|
Rereplication
DNA re-replication (or simply rereplication) is an undesirable and possibly fatal occurrence in eukaryotic cells in which the genome is replicated more than once per cell cycle. Rereplication is believed to lead to genomic instability and has been implicated in the pathologies of a variety of human cancers. To prevent rereplication, eukaryotic cells have evolved multiple, overlapping mechanisms to inhibit chromosomal DNA from being partially or fully rereplicated in a given cell cycle. These control mechanisms rely on cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity. DNA replication control mechanisms cooperate to prevent the relicensing of replication origins and to activate cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. DNA rereplication must be strictly regulated to ensure that genomic information is faithfully transmitted through successive generations. Initiating Replication at Origins Replication of DNA always begins at an origin of replication. In yeast, the origins contain autonomousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cdc6
Cell division control protein 6 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC6'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc6, a protein essential for the initiation of DNA replication. This protein functions as a regulator at the early steps of DNA replication. It localizes in the cell nucleus during cell cycle phase G1, but translocates to the cytoplasm at the start of S phase. The subcellular translocation of this protein during the cell cycle is regulated through its phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinases. Transcription of this protein was reported to be regulated in response to mitogenic signals through a transcriptional control mechanism involving E2F proteins. Interactions CDC6 has been shown to interact with ORC1L, ORC2L, Cyclin A2, PPP2R3B, MCM3, PPP2R3A, MCM7 DNA replication licensing factor MCM7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MCM7'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
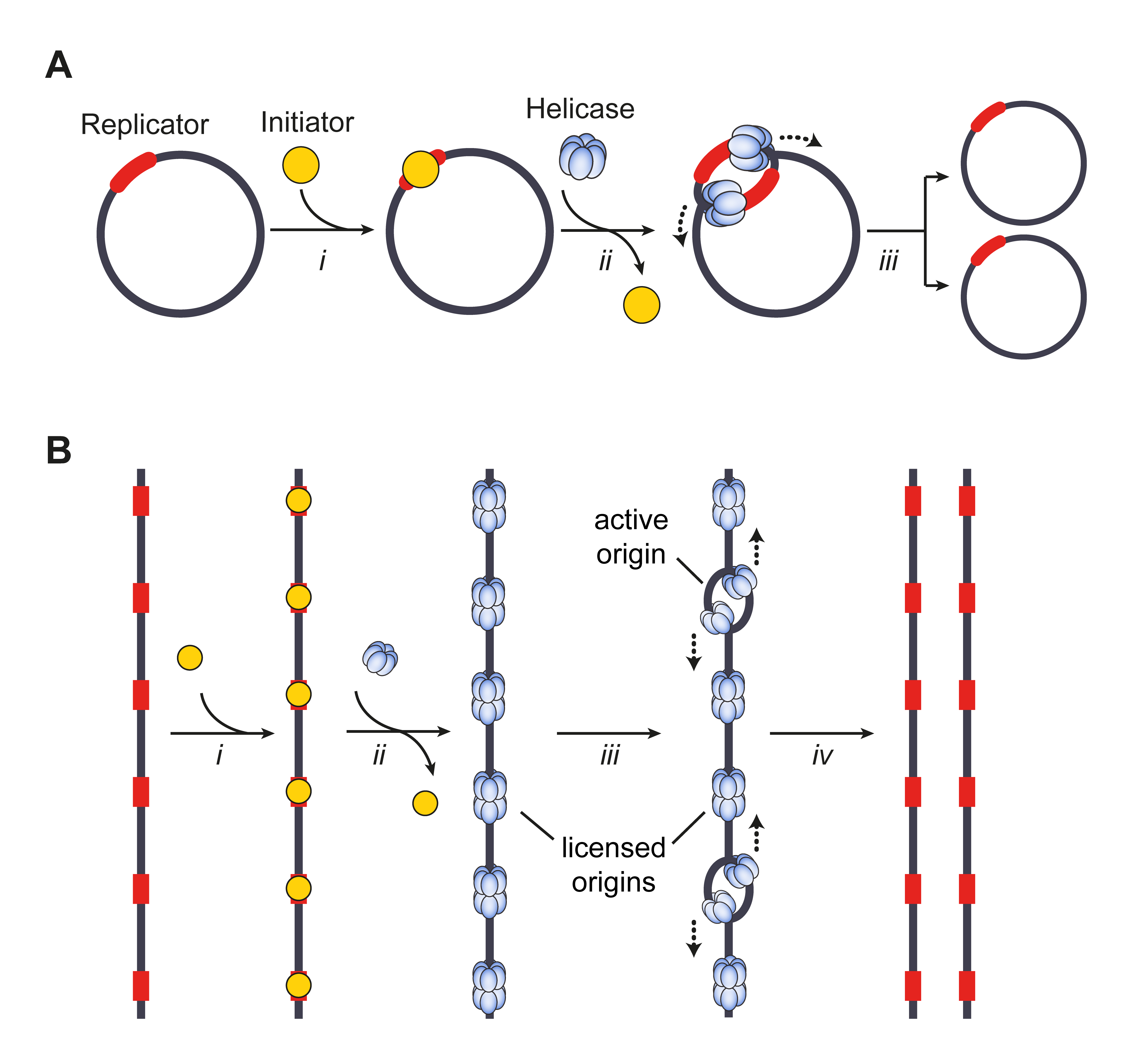
Origin Of Replication
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License This can either involve the replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA or RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. Although the specific replication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication Factor CDT1
CDT1 (Chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDT1'' gene. It is a licensing factor that functions to limit DNA from replicating more than once per cell cycle. Role in pre-replication complexes The protein encoded by this gene is a key licensing factor in the assembly of pre-replication complexes (pre-RC), which occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. In the assembly of pre-RCs, origin recognition complexes (ORC1-6) recognize and bind to DNA replication origins. CDT1, along with the protein CDC6, are then recruited to the forming pre-RC, followed by minichromosome maintenance complexes (MCM2-7). The activity of CDT1 during the cell cycle is tightly regulated during the S phase by the protein geminin, which inhibits it, and by SCFSKP2, which ubiquinates the protein to tag it for proteasomal degradation. This regulation is important in preventing relicensing, thus ensuring that DNA is only replicated once per cell cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Recognition Complex
In molecular biology, origin recognition complex (ORC) is a multi-subunit DNA binding complex (6 subunits) that binds in all eukaryotes and archaea in an ATP-dependent manner to origins of replication. The subunits of this complex are encoded by the ORC1, ORC2, ORC3, ORC4, ORC5 and ORC6 genes. ORC is a central component for eukaryotic DNA replication, and remains bound to chromatin at replication origins throughout the cell cycle. ORC directs DNA replication throughout the genome and is required for its initiation. ORC and Noc3p bound at replication origins serve as the foundation for assembly of the pre-replication complex (pre-RC), which includes Cdc6, Tah11 (a.k.a. Cdt1), and the Mcm2-Mcm7 complex. Pre-RC assembly during G1 is required for replication licensing of chromosomes prior to DNA synthesis during S phase. Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of Orc2, Orc6, Cdc6, and MCM by the cyclin-dependent protein kinase Cdc28 regulates initiation of DNA replication, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overview Of Chromosome Duplication In The Cell Cycle
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Overview may refer to: * Overview article, an artícle that summarizes the current state of understanding on a topic * Overview map, generalised view of a geographic area See also * Summary (other) * Outline (list) * ''A Brief Overview'' * Overview and Scrutiny * Overview effect The overview effect is a cognitive shift reported by some astronauts while viewing the Earth from space. Researchers have characterized the effect as "a state of awe with self-transcendent qualities, precipitated by a particularly striking visu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP :ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. cerevis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G1/S Transition
The G1/S transition is a stage in the cell cycle at the boundary between the G1 phase, in which the cell grows, and the S phase, during which DNA is replicated. It is governed by cell cycle checkpoints to ensure cell cycle integrity and the subsequent S phase can pause in response to improperly or partially replicated DNA. During this transition the cell makes decisions to become quiescent (enter G0), differentiate, make DNA repairs, or proliferate based on environmental cues and molecular signaling inputs. The G1/S transition occurs late in G1 and the absence or improper application of this highly regulated check point can lead to cellular transformation and disease states such as cancer During this transition, G1 cyclin D-Cdk4/6 dimer phosphorylates retinoblastoma releasing transcription factor E2F, which then drives the transition from G1 to S phase. The G1/S transition is highly regulated by transcription factor p53 in order to halt the cell cycle when DNA is damaged. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licensing Factor
A licensing factor is a protein or complex of proteins that allows an origin of replication to begin DNA replication at that site. Licensing factors primarily occur in eukaryotic cells, since bacteria use simpler systems to initiate replication. However, many archaea use homologues of eukaryotic licensing factors to initiate replication. Function Origins of replication represent start sites for DNA replication and so their "firing" must be regulated to maintain the correct karyotype of the cell in question. The origins are required to fire only once per cell cycle, an observation that led to the postulated existence of licensing factors by biologists in the first place. If the origins were not carefully regulated then DNA replication could be restarted at that origin giving rise to multiple copies of a section of DNA. This could be damaging to cells and could have detrimental effects on the organism as a whole. The control that licensing factors exert over the cycle represents a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibition Of Pre-RC Assembly
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to: In biology * Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity * Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotransmitter * Lateral inhibition, a neural mechanism that increases contrast between active and (neighbouring) inactive neurons * Inhibitory postsynaptic potential, a synaptic potential that decreases the firing of a neuron In chemistry * Corrosion inhibitor, a substance that decreases the rate of metal oxidation * Reaction inhibitor, a substance that prevents or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction * Polymerisation inhibitor, a substance that inhibits unwanted polymerisation of monomers In psychology * Cognitive inhibition, the mind's ability to tune out irrelevant stimuli ** Inhibitory control, a cognitive process that permits an individual to inhibit their impulses * Inhibition of return, a feature of attention * Inhibition theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Licensing
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Comics and manga * ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002 * ''The Origin'' (Buffy comic), a 1999 ''Buffy the Vampire Slayer'' comic book series * Origins (''Judge Dredd'' story), a major ''Judge Dredd'' storyline running from 2006 through 2007 * ''Origin'' (manga), a 2016 manga by Boichi * '' Mobile Suit Gundam: The Origin'', a 2002 manga by Yoshikazu Yasuhiko * '' Wolverine: Origins'', a Marvel Comics series Films and television * ''Origin'' (TV series), 2018 science-fiction TV series * "Origin" (''Angel''), a fifth-season episode of ''Angel'' * '' Origin: Spirits of the Past'', a 2006 anime movie also known as ''Gin-iro no Kami no Agito'' * Origin (''Stargate''), the religion of the Ori * "Origin" (''Stargate SG-1''), a ninth-season episode of ''Stargate SG-1'' * '' X-Men Origins: Wolverine'', a 2009 superhero film, prequel to the ''X-Men'' film tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |