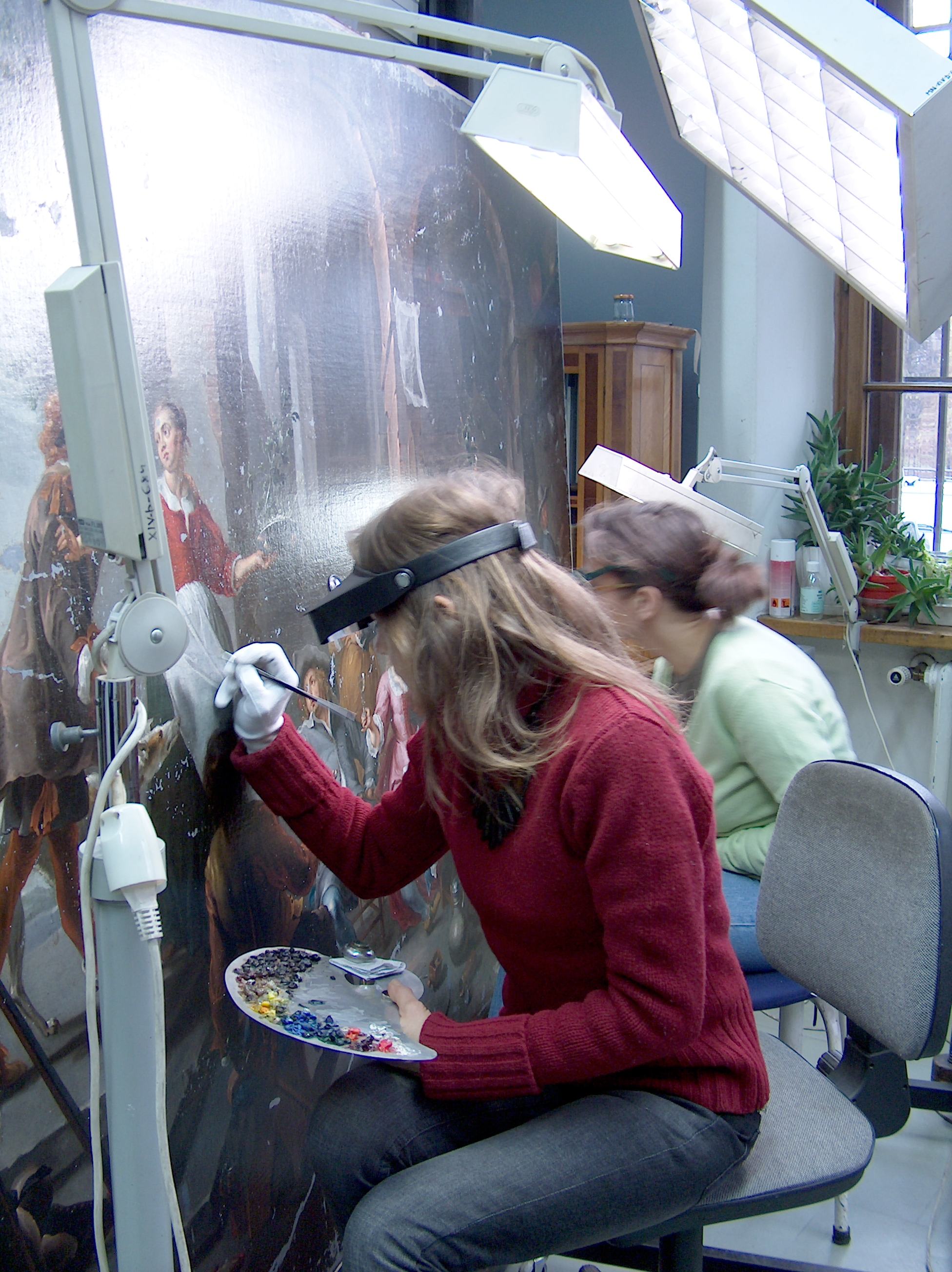|
Registrar (museum)
A museum/library/archival registrar is responsible for implementing policies and procedures that relate to caring for collections of cultural institutions like archives, libraries, and museums. These policies are found in the museum's collections policy, the guiding tenet of the museum explaining why the institution is in operation, dictating the museum's professional standards regarding the objects left in its care. Registrars focus on sections that include acquisitions, loans, exhibitions, deaccessions, storage, packing and shipping, security of objects in transit, insurance policies, and risk management. As a collections care professional, they work with collection managers, conservators, and curators to balance public access to objects with the conditions needed to maintain preservation. Focusing on documentation, registrars are responsible for developing and maintaining records management systems, with individual files for each object in the collection. Smaller and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registrar Materials
A registrar is an official keeper of records made in a register. The term may refer to: Education * Registrar (education), an official in an academic institution who handles student records * Registrar of the University of Oxford, one of the senior officials of the university Government records * Registrar (law), the official in charge of a court registry, usually a judicial appointment * Registrar of Companies, India * Registrar general, government officer in Britain and Commonwealth nations concerned with civil registration * Registrar General's Department, the Government of Ghana agency responsible for the registration of companies and business * Registrar of the treasury, an office of the United States Treasury Department * County registrar, an official of the Irish Circuit Court who carries out quasi-judicial and administrative functions * Office of the Registrar of Indigenous Corporations, an Australian Government statutory office * Superintendent Registrar, the senior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms." Entomologists and ecologists have urged the adoption of IPM pest control since the 1970s. IPM is a safer pest control framework than reliance on the use of chemical pesticides, mitigating risks such as: insecticide-induced resurgence, pesticide resistance and (especially food) crop residues.Bateman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provenance
Provenance () is the chronology of the ownership, custody or location of a historical object. The term was originally mostly used in relation to works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including archaeology, paleontology, archival science, circular economy, economy, computing, and Scientific method, scientific inquiry in general. The primary purpose of tracing the provenance of an object or entity is normally to provide contextual and circumstantial evidence for its original production or discovery, by establishing, as far as practicable, its later history, especially the sequences of its formal ownership, custody and places of storage. The practice has a particular value in helping Authentication, authenticate objects. Comparative techniques, expert opinions and the results of scientific tests may also be used to these ends, but establishing provenance is essentially a matter of documentation. The term dates to the 1780s in English. Provenance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Conservation
Conservation and restoration of movable cultural property is a term used to denote the conservation of movable cultural property items in libraries, archives, museums and private collections. Conservation encompasses all the actions taken toward the long-term preservation of cultural heritage. Activities include examination, documentation, treatment, and preventive care, which is supported by research and education. Object conservation is specifically the actions taken to preserve and restore cultural objects. The objects span a wide range of materials from a variety of cultures, time periods, and functions. Object conservation can be applied to both art objects and artifacts. Conservation practice aims to prevent damage from occurring, a process known as 'preventive conservation'. The purpose of preventive conservation is to maintain, and where possible enhance, the condition of an object, as well as managing deterioration risks, such as handling and environmental conditions. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Plunder
Nazi plunder () was organized stealing of art and other items which occurred as a result of the Art theft and looting during World War II, organized looting of European countries during the time of the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, Germany. Jewish property was looted beginning in 1933 in Germany and was a key part of the Holocaust. Nazis also plundered occupied countries, sometimes with direct seizures, and sometimes under the guise of protecting art through Kunstschutz units. In addition to gold, silver, and currency, cultural items of great significance were stolen, including paintings, ceramics, books, and religious treasures. Many of the artworks looted by the Nazis were recovered by the Allies of World War II, Allies' Monuments, Fine Arts, and Archives program (MFAA, also known as the Monuments Men and Women), following the war; however many of them are still missing or were returned to countries but not to their original owners. An international effort to identify Nazi plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disaster Recovery Plan
Given organizations' increasing dependency on information technology (IT) to run their operations, business continuity planning (and its subset IT service continuity planning) covers the entire organization, while disaster recovery focuses on IT. Auditing documents covering an organization's business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plans provides a third-party validation to stakeholders that the documentation is complete and does not contain material misrepresentations. Overview Often used together, the terms business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) are very different. BC refers to the ability of a business to continue critical functions and business processes after the occurrence of a disaster, whereas DR refers specifically to the IT functions of the business, albeit a subset of BC. Metrics The primary objective is to protect the organization in the event that all or part of its operations and/or computer services are rendered partially or completely un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Preservation
In library science, library and archival science, digital preservation is a formal process to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable in the long term. It involves planning, resource allocation, and application of Preservation (library and archive), preservation methods and Technology, technologies,Day, Michael. "The long-term preservation of Web content". Web archiving (Berlin: Springer, 2006), pp. 177-199. . and combines policies, strategies and actions to ensure access to digital reformatting, reformatted and "born-digital" content, regardless of the challenges of media failure and technological change. The goal of digital preservation is the accurate rendering of authenticated content over time.Evans, Mark; Carter, Laura. (December 2008). The Challenges of Digital Preservation. Presentation at the Library of Parliament, Ottawa. The Association for Library Collections and Technical Services Preservation and Reformatting Section of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curation (other) , an accu ...
Curation may refer to: Activities * Algorithmic curation, curation using computer algorithms * Content curation, the collection and sorting of information * Data curation, management activities required to maintain research data * Digital curation, the preservation and maintenance of digital assets * Evidence management, the indexing and cataloguing of evidence related to an event * Cultural heritage management, conservation of cultural sites and resources People who perform curation * Curator, manager or interpreter, traditionally of tangible assets of a library or museum * Biocurator, professional scientist who maintains information for biological databases See also * Curate, office and person holding it * Archive An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials, in any medium, or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation-restoration
conservation and restoration of cultural property focuses on protection and care of cultural property (tangible cultural heritage), including artworks, architecture, archaeology, and museum collections. Conservation activities include preventive conservation, examination, documentation, research, treatment, and education. This field is closely allied with conservation science, curators and registrars. Definition Conservation of cultural property involves protection and restoration using "any methods that prove effective in keeping that property in as close to its original condition as possible for as long as possible." Conservation of cultural heritage is often associated with art collections and museums and involves collection care and management through tracking, examination, documentation, exhibition, storage, preventive conservation, and restoration. The scope has widened from art conservation, involving protection and care of artwork and architecture, to conservat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
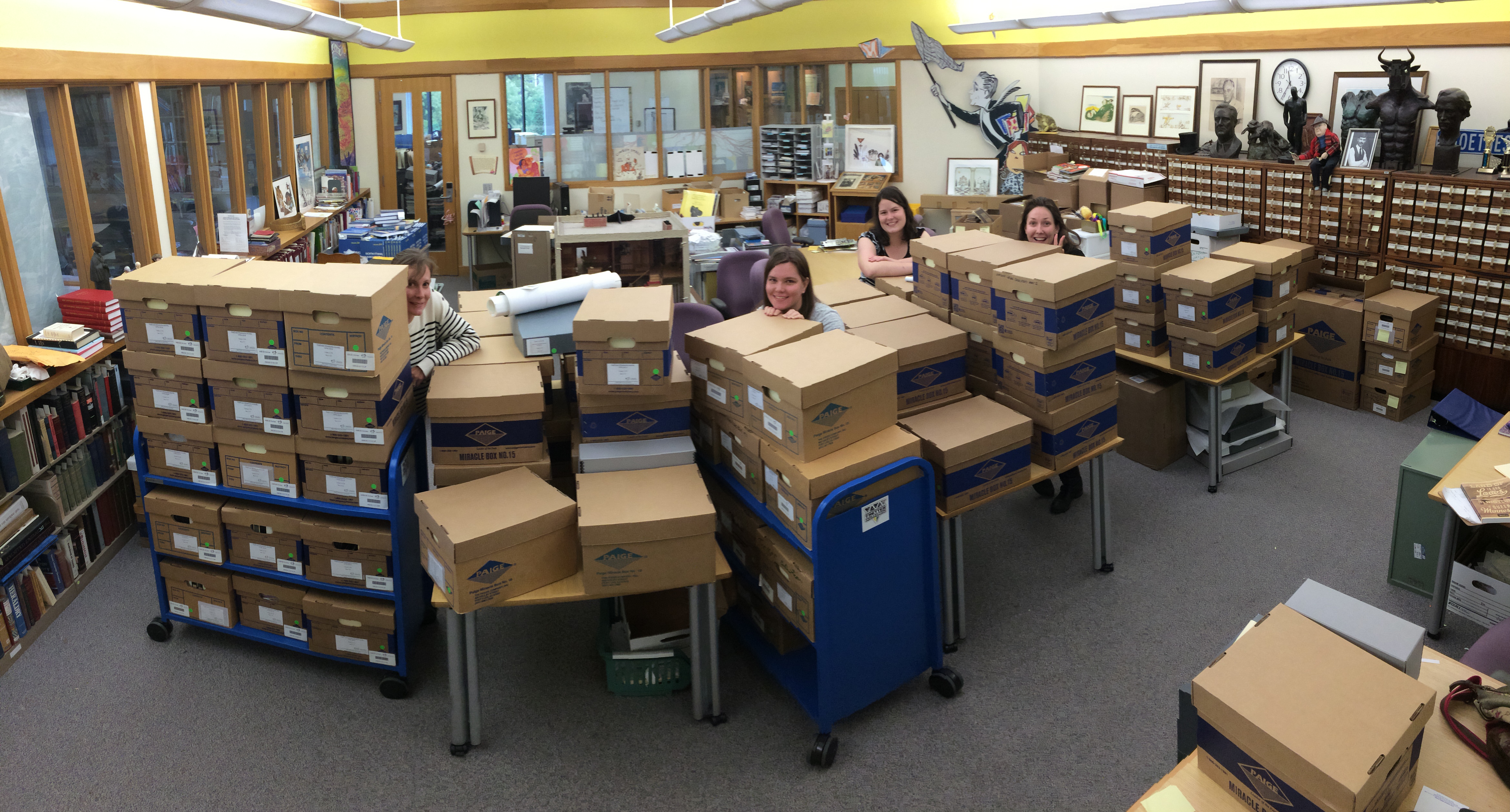
Collections Policy
Collections management involves the development, storage, and preservation of cultural property, as well as objects of contemporary culture (including contemporary art, literature, technology, and documents) in museums, libraries, archives and private collections. The primary goal of collections management is to meet the needs of the individual collector or collecting institution's mission statement, while also ensuring the long-term safety and sustainability of the cultural objects within the collector's care. Collections management, which consists primarily of the administrative responsibilities associated with collection development, is closely related to collections care, which is the physical preservation of cultural heritage. The professionals most influenced by collections management include collection managers, registrars, and archivists. Definition Cultural property collections require a great deal of care and protection in order to ensure their safety from external lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collections Care
Disaster preparedness in museums, galleries, libraries, archives and private collections, involves any actions taken to plan for, prevent, respond or recover from natural disasters and other events that can cause damage or loss to cultural property. 'Disasters' in this context may include large-scale natural events such as earthquakes, flooding or bushfire, as well as human-caused events such as theft and vandalism. Increasingly, anthropogenic climate change is a factor in cultural heritage disaster planning, due to rising sea levels, changes in rainfall patterns, warming average temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events. The primary goal of disaster preparedness is to identify actions that can be taken to reduce either the chance of a disaster occurring or to lessen its effects. For example, clearing building gutters reduces the chance of overflow and leaks during heavy rainfall; storing collection objects inside closed cabinets reduces the chance of water damage sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collection (museum)
A museum is distinguished by a collection of often unique objects that forms the core of its activities for exhibitions, education, research, etc. This differentiates it from an archive or library, where the contents may be more paper-based, replaceable and less exhibition oriented, or a private collection of art formed by an individual, family or institution that may grant no public access. A museum normally has a collecting policy for new acquisitions, so only objects in certain categories and of a certain quality are accepted into the collection. The process by which an object is formally included in the collection is called ''accessioning'' and each object is given a unique accession number. Museum collections, and archives in general, are normally catalogued in a collection catalogue, traditionally in a card index, but nowadays in a computerized database. Transferring collection catalogues onto computer-based media is a major undertaking for most museums. All new acquis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |