|
Reactive Centrifugal Force
In classical mechanics, a reactive centrifugal force forms part of an action–reaction pair with a centripetal force. In accordance with Newton's first law of motion, an object moves in a straight line in the absence of a net force acting on the object. A curved path ensues when a force that is orthogonal to the object's motion acts on it; this force is often called a centripetal force, as it is directed toward the center of curvature of the path. Then in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, there will also be an equal and opposite force exerted by the object on some other object, and this reaction force is sometimes called a ''reactive centrifugal force'', as it is directed in the opposite direction of the centripetal force. In the case of a ball held in circular motion by a string, the centripetal force is the force exerted by the string on the ball. The reactive centrifugal force on the other hand is the force the ball exerts on the string, placing it under tens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved Scientific Revolution, substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the History of physics#20th century: birth of modern physics, revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of Physical body, bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Newton's First Law
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: # A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by a force. # At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time. # If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions. The three laws of motion were first stated by Isaac Newton in his '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), originally published in 1687. Newton used them to investigate and explain the motion of many physical objects and systems. In the time since Newton, new insights, especially aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and Direction (geometry, geography), direction of a force are both important, force is a Euclidean vector, vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (unit), newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol . Force plays an important role in classical mechanics. The concept of force is central to all three of Newton's laws of motion. Types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include Elasticity (physics), elastic, frictional, Normal force, contact or "normal" forces, and gravity, gravitational. The rotational version of force is torque, which produces angular acceleration, changes in the rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part applies forces on the adjacent pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barycentre
In astronomy, the barycenter (or barycentre; ) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that orbit one another and is the point about which the bodies orbit. A barycenter is a dynamical point, not a physical object. It is an important concept in fields such as astronomy and astrophysics. The distance from a body's center of mass to the barycenter can be calculated as a two-body problem. If one of the two orbiting bodies is much more massive than the other and the bodies are relatively close to one another, the barycenter will typically be located within the more massive object. In this case, rather than the two bodies appearing to orbit a point between them, the less massive body will appear to orbit about the more massive body, while the more massive body might be observed to wobble slightly. This is the case for the Earth–Moon system, whose barycenter is located on average from Earth's center, which is 74% of Earth's radius of . When the two bodies are of similar m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kinetics (physics)
In physics and engineering, kinetics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the relationship between the motion In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and frame of reference to an o ... and its causes, specifically, forces and torques. Since the mid-20th century, the term "Dynamics (mechanics), dynamics" (or "analytical dynamics") has largely superseded "kinetics" in physics textbooks, though the term is still used in engineering. In Plasma (physics), plasma physics, kinetics refers to the study of Continuum mechanics, continua in velocity space. This is usually in the context of non-thermal (Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution#Physical applications, non-Maxwellian) velocity distributions, or processes that Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), perturb thermal distributions. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coriolis Force
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect. Though recognized previously by others, the mathematical expression for the Coriolis force appeared in an 1835 paper by French scientist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis, in connection with the theory of water wheels. Early in the 20th century, the term ''Coriolis force'' began to be used in connection with meteorology. Newton's laws of motion describe the motion of an object in an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference. When Newton's laws are transformed to a rotating frame of reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal accelerations appear. When applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fictitious Force
A fictitious force, also known as an inertial force or pseudo-force, is a force that appears to act on an object when its motion is described or experienced from a non-inertial reference frame, non-inertial frame of reference. Unlike real forces, which result from physical interactions between objects, fictitious forces occur due to the acceleration of the observer’s frame of reference rather than any actual force acting on a body. These forces are necessary for describing motion correctly within an accelerating frame, ensuring that Newton's laws of motion#Second, Newton's second law of motion remains applicable. Common examples of fictitious forces include the centrifugal force, which appears to push objects outward in a rotating system; the Coriolis force, which affects moving objects in a rotating frame such as the Earth; and the Euler force, which arises when a rotating system changes its angular velocity. While these forces are not real in the sense of being caused by ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
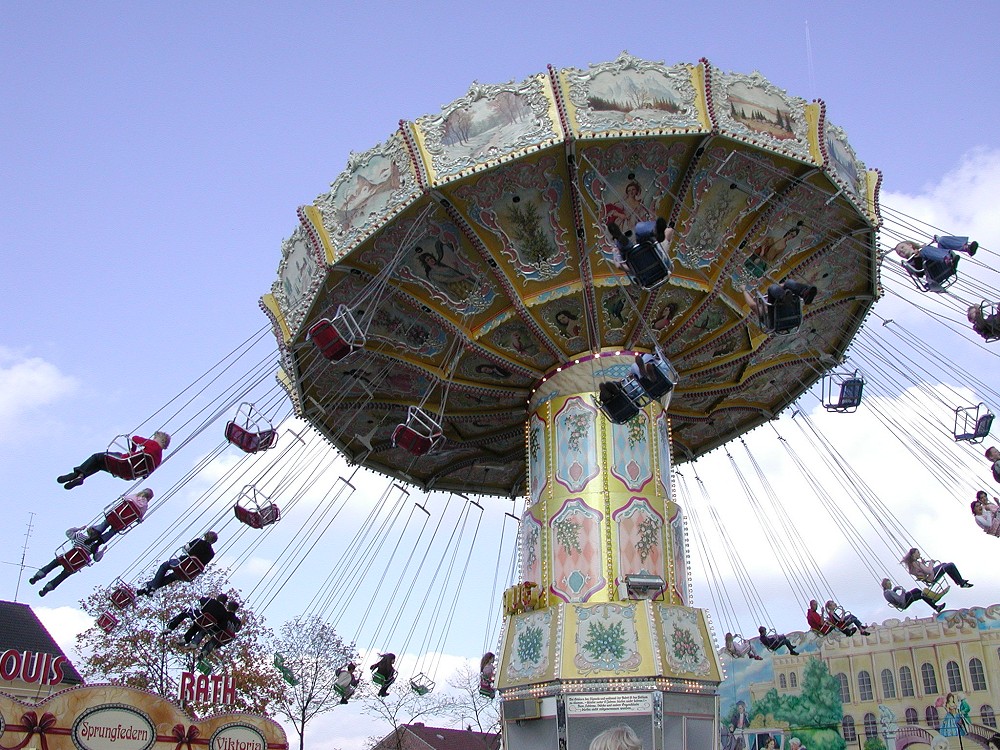
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is a fictitious force in Newtonian mechanics (also called an "inertial" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It appears to be directed radially away from the axis of rotation of the frame. The magnitude of the centrifugal force ''F'' on an object of mass ''m'' at the perpendicular distance ''ρ'' from the axis of a rotating frame of reference with angular velocity is F = m\omega^2 \rho. This fictitious force is often applied to rotating devices, such as centrifuges, centrifugal pumps, centrifugal governors, and centrifugal clutches, and in centrifugal railways, planetary orbits and banked curves, when they are analyzed in a non–inertial reference frame such as a rotating coordinate system. The term has sometimes also been used for the '' reactive centrifugal force'', a real frame-independent Newtonian force that exists as a reaction to a centripetal force in some scenarios. History F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Centrifugal Clutch
A centrifugal clutch is an automatic clutch that uses centrifugal force to operate. The output shaft is disengaged at lower rotational speed and engages as the output increases to a certain speed. It is often used in mopeds, underbones, lawn mowers, go-karts, chainsaws, mini bikes, and some paramotors and boats to keep the internal combustion engine, engine from stalling when the output shaft is slowed or stopped abruptly, and to remove load when starting and idling. It has been superseded for automobile applications by the fluid coupling, torque converter and automated manual transmissions. Operation The input of the clutch is connected to the engine crankshaft while the output may drive a shaft, chain, or belt. As engine revolutions per minute increase, weighted arms in the clutch swing outward and force the clutch to engage. The most common types have friction pads or shoes radially mounted that engage the inside of the rim of a housing. On the center shaft, there is an assorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Body Diagram
In physics and engineering, a free body diagram (FBD; also called a force diagram) is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces, moments, and resulting reactions on a free body in a given condition. It depicts a body or connected bodies with all the applied forces and moments, and reactions, which act on the body(ies). The body may consist of multiple internal members (such as a truss), or be a compact body (such as a beam). A series of free bodies and other diagrams may be necessary to solve complex problems. Sometimes in order to calculate the resultant force graphically the applied forces are arranged as the edges of a polygon of forces or force polygon (see ). Free body A body is said to be "free" when it is singled out from other bodies for the purposes of dynamic or static analysis. The object does not have to be "free" in the sense of being unforced, and it may or may not be in a state of equilibrium; rather, it is not fixed in place and is thus " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
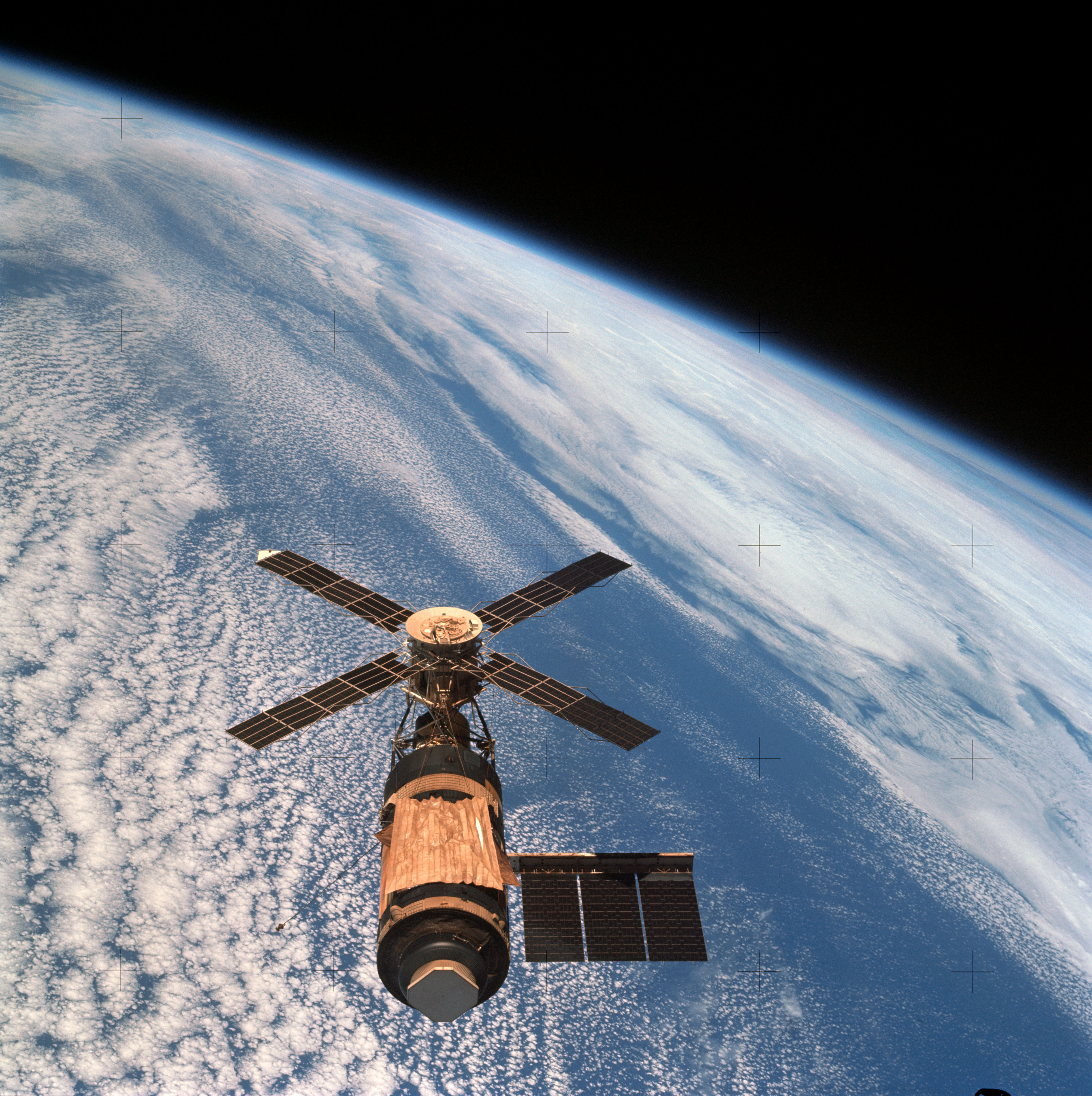
Uniform Circular Motion
In physics, circular motion is movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular arc. It can be uniform, with a constant rate of rotation and constant tangential speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation. The rotation around a fixed axis of a three-dimensional body involves the circular motion of its parts. The equations of motion describe the movement of the center of mass of a body, which remains at a constant distance from the axis of rotation. In circular motion, the distance between the body and a fixed point on its surface remains the same, i.e., the body is assumed rigid. Examples of circular motion include: special satellite orbits around the Earth (circular orbits), a ceiling fan's blades rotating around a hub, a stone that is tied to a rope and is being swung in circles, a car turning through a curve in a race track, an electron moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field, and a gear turning inside a mechanism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |