse during the Mesozoic era. Rhynchocephalians first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic, around 240 million years ago, and reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic, when they represented the world's dominant group of small reptiles. Rhynchocephalians declined during the Cretaceous, with their youngest records outside New Zealand dating to the Paleocene. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). Tuatara are of interest for studying the evolution of reptiles. Tuatara are greenish brown an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sphenodon Punctatus
The tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') is a species of reptile endemic to New Zealand. Despite its close resemblance to lizards, it is actually the only extant member of a distinct lineage, the previously highly diverse order Rhynchocephalia. The name is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order, which was highly diverse during the Mesozoic era. Rhynchocephalians first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic, around 240 million years ago, and reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic, when they represented the world's dominant group of small reptiles. Rhynchocephalians declined during the Cretaceous, with their youngest records outside New Zealand dating to the Paleocene. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). Tuatara are of interest for studying the evolution of reptiles. Tuatara are greenish brown and gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a Order (biology), superorder or Class (biology), subclass of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata also includes Lizard, lizards and Snake, snakes. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, making it by far the most species-rich and diverse order of non-avian reptiles in the present day. Rhynchocephalia was a formerly widespread and diverse group of reptiles in the Mesozoic era, Mesozoic Era. However, it is represented by only one living species: the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus),'' a superficially lizard-like reptile native to New Zealand. Lepidosauria is a monophyletic group (i.e. a clade), containing all descendants of the Most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor of squamates and rhynchocephalians. Lepidosaurs can be distinguished from other reptiles via several traits, such as large Keratin, keratinous Scale (anatomy), scales which may overlap one another. Purely in the conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vadasaurus
''Vadasaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian closely related to the aquatic pleurosaurids. Although this genus was not as specialized as the eel-like pleurosaurs for aquatic life, various skeletal features support the idea that it had a semiaquatic lifestyle. The type species, ''Vadasaurus herzogi'', was described and named in 2017. It was discovered in the Solnhofen Limestone in Germany, which is dated to the Late Jurassic. The generic name "''Vadasaurus"'' is derived from "''vadare''", which is Latin for "to go" or "to walk forth", and "''saurus''", which means "lizard" (although rhynchocephalians are not lizards). "''Vadare"'' is the root of the English word "wade", which is the reason it was chosen for this genus, in reference to its perceived semiaquatic habits. The specific name, "''herzogi''", refers to Werner Herzog, a Bavarian filmmaker. Description The holotype of ''Vadasaurus herzogi'' is AMNH FARB 32768, a well-preserved but slightly flattened skeleton wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic islands, oceanic Archipelago, island chains. The grouping is Paraphyly, paraphyletic as some lizards are more closely related to snakes than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards") have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some lizards, such as the forest-dwelling ''Draco (genus), Draco'', are able to glide. They are often Territory (animal), territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest Order (biology), order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as Lizard, lizards, with the group also including Snake, snakes. With over 11,991 species, it is also the second-largest order of Neontology, extant (living) vertebrates, after the Perciformes, perciform fish. Squamates are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scale (zoology), scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the Maxilla, upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very widely to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamates are the most variably sized living reptiles, ranging from the Sphaerodactylus ariasae, dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus''). The now-Extinction, extinct mosasaurs reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the second and middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era as well as the eighth period of the Phanerozoic, Phanerozoic Eon and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). The beginning of the Toarcian Age started around 183 million years ago and is marked by the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event, a global episode of Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated global temperatures associated with extinctions, likely caused by the eruption of the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pleurosauridae
Pleurosauridae, from Ancient Greek πλευρά (''pleurá''), meaning "rib" or "side", and σαῦρος (''saûros''), meaning "lizard", is an extinct family of sphenodontian reptiles, known from the Jurassic of Europe. Members of the family had long-snake like bodies with reduced limbs that were adapted for aquatic life in marine environments. It contains two genera, '' Palaeopleurosaurus,'' which is known from the Early Jurassic (Toarcian The Toarcian is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS' geologic timescale, an age (geology), age and stage (stratigraphy), stage in the Early Jurassic, Early or Lower Jurassic. It spans the time between 184.2 Megaannum, Ma (million ...) Posidonia Shale of Germany, as well as '' Pleurosaurus'' from the Late Jurassic of Germany and France. ''Paleopleurosaurus'' is more primitive than the later ''Pleurosaurus'', with a skull similar to those of other sphenodontians, while that of ''Pleurosaurus'' is highly modified relative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Albert Günther
Albert Karl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther , also Albert Charles Lewis Gotthilf Günther (3October 18301February 1914), was a German-born British zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. Günther is ranked the second-most productive reptile taxonomist (after George Albert Boulenger) with more than 340 reptile species described. Early life and career Günther was born in Esslingen in Swabia ( Württemberg). His father was a ''Stiftungs-Commissar'' in Esslingen and his mother was Eleonora Nagel. He initially schooled at the Stuttgart Gymnasium. His family wished him to train for the ministry of the Lutheran Church for which he moved to the University of Tübingen. A brother shifted from theology to medicine, and he, too, turned to science and medicine at Tübingen in 1852. His first work was "''Ueber den Puppenzustand eines Distoma''" (On the pupal state of ''Distoma''). He graduated in medicine with an M.D. from Tübingen in 1858, the same year in which he published a handbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |