|
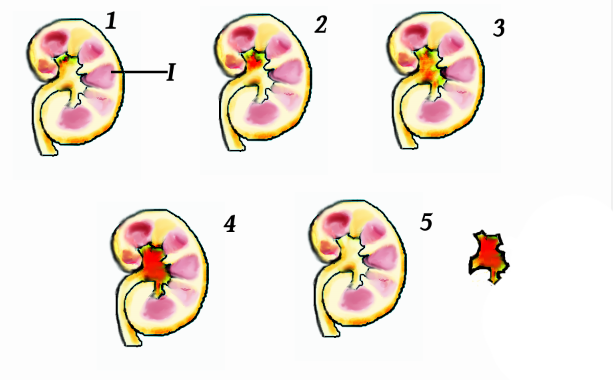
Renal Pelvis
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the convergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous membrane and is covered with transitional epithelium and an underlying lamina propria of loose-to-dense connective tissue. The renal pelvis is situated within the renal sinus alongside the other structures of the renal sinus. Clinical significance The renal pelvis is the location of several kinds of kidney cancer and is affected by infection in pyelonephritis. A large " staghorn" kidney stone may block all or part of the renal pelvis. The size of the renal pelvis plays a major role in the grading of hydronephrosis. Normally, the anteroposterior diameter of the renal pelvis is less than 4 mm in fetuses up to 32 weeks of gestational age and 7 mm afterwards. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureteric Bud
The ureteric bud, also known as the metanephric diverticulum, is a protrusion from the mesonephric duct during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It later develops into a conduit for urine drainage from the kidneys, which, in contrast, originate from the metanephric blastema. References {{Authority control Embryology of urogenital system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Latin
Neo-LatinSidwell, Keith ''Classical Latin-Medieval Latin-Neo Latin'' in ; others, throughout. (also known as New Latin and Modern Latin) is the style of written Latin used in original literary, scholarly, and scientific works, first in Italy during the Italian Renaissance of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, and then across northern Europe after about 1500, as a key feature of the humanist movement. Through comparison with Classical Latin, Latin of the Classical period, scholars from Petrarch onwards promoted a standard of Latin closer to that of the ancient Romans, especially in grammar, style, and spelling. The term ''Neo-Latin'' was however coined much later, probably in Germany in the late eighteenth century, as ''Neulatein'', spreading to French and other languages in the nineteenth century. Medieval Latin had diverged quite substantially from the classical standard and saw notable regional variation and influence from vernacular languages. Neo-Latin attempts to retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryology
Embryology (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logy, -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the Prenatal development (biology), prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology. Early embryology was proposed by Marcello Malpighi, and known as preformationism, the theory that organisms develop from pre-existing miniature versions of themselves. Aristotle proposed the theory that is now accepted, Epigenesis (biology), epigenesis. Epigenesis (biology), Epigenesis is the idea that organisms develop from seed or egg in a sequence of steps. Modern embryology developed from the work of Karl Ernst von Baer, though accurate observations had been made in Italy by anatomists such as Aldrovandi and Leonardo da Vinci in the Renaissance. Comparative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accidental Gap
In linguistics an accidental gap, also known as a gap, paradigm gap, accidental lexical gap, lexical gap, lacuna, or hole in the pattern, is a potential word, word sense, morpheme, or other form that does not exist in some language despite being theoretically permissible by the grammatical rules of that language. For example, a word pronounced is theoretically possible in English, as it would obey English phonological rules, but does not currently exist. Its absence is therefore an accidental gap, in the ontologic sense of the word ''accidental'' (that is, circumstantial rather than essential). Accidental gaps differ from systematic gaps, those words or other forms which do not exist in a language due to the boundaries set by phonological, morphological, and other rules of that specific language. In English, a word pronounced does not and ''cannot'' exist because it has no vowels and therefore does not obey the word-formation rules of English. This is a systematic, rather th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choana
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the pharynx, in humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians and most skinks). They are considered one of the most important synapomorphies of tetrapodomorphs, that allowed the passage from water to land. In animals with secondary palates, they allow breathing when the mouth is closed. Janvier, Philippe (2004) "Wandering nostrils". ''Nature'', 432 (7013): 23–24. In tetrapods without secondary palates their function relates primarily to olfaction (sense of smell). The choanae are separated in two by the vomer. Boundaries A choana is the opening between the nasal cavity and the nasopharynx. It is therefore not a structure but a space bounded as follows: * anteriorly and inferiorly by the horizontal plate of palatine bone, * superiorly and posteriorly by the sphenoid bone * laterally by the medial pterygoid pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infundibulum
An infundibulum (Latin for ''funnel''; plural, ''infundibula'') is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ. Anatomy * Brain: the pituitary stalk, also known as the ''infundibulum'' and ''infundibular stalk'', is the connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary. * Hair follicle: the infundibulum is the cup or funnel in which a hair follicle grows. * Infundibulum (heart): The infundibulum of the heart, or conus arteriosus, is the outflow portion of the right ventricle. * Lung: The alveolar sacs of the lungs, from which the air chambers (alveoli) open, are also called ''infundibula''. * Sinus (anatomy): The ethmoidal infundibulum is the most important of three infundibula of the nose: the frontal infundibulum and the maxillary infundibulum flow into it. * Infundibulum of uterine tube: the funnel-like end of the mammal oviduct nearest to the ovary. * Gallbladder: The Infundibulum of the gallbladder (also known as the "neck" of the gallbladder) is the end of nearest to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyelo-
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the convergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous membrane and is covered with transitional epithelium and an underlying lamina propria of loose-to-dense connective tissue. The renal pelvis is situated within the renal sinus alongside the other structures of the renal sinus. Clinical significance The renal pelvis is the location of several kinds of kidney cancer and is affected by infection in pyelonephritis. A large " staghorn" kidney stone may block all or part of the renal pelvis. The size of the renal pelvis plays a major role in the grading of hydronephrosis. Normally, the anteroposterior diameter of the renal pelvis is less than 4 mm in fetuses up to 32 weeks of gestational age and 7 mm afterwards. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Compound
Neoclassical compounds are compound words composed from combining forms (which act as affixes or stems) derived from Classical_language#Classical_studies, classical languages (classical Latin or ancient Greek) root (linguistics), roots. Neo-Latin comprises many such words and is a substantial component of the technology, technical and science, scientific lexicon of English language, English and other languages, via international scientific vocabulary (ISV). For example, Greek ''wikt:bio-#Prefix, bio-'' combines with ''wikt:-graphy#Suffix, -graphy'' to form ''biography'' ("life" + "writing/recording"). Source of international technical vocabulary Neoclassical compounds represent a significant source of Neo-Latin vocabulary. Moreover, since these words are composed from classical languages whose prestige is or was respected throughout the Western European culture, these words typically appear in many different languages. Their widespread use makes technical writing generally acces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drain-waste-vent System
A drain-waste-vent system (or DWV) is the combination of pipes and plumbing fittings that captures sewage and greywater within a structure and routes it toward a water treatment system. It includes venting to the exterior environment to prevent a vacuum from forming and impeding plumbing fixture, fixtures such as sinks, showers, and toilets from draining freely, and employs water-filled trap (plumbing), traps to block dangerous sewer gasses from entering a plumbed structure. DWV systems capture both sewage and greywater within a structure and safely route it out via the low point of its "soil stack" to a waste treatment system, either via a municipal sanitary sewer system, or to a septic tank and septic drain field, leach field. (Cesspits are generally prohibited in developed areas.) For such drainage systems to work properly it is crucial that pressure, neutral air pressure be maintained within all pipes, allowing free gravity flow of water and sanitary sewer, sewage through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Calyx
The renal calyces ( calyx) are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; four or five minor calyces converge to form a major calyx through which urine passes into the renal pelvis (which in turn drains urine out of the kidney through the ureter). Function Peristalsis of the smooth muscle originating in pace-maker cells originating in the walls of the calyces propels urine through the renal pelvis and ureters to the bladder. The initiation is caused by the increase in volume that stretches the walls of the calyces. This causes them to fire impulses which stimulate rhythmical contraction and relaxation, called peristalsis. Parasympathetic innervation enhances the peristalsis while sympathetic innervation inhibits it. Clinical significance A " staghorn calculus" is a kidney stone that may exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |