|
Racemorphan
Racemorphan, or morphanol, is the racemic mixture of the two stereoisomers of 17-methylmorphinan-3-ol, each with differing pharmacology and effects: * Dextrorphan - an antitussive and dissociative hallucinogen (NMDA receptor antagonist) * Levorphanol - an opioid analgesic Racemorphan itself is under international control per the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961 and is therefore listed as a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance in the US Controlled Substances Act 1970; it has an ACSCN of 9733 and in 2014 it had an aggregate annual manufacturing quota of zero. The salts in use are hydrobromide (free base conversion ratio 0.741), hydrochloride (0.876), and tartrate (0.632). See also * Levallorphan * Methorphan * Morphinan * Cyclorphan See also * Cough syrup * Noscapine * Codeine; Pholcodine * Dextromethorphan; Dimemorfan * Dextrorphan; Levorphanol * Butamirate Butamirate (or brospamin, trade names Acodeen, Codesin, Pertix, Sinecod, Sinecoden, Sinecodix) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levorphanol
Levorphanol (brand name Levo-Dromoran) is an opioid medication used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is the levorotatory enantiomer of the compound racemorphan. Its dextrorotatory counterpart is dextrorphan. It was first described in Germany in 1946. The drug has been in medical use in the United States since 1953. Pharmacology Levorphanol acts predominantly as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), but is also an agonist of the δ-opioid receptor (DOR), κ-opioid receptor (KOR), and the nociceptin receptor (NOP), as well as an NMDA receptor antagonist and a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). Levorphanol, similarly to certain other opioids, also acts as a glycine receptor antagonist and GABA receptor antagonist at very high concentrations. Levorphanol is 6 to 8 times as potent as morphine at the MOR. Relative to morphine, levorphanol lacks complete cross-tolerance and possesses greater intrinsic activity at the MOR. The duration of action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
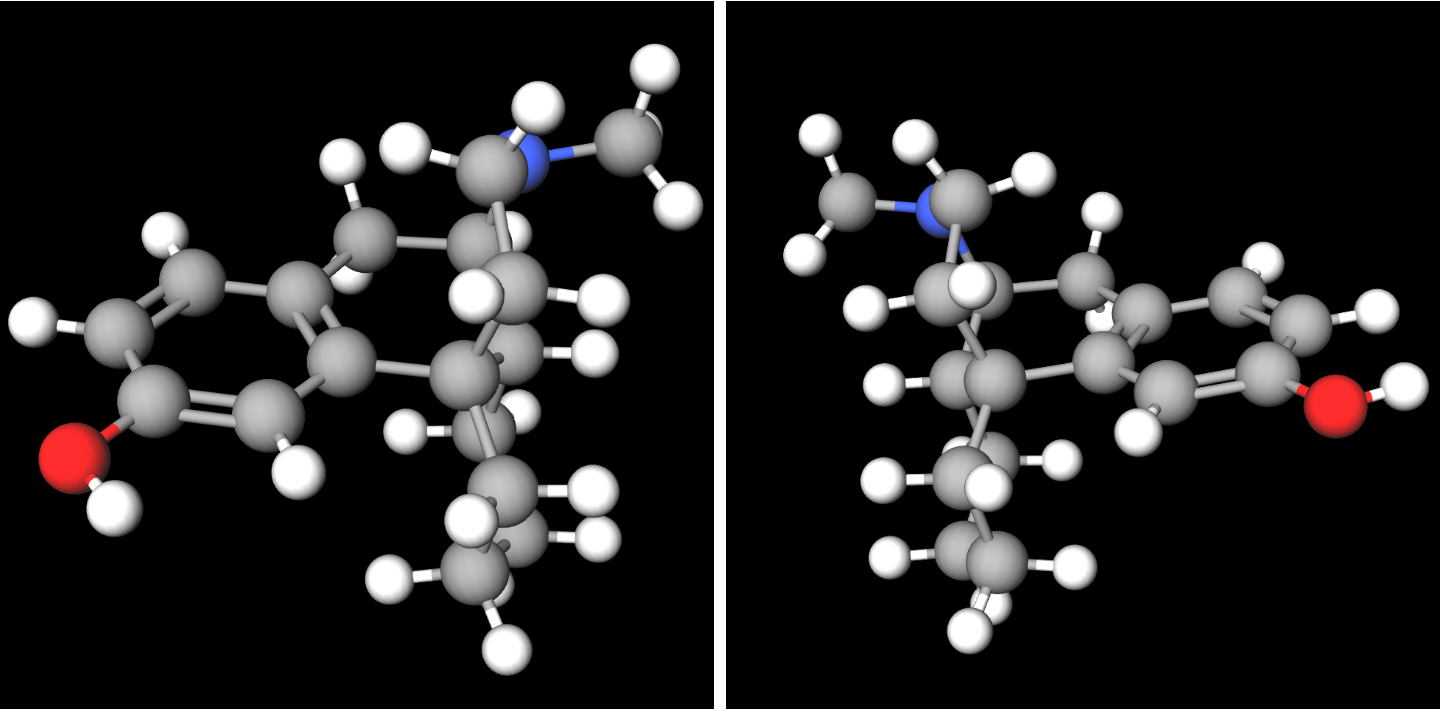
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder. It is in the morphinan class of medications with sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties (at lower doses). Dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity typical of morphinan compounds and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder. Dextromethorphan is also used recreationally. When exceeding approved dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. It has multiple mechanisms of action, including actions as a nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a sigma-1 receptor agonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methorphan
Methorphan comes in two isomeric forms, each with differing pharmacology and effects: * Dextromethorphan - An over-the-counter cough suppressant, as well as dissociative hallucinogen. * Levomethorphan - A potent opioid analgesic that was never clinically developed; a prodrug of the powerful opioid agonist analgesic levorphanol (Levo-Dromoran). Racemethorphan refers to the racemic mixture of both of these stereoisomers. It is listed under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961 and is therefore listed in the United States as a Controlled Substance, specifically as a Narcotic in Schedule II with an ACSCN of 9732 and an annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 3 grams in 2014. The salts in use are the hydrobromide (free base conversion ratio 0.770) and the tartrate (0.644) See also * Morphinan Morphinan is the prototype chemical structure of a large chemical class of psychoactive drugs, consisting of opiate analgesics, cough suppressants, and dissociative ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dextrorphan
Dextrorphan (DXO) is a psychoactive drug of the morphinan class which acts as an antitussive or cough suppressant and dissociative hallucinogen. It is the dextrorotatory enantiomer of racemorphan; the levorotatory enantiomer is levorphanol. Dextrorphan is produced by O-demethylation of dextromethorphan by CYP2D6. Dextrorphan is an NMDA antagonist and contributes to the psychoactive effects of dextromethorphan. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics The pharmacology of dextrorphan is similar to that of dextromethorphan (DXM). However, dextrorphan is much more potent as an NMDA receptor antagonist as well much less active as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, but retains DXM's activity as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It also has more affinity for the opiod receptors than dextromethorphan, significantly so at high doses. Pharmacokinetics Dextrorphan has a notably longer elimination half-life than its parent compound, and therefore has a tendency to accumulate in the blood after r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobromide
In chemistry, a hydrobromide is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrobromic acid with an organic base (chemistry), base (e.g. an amine). The compounds are similar to hydrochlorides. Some drugs are formulated as hydrobromides, e.g. eletriptan hydrobromide. See also *Bromide, inorganic salts of hydrobromic acid *Bromine, the element Br *Free base (chemistry) Acid salts Salts Organobromides {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholcodine
Pholcodine is an opioid cough suppressant (antitussive). It helps suppress unproductive coughs and also has a mild sedative effect, but has little or no analgesic effects. It is also known as morpholinylethylmorphine and homocodeine. Pholcodine is found in certain cough lozenges, and more commonly as an oral solution, typically 5 mg / 5 ml. Adult dosage is 5-10 ml up to 3-4 times daily. Pholcodine now largely replaces the previously more common codeine linctus, as it has a much lower potential for dependence. Pholcodine is used as an antitussive agent in Australia, Belgium, Finland, France, Ireland, New Zealand, Norway, and the U It is a Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs Act#Class B drugs, class B substance in the United Kingdom but can be purchased over-the-counter in most UK pharmacies. Pholcodine is not prescribed in the United States where it is classed as a Schedule I drug, the most highly controlled drug category, which includes the likes of heroin, LSD an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimemorfan
Dimemorfan (INN) (or dimemorphan) (brand names Astomin, Dastosirr, Tusben), or dimemorfan phosphate ( JAN), also known as 3,17-dimethylmorphinan, is an antitussive (cough suppressant) of the morphinan family that is widely used in Japan and is also marketed in Spain and Italy. It was developed by Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical (now Astellas Pharma) and introduced in Japan in 1975. It was later introduced in Spain in 1981 and Japan in 1985. Side effects Adverse effects include nausea, somnolence, dry mouth, and decreased appetite. Pharmacology Dimemorfan is an analogue of dextromethorphan (DXM) and its active metabolite dextrorphan (DXO), and similarly to them, acts as a potent agonist of the σ1 receptor (Ki = 151 nM). However, unlike DXM and DXO, it does not act significantly as an NMDA receptor antagonist (Ki = 16,978 nM), and for this reason, lacks dissociative effects, thereby having reduced side effects and abuse potential in comparison. Similarly to DXM and DXO, dimemor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butamirate
Butamirate (or brospamin, trade names Acodeen, Codesin, Pertix, Sinecod, Sinecoden, Sinecodix) is a cough suppressant. It has been marketed in Europe and Mexico, but not in the United States. As the citrate salt, it is sold in the form of lozenges, syrup, tablets, dragées, or pastilles. Adverse effects can include nausea, diarrhea, vertigo, and exanthema. Pharmacology A study found it to bind to the cough center in the medulla oblongata, more specifically the dextromethorphan-binding site in guinea pig brain with high affinity. As a 2-(2-diethylaminoethoxy)ethyl ester, it is chemically related to oxeladin and pentoxyverine, which are in the same class. (Oxeladin has an additional ethyl group in its carboxylic acid, pentoxyverine has both ethyl groups of oxeladin replaced by one cyclopentyl in the same place.) File:Oxeladin.png, Oxeladin File:Pentoxyverine skeletal.svg, Pentoxyverine See also * Cough syrup * Noscapine * Codeine; Pholcodine * Dextromethorphan; Dimemo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipepidine
Tipepidine (INN) (brand names Asverin, Antupex, Asvelik, Asvex, Bitiodin, Cofdenin A, Hustel, Nodal, Sotal), also known as tipepidine hibenzate ( JAN), is a synthetic, non-opioid antitussive and expectorant of the thiambutene class. It acts as an inhibitor of G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channels (GIRKs). The drug was discovered in the 1950s,ES Patent 272195 and was developed in Japan in 1959. It is used as the hibenzate and citrate salts. The usual dose is 20 mg every 4–6 hours. Possible side effects of tipepidine, especially in overdose, may include drowsiness, vertigo, delirium, disorientation, loss of consciousness, and confusion. Tipepidine has been investigated as a potential psychiatric drug. It is being investigated in depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Through inhibition of GIRK channels, tipepidine increases dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens, but without increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentoxyverine
Pentoxyverine ( rINN) or carbetapentane is an antitussive (cough suppressant) commonly used for cough associated with illnesses like common cold. It is sold over-the-counter in the United States as Solotuss, or in combination with other medications, especially decongestants. One such product is ''Certuss'', a combination of guaifenesin and pentoxyverine. The drug is available in the form of drops, suspensions and suppositories. Uses The drug is used for the treatment of dry cough associated with conditions such as common cold, bronchitis or sinusitis. Like codeine and other antitussives, it relieves the symptom, but does not heal the illness. No controlled clinical trials regarding the efficiency of pentoxyverine are available. Pharmacologists use the substance as a selective agonist at the sigma-1 receptor in animal and in vitro experiments. Contraindications Pentoxyverine is contraindicated in persons with bronchial asthma or other kinds of respiratory insufficiency (bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noscapine
Noscapine (also known as Narcotine, Nectodon, Nospen, Anarcotine and (archaic) Opiane) is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae (poppy family). It lacks significant hypnotic, euphoric, or analgesic effects affording it with very low addictive potential. This agent is primarily used for its antitussive (cough-suppressing) effects. Medical uses Noscapine is often used as an antitussive medication. A 2012 Dutch guideline, however, does not recommend its use for acute coughing. Side effects *Nausea *Vomiting *Loss of coordination *Hallucinations (auditory and visual) *Loss of sexual drive *Swelling of prostate * Loss of appetite * Dilated pupils * Increased heart rate * Shaking and muscle spasms *Chest pains *Increased alertness *Loss of any sleepiness *Loss of stereoscopic vision Interactions Noscapine can increase the effects of centrally sedating substances such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloperastine
Cloperastine (INN) or cloperastin, in the forms of cloperastine hydrochloride ( JAN) (brand names Hustazol, Nitossil, Seki) and cloperastine fendizoate (or hybenzoate), is an antitussive and antihistamine that is marketed as a cough suppressant in Japan, Hong Kong, and in some European countries. It was first introduced in 1972 in Japan, and then in Italy in 1981. Side effects Adverse effects may include sedation, drowsiness, heartburn, and thickening of bronchial secretions. Pharmacology The precise mechanism of action of cloperastine is not fully clear, but several different biological activities have been identified for the drug, of which include: ligand of the σ1 receptor (Ki = 20 nM) (likely an agonist), GIRK channel blocker (described as "potent"), antihistamine (Ki = 3.8 nM for the H1 receptor), and anticholinergic. It is thought that the latter two properties contribute to side effects, such as sedation and somnolence, while the former two may be involved in or res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |