|
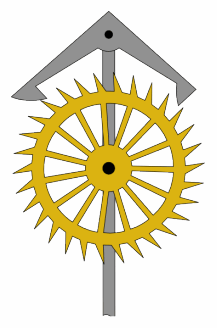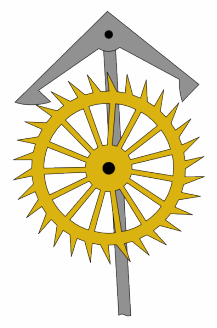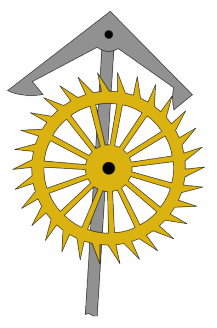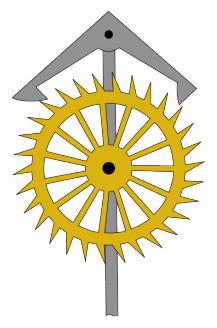
Remontoire
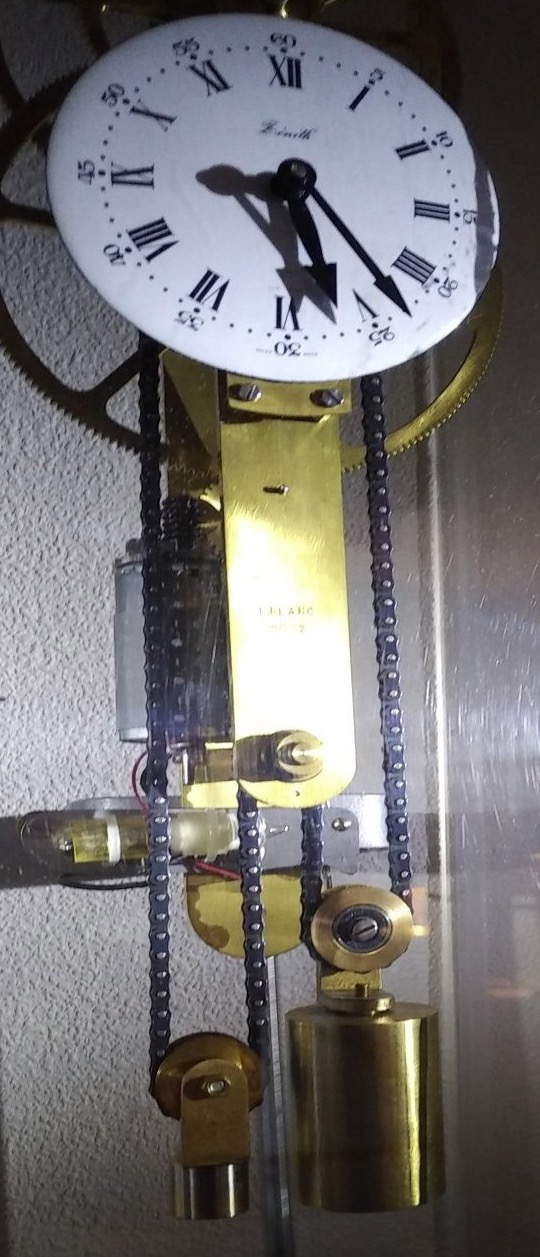
In mechanical horology, a remontoire (from the French ''remonter'', meaning 'to wind') is a small secondary source of power, a weight or spring, which runs the timekeeping mechanism and is itself periodically rewound by the timepiece's main power source, such as a mainspring. It was used in a few precision clocks and watches to place the source of power closer to the escapement, thereby increasing the accuracy by evening out variations in drive force caused by unevenness of the friction in the geartrain. In spring-driven precision clocks, a gravity remontoire is sometimes used to replace the uneven force delivered by the mainspring running down by the more constant force of gravity acting on a weight. In turret clocks, it serves to separate the large forces needed to drive the hands from the modest forces needed to drive the escapement which keeps the pendulum swinging. A remontoire should not be confused with a ''maintaining power spring'', which is used only to keep the timepi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was an English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the History of longitude, problem of how to calculate longitude while at sea. Harrison's solution revolutionized navigation and greatly increased the safety of long-distance sea travel. The problem he solved had been considered so important following the Scilly naval disaster of 1707 that the Parliament of Great Britain, British Parliament was offering financial rewards of up to £20,000 (equivalent to £ in ) under the 1714 Longitude Act, though Harrison never received the full reward due to political rivalries. He presented his first design in 1730, and worked over many years on improved designs, making several advances in time-keeping technology, finally turning to what were called sea watches. Harrison gained support from the Board of Longitude, Longitude Board in building and testing his designs. Towards the end of his life, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maintaining Power
In horology, a maintaining power is a mechanism for keeping a clock or watch going while it is being wound. Huygens The weight drive used by Christiaan Huygens in his early clocks acts as a maintaining power. In this layout, the weight which drives the clock is carried on a pulley and the cord (or chain) supporting the weight is wrapped around the main driving wheel on one side and the rewinding wheel on the other. The chain then loops down from the rewinding wheel and up again to the main driving wheel via a second pulley carrying a small tensioning weight which ensures the loop stays taut and the chain engages well with the main driving wheel and rewinding wheel. In the first illustration the clock is fully wound, the driving weight is up and the tensioning weight down, a ratchet on the winding wheel prevents it from turning back. The driving weight pulls the main wheel in the direction of the arrow. In the second illustration the driving weight has reached its lowest point a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jost Bürgi
Jost Bürgi (also ''Joost, Jobst''; Latinized surname ''Burgius'' or ''Byrgius''; 28 February 1552 – 31 January 1632), active primarily at the courts in Kassel and Prague, was a Swiss clockmaker, mathematician, and writer. Life Bürgi was born in 1552 Lichtensteig, Toggenburg, at the time a subject territory of the Abbey of St. Gall (now part of the canton of St. Gallen, Switzerland). Not much is known about his life or education before his employment as astronomer and clockmaker at the court of William IV in Kassel in 1579; it has been theorized that he acquired his mathematical knowledge at Strasbourg, among others from Swiss mathematician Conrad Dasypodius, but there are no facts to support this. Although an autodidact, he was already during his lifetime considered as one of the most excellent mechanical engineers of his generation. His employer, William IV, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, in a letter to Tycho Brahe praised Bürgi as a "second Archimedes" (''quasi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mainspring
A mainspring is a spiral torsion spring of metal ribbon—commonly spring steel—used as a power source in mechanical watches, some clocks, and other clockwork mechanisms. ''Winding'' the timepiece, by turning a knob or key, stores energy in the mainspring by twisting the spiral tighter. The force of the mainspring then turns the clock's wheels as it unwinds, until the next winding is needed. The adjectives wind-up and spring-powered refer to mechanisms powered by mainsprings, which also include kitchen timers, metronomes, music boxes, wind-up toys and clockwork radios. Modern mainsprings A modern watch mainspring is a long strip of hardened and blued steel, or specialised steel alloy, 20–30 cm long and 0.05-0.2 mm thick. The mainspring in the common 1-day movement is calculated to enable the watch to run for 36 to 40 hours, i.e. 24 hours between daily windings with a power-reserve of 12 to 16 hours, in case the owner is late winding the watch. This is the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clock
A clock or chronometer is a device that measures and displays time. The clock is one of the oldest Invention, human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month, and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the Millennium, millennia. Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheels., pp. 103–104., p. 31. Traditionally, in horology (the study of timekeeping), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pendulum Clock
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is an approximate harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive synchronous electric clocks in the 1930s and 1940s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their Interior decor, decorative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Escapement
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element (usually a pendulum or balance wheel) to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring (device), spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's ''escape wheel'', allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stoppi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rover P6
The Rover P6 series (named as the 2000, 2200, or 3500, depending on engine displacement) is a Sedan (automobile), saloon car produced by Rover Company, Rover and subsequently British Leyland from 1963 to 1977 in Solihull, West Midlands, England, UK. The P6 was the first winner of the European Car of the Year award. Development The P6 was announced on 9 October 1963, just before the British International Motor Show, Earls Court Motor Show. The vehicle was marketed first as the Rover 2000 and was a complete "clean sheet" design intended to appeal to a larger number of buyers than earlier models such as the Rover P4, P4 it replaced. Rover had identified a developing market between the standard '1.5-litre' saloon car class (such as the Ford Consul#Ford Consul Mark II .281956.E2.80.931962.29, Ford Consul and the Singer Gazelle#Gazelle IIA to IIIC, Singer Gazelle) and the accepted 'three-litre' large saloon cars (typified by the Wolseley 6/99 and the Vauxhall Cresta#Cresta PA, Vauxha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational corporation, multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobiles and commercial vehicles under the List of Ford vehicles, Ford brand, and luxury cars under its Lincoln Motor Company, Lincoln brand. The company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the single-letter ticker symbol F and is controlled by the Ford family (Michigan), Ford family. They have minority ownership but a plurality of the voting power. Ford introduced methods for large-scale manufacturing of cars and large-scale management of an industrial workforce using elaborately engineered manufacturing sequences typified by moving assembly lines. By 1914, these methods were known around the world as Fordism. Ford's former British subsidiaries Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Land Rover, acquired in 1989 and 2000, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ford Cortina
The Ford Cortina is a medium-sized family car manufactured in various body styles from 1962 to 1982. It was the United Kingdom's best-selling car of the 1970s. The Cortina was produced in five generations (Mark I through to Mark V, although officially the last one was only the Cortina 80 facelift of the Mk IV) from 1962 until 1982. From 1970 onward, it was almost identical to the German-market Ford Taunus (being built on the same platform), which was originally a different car model. This was part of Ford's attempt to unify its European operations. By 1976, when the revised Taunus was launched, the Cortina was identical. The new Taunus/Cortina used the doors and some panels from the 1970 Taunus. It was replaced in 1982 by the Ford Sierra. In Asia and Australasia, it was replaced by the Mazda 626-based Ford Telstar, though Ford New Zealand, which built the sedan until 1983 and the estate car until 1984, did import British-made complete knock-down kits of the Sierra estate for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Horology
Chronometry or horology () is the science studying the measurement of time and timekeeping. Chronometry enables the establishment of standard measurements of time, which have applications in a broad range of social and scientific areas. ''Horology'' usually refers specifically to the study of mechanical timekeeping devices, while ''chronometry'' is broader in scope, also including biological behaviours with respect to time (biochronometry), as well as the dating of geological material (geochronometry). Horology is commonly used specifically with reference to the mechanical instruments created to keep time: clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, Water clock, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clocks are all examples of Measuring instrument, instruments used to measure time. People interested in horology are called ''horologists''. That term is used both by people who deal professionally with timekeeping apparatuses, as well as enthus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ford Capri
The Ford Capri is a fastback coupé built by Ford of Europe and designed by Philip T. Clark, who had been involved in the design of the Ford Mustang. It used the mechanical components from the Mk2 Ford Cortina and was intended as the European equivalent of the Ford Mustang. The Capri went on to be highly successful for Ford, selling nearly 1.9 million units in its lifetime. A wide variety of engines were used in the car throughout its production lifespan, which included the Essex and Cologne V6 at the top of the range, while the Kent straight-four and Taunus V4 engines were used in lower-specification models. Although the Capri was not officially replaced, the second-generation Probe was effectively its replacement after the later car's introduction to the European market in 1994. History Ford Capri Mk I (1969–1974) Production of the Capri began in November 1968. It was unveiled in January 1969 at the Brussels Motor Show, with sales starting the following month. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |