|
Rail Interface System
A dovetail rail on a rifle receiver for mounting a sight A rail integration system (RIS; also called a rail accessory system (RAS), rail interface system, rail system, mount, base, gun rail, or simply a rail) is a generic term for any standardized attachment system for mounting firearm accessories via bar-like straight brackets (i.e. "rails") often with regularly spaced slots. Rail systems are usually made of strips of metal or polymer screw-fastened onto the gun's receiver, handguard, or fore-end stock to allow variable-position attachments. An advantage of the multiple rail slots is the moveable positions to adjust for optimal placement of each item for a user's preferences, along with the ability to switch different items at different placements due to varying eye reliefs on gun sights. Firearm accessories commonly compatible with or intended for rail systems include tactical lights, laser sights, vertical forward grips, telescopic sights, holographic sights, reflex si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
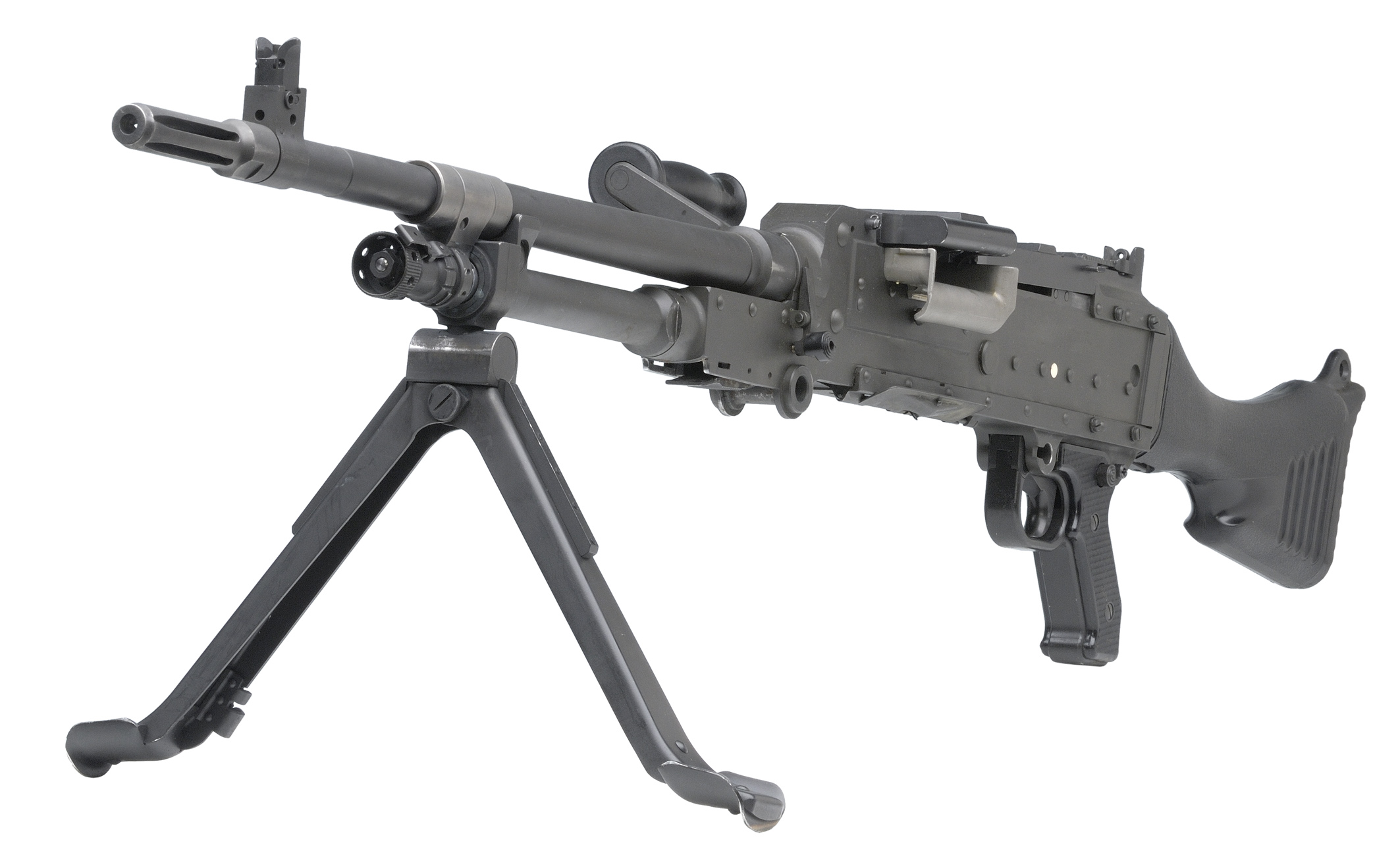
Bipod
A bipod is a V-shaped portable attachment that helps support and steady a device, usually a weapon such as a long gun or a mortar. The term comes from the Latin prefix and Greek root , meaning "two" and "foot" respectively. Bipods are designed to support the weight of the weapon's front portion and barrel, and provide significant stability against unwanted side-to-side movements (i.e. canting) while allowing free movements pivoting around the transverse axis ( pitching). Most modern bipods have foldable and/or telescoping legs, and allow some limited movements around the vertical axis (panning) and even the longitudinal axis ( tilting). A bipod by itself, with only two supporting legs, is not completely stable and needs to be reinforced by at least one more point of support to be steady, especially against the horizontal shearing force from recoils. This third point of support is typically the buttstock that is firmly pushed/braced against the shooter's body, but can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UIT Rail
The UIT rail, also known as Anschutz rail, is a standard used for mounting slings and other gun accessories in competition shooting, and is essentially a T-slot track shaped aluminium extrusion profile accepting attachments in the form of T-slot nuts, or similar. A similar design is called Freeland rail, but the dimensions of Anschütz (UIT) and Freeland rails differ. The Anschütz rail is wide and shallow, and the Freeland is narrower and deeper. Accessories made for one of the two types are not necessarily compatible with the other. Dimensions Dimensions below are approximate. Equipment rails - Anschutz-UIT left, Freeland right.png, Drawing comparing Anschütz (left) and Freeland equipment rails (right). See also * Rail Integration System, generic term for a system for attaching accessories to small firearms * Weaver rail mount, early system used for scope mounts, still has some popularity in the civilian market * Sling swivel, older standard used for mounting sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sling (firearms)
In the context of firearms, a sling is a type of strap or harness designed to allow a shooter to conveniently carry a firearm (usually a long gun such as a rifle, carbine, shotgun, submachine gun or GPMG) on their body, and/or to aid in greater hit probability by allowing the firearm to be better braced and stabilized during aiming. Various types of slings offer their own advantages and disadvantages, and can generally be divided into several categories. Types of setup ; Simple/traditional sling (two-point): The oldest and most familiar design, this sling design has two connection points that attach to the front and rear of the weapon, and allows the shooter to carry the weapon over their back, with the sling draped across the torso, around the neck or over one shoulder. Some two-point slings, if properly made, can act as a shooting aid. ; Ching/CW sling: This type of sling is a component of the Scout Rifle concept, and serves not just as a carrying strap, but as an aid to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-LOK
M-LOK, for Modular Lock, is a firearm Rail Integration System, rail interface system developed and patented by Magpul Industries. The license is free-of-charge, but subject to an approval process. M-LOK allows for direct accessory attachment onto the "negative space" (hollow slot) mounting points, and is a competing standard to VLTOR's open sourced KeyMod system for replacing the ubiquitous Picatinny rail in some applications. Both M-LOK and KeyMod enable the user to have a slimmer, lighter, smoother and more fenestration (architecture), fenestrated handguard/Forearm (firearm component), fore-end with accessories and gadgets mounted only where needed as compared to a Picatinny handguard, which typically has whole length rail slots, resulting in a heavier weight, bulkier handguard and poorer Gun barrel, barrel ventilation, resulting in the barrel overheating more quickly. The M-LOK system can be seen as an evolution of the Magpul Original Equipment (MOE) system, but the two are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KeyMod
KeyMod is a universal interface system for firearm accessory components. The concept was first created by VLTOR Weapon Systems of Tucson, Arizona, and released through Noveske Rifleworks of Grants Pass, Oregon, before being published Open-source software, open sourced in the public domain for adoption by the entire firearms accessory industry. The name "KeyMod" was coined by Eric Kincel (then working for VLTOR Weapon Systems) following the naming trend of other VLTOR accessories with the suffix "Mod" meaning modular, and "Key" being a reference to the key-hole profile of the mounting slots. History VLTOR Weapon Systems had previously pursued a design which was the basis for the KeyMod system. While developing the first prototype systems, Eric Kincel of VLTOR Weapon systems was approached by John Noveske of Noveske Rifleworks with a design for a universal accessory attachment system. After a short collaboration, during which Todd Krawczyk of Noveske Rifleworks suggested an improveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOPMOD
The Special Operations Peculiar MODification (SOPMOD) kit is an accessory system for the M4A1 carbine, CQBR, FN SCAR Mk 16/17, HK416 and other weapons used by United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM) special forces units, though it is not specific to SOCOM. The kit allows US Special Operations Forces (US SOF) personnel to configure their weapons to individual preferences and customize for different mission requirements. The program dates back to September 1989, when the Special Operations Special Technology (SOST) ''Modular Close Combat Carbine Project'' was founded. This was the first program to standardize components from the 1970s/1980s era of "duct tape and hose clamps". The ''Material Need Statement'' (MNS) was signed in May 1992 and, by September 1993, the ''Operational Requirements Document'' (ORD) for the program was validated. Responsibility for the program was then assigned to the Naval Surface Warfare Center Crane Division. The SOPMOD kit is composed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picatinny Rail
The 1913 rail (MIL-STD-1913 rail) is an American rail integration system designed by Richard Swan that provides a mounting platform for firearm accessories. It forms part of the NATO standard STANAG 2324 rail. It was originally used for mounting of telescopic sights atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles. Once established as United States Military Standard, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: iron sights, tactical lights, laser sights, night-vision devices, reflex sights, holographic sights, foregrips, bipods, slings and bayonets. An updated version of the rail is adopted as a NATO standard as the STANAG 4694 NATO Accessory Rail. History Attempts to standardize the Weaver rail mount designs date from work by the A.R.M.S. company and Richard Swanson in the early 1980s. Specifications for the M16A2E4 rifle and the M4E1 carbine received type classification generic in December 1994. These were the M16A2 and the M4 modified wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
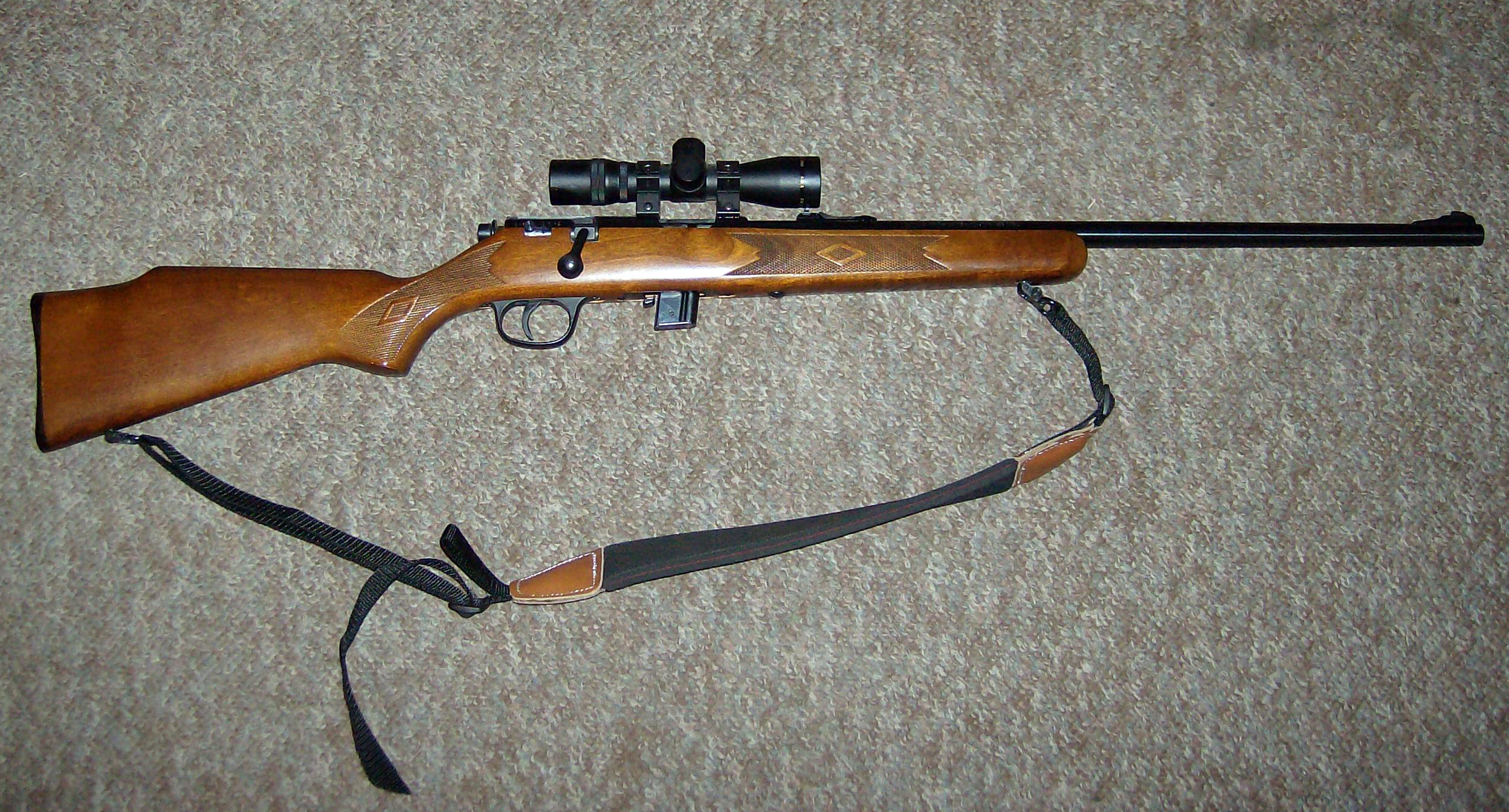
Weaver Rail
A Weaver rail mount is a system to connect telescopic sights (often via a scope mount) and other accessories to firearms and certain crossbows. It uses a pair of parallel rails and several slots perpendicular to these rails. The later Picatinny rail, developed by the US military, is a development of the key concepts of the Weaver system, and they are partially compatible. History The Weaver mount was developed by William Ralph Weaver (1905 – 8 November 1975) at his telescopic sight company W.R. Weaver Co., which he founded in 1930. Previous systems included the Leupold/Redfield mounts. Compared to the Leupold mount, the Weaver rail is not as strong and cannot be adjusted for windage. W.R. Weaver Co. became Weaver Optics, and was a subsidiary of Meade Instruments Corporation from 2002 to 2008, when it was on-sold to become part of Alliant Techsystems's Security and Sporting division in Onalaska, Wisconsin. Features Older Weaver systems used two pieces mounted a distanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a Collective security#Collective defense, collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Polish People's Republic, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc List of non-communist socialist states, socialist republics in Central and Eastern Europe in May 1955, during the Cold War. The term "Warsaw Pact" commonly refers to both the treaty itself and its resultant military alliance, the Warsaw Pact OrganisationPage 22, �NATO and OSCE, Partners or Rivals?��, Edward Killham (WPO) (also known as ‘Warsaw Treaty Organization’ (‘WTO’)). The Warsaw Pact was the military complement to the Comecon, Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon), the economic organization for the Eastern Bloc states. Dominated by the Soviet Union, the Warsaw Pact was established as a balance of power or counterweight to the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovetail Rail
A dovetail joint or simply dovetail is a joinery technique most commonly used in woodworking joinery (carpentry), including furniture, cabinets, log buildings, and traditional timber framing. Noted for its resistance to being pulled apart, also known as tensile strength, the dovetail joint is commonly used to join the sides of a drawer to the front. A series of pins cut to extend from the end of one board interlock with a series of 'tails' cut into the end of another board. The pins and tails have a trapezoidal shape. Once glued, a wooden dovetail joint requires no mechanical fasteners. History The dovetail joint technique probably pre-dates written history. Some of the earliest known examples of the dovetail joint are in ancient Egyptian furniture entombed with mummies dating from First Dynasty, the tombs of Chinese emperors, and a stone pillar at the Vazhappally Maha Siva Temple in India. The dovetail design is an important method of distinguishing various periods of furni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |