|
Resazurin
Resazurin (7-Hydroxy-3''H''-phenoxazin-3-one 10-oxide) is a phenoxazine dye that is weakly fluorescent, nontoxic, cell-permeable, and redox‐sensitive. Resazurin has a blue to purple color above pH 6.5 and an orange color below pH 3.8. It is used in microbiological, cellular, and enzymatic assays because it can be irreversibly reduced to the pink-colored and highly fluorescent resorufin (7-Hydroxy-3''H''-phenoxazin-3-one). At circum-neutral pH, resorufin can be detected by visual observation of its pink color or by fluorimetry, with an excitation maximum at 530-570 nm and an emission maximum at 580-590 nm. When a solution containing resorufin is submitted to reducing conditions (Eh < -110 mV), almost all resorufin is reversibly reduced to the translucid non-fluorescent [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interchim
Interchim is a privately owned French language, French company specialized in manufacturing and distribution of reagents, consumables and dedicated instruments for the Research and development, R&D and industry laboratory in the fields of Fine chemicals, fine chemistry, chromatography and bioanalysis, bio-analysis. It has become a provider of reference Scientific method, methods, products for analytics (analytical chemistry and bioassays) serving research and quality control in the biomedical field, Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical industry, but also cosmetics and Environmental science, environment. History Interchim was founded by Boch Jean (formerly chemical engineer at Rhone-Poulenc) and Boch Colette in 1970. Their initial activity started with distribution of fine chemicals, then chromatography and Biology. Production was developed as well, in each fields. Affiliate companies were created for production and commercial activities in France, UK (2003), USA (2007) and Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenoxazine
Phenoxazine is a heterocyclic compound. The structure of phenoxazine consists of an oxazine fused to two benzene rings. It occurs as the central core of a number of naturally occurring chemical compounds such as dactinomycin and litmus. The dyes Nile blue and Nile red are also based on a phenoxazine core. Phenoxazine dyes were once widely used for silk dyeing, but due to their lack of lightfastness they have disappeared over time from the market. However, since their light resistance is significantly better on acrylic fiber Acrylic fibers are synthetic fibers made from a polymer ( polyacrylonitrile) with an average molecular weight of ~100,000, about 1900 monomer units. For a fiber to be called "acrylic" in the US, the polymer must contain at least 85% acrylonit ...s, these dyes have experienced a renaissance. See also * Phenothiazine References {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells. The two major types of growth media are those used for cell culture, which use specific cell types derived from plants or animals, and those used for microbiological culture, which are used for growing microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths and agar plates; specialized media are sometimes required for microorganism and cell culture growth. Some organisms, termed fastidious organisms, require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirements. Viruses, for example, are obligate intracellular parasites and require a growth medium containing living cells. Types The most common growth media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) is the lowest concentration of an antibacterial agent required to kill a particular bacterium. It can be determined from broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests by subculturing to agar plates that do not contain the test agent. The MBC is identified by determining the lowest concentration of antibacterial agent that reduces the viability of the initial bacterial inoculum by ≥99.9%. The MBC is complementary to the MIC; whereas the MIC test demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that inhibits growth, the MBC demonstrates the lowest level of antimicrobial agent that results in microbial death. This means that even if a particular MIC shows inhibition, plating the bacteria onto agar might still result in organism proliferation because the antimicrobial did not cause death. Antibacterial agents are usually regarded as bactericidal if the MBC is no more than four times the MIC. Because the MBC test uses col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
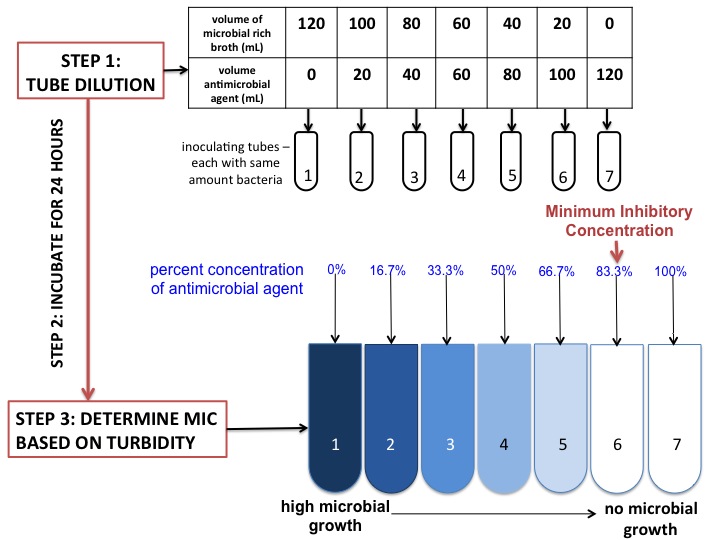
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
In microbiology, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical, usually a drug, which prevents visible ''in vitro'' cell growth, growth of bacteria or Fungus, fungi. MIC testing is performed in both diagnostic and drug discovery laboratories. The MIC is determined by preparing a Serial dilution, dilution series of the chemical, adding agar dilution, agar or broth microdilution, broth, then inoculating with bacteria or fungi, and incubating at a suitable temperature. The value obtained is largely dependent on the susceptibility of the microorganism and the antimicrobial potency of the chemical, but other variables can affect results too. The MIC is often expressed in micrograms per milliliter (μg/mL) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). In diagnostic labs, MIC test results are used to grade the susceptibility of microbes. These grades are assigned based on agreed upon values called breakpoints. Breakpoints are published by standards organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite these terms sometimes being used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration after da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Culture Assays
A cell culture assay is any method used to assess the cytotoxicity of a material. This refers to the ''in vitro'' assessment of a material to determine whether it releases toxic chemicals in the cell. It also determines if the quantity is sufficient to kill cells, either directly or indirectly, through the inhibition of cell metabolic pathways. Cell culture evaluations are the precursor to whole animal studies and are a way to determine if significant cytotoxicity exists for the given material. Cell culture assays are standardized by ASTM, ISO, and BSI (British Standards Institution The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the Standards organization, national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies standards certification services ....) See also * Microphysiometry References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cell Culture Assays Biotechnology Cell biology * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTT Assay
The MTT assay is a colorimetric assay for assessing cell metabolic activity. NAD(P)H-dependent cellular oxidoreductase enzymes may, under defined conditions, reflect the number of viable cells present. These enzymes are capable of reducing the tetrazolium dye MTT, which is chemically 3-(4,5- di methyl thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, to its insoluble formazan, which has a purple color. Other closely related tetrazolium dyes including XTT, MTS and the WSTs, are used in conjunction with the intermediate electron acceptor, 1-methoxy phenazine methosulfate (PMS). With WST-1, which is cell-impermeable, reduction occurs outside the cell via plasma membrane electron transport. However, this traditionally assumed explanation is currently contended as proof has also been found of MTT reduction to formazan in lipidic cellular structures without apparent involvement of oxidoreductases. Tetrazolium dye assays can also be used to measure cytotoxicity (loss of viable cells) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formazan
The formazans are compounds of the general formula [R-N=N-C(R')=N-NH-R"], formally derivatives of formazan [H2NN=CHN=NH], unknown in free form. Formazan dyes are artificial Chromogen, chromogenic products obtained by reduction of tetrazolium salts by dehydrogenases and Reductase, reductases. They have a variety of colors from dark blue to deep red to orange, depending on the original tetrazolium salt used as the substrate for the reaction. Structure and reactivity Formazans are intensely colorful compounds characterized by the following structure: [-N=N-C(R)=N-NH-], and are closely related to Azo group, azo (−N=N−) dyes. Their structure was first defined in 1892, by Hans von Pechmann, von Pechmann and by Eugen Bamberger, Bamberger and Wheelwright independently. Their deep colour and redox chemistry derive from their nitrogen-rich backbone. Formazans have a high Tautomer, tautomeric and Conformational isomerism, conformational flexibility. Due to the two alternating double bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Probes
Molecular Probes was a biotechnology company located in Eugene, Oregon specializing in fluorescence. The company was founded in 1975 by Richard and Rosaria Haugland in their kitchen in Minnesota, then moved briefly to Texas and finally to Oregon in the early 1980s. In 1989, Molecular Probes moved from Junction City to its current location in Eugene. While in Texas, the Hauglands developed the Texas Red dye, a rhodamine derivative. Other dyes have names that reflect their Oregon heritage, including the Oregon Green and Cascade Blue dyes, while Marina Blue and the Alexa Fluor dyes are named after the Hauglands' children, Marina and Alex. Invitrogen bought Molecular Probes in 2003 for approximately $325 million in cash. The business subsequently became a part of Life Technologies, through the merger of Invitrogen and Applied Biosystems, and is now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. is an American life science and clinical research company. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to transfer chemical energy from nutrients to ATP, with the flow of electrons to an electron acceptor, and then release waste products. If the electron acceptor is oxygen, the process is more specifically known as aerobic cellular respiration. If the electron acceptor is a molecule other than oxygen, this is anaerobic cellular respiration. Fermentation, which is also an anaerobic process, is not respiration, as no external electron acceptor is involved. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, producing large amounts of energy (ATP). Respiration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions ( anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network. Salts usually form crystalline structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |