|
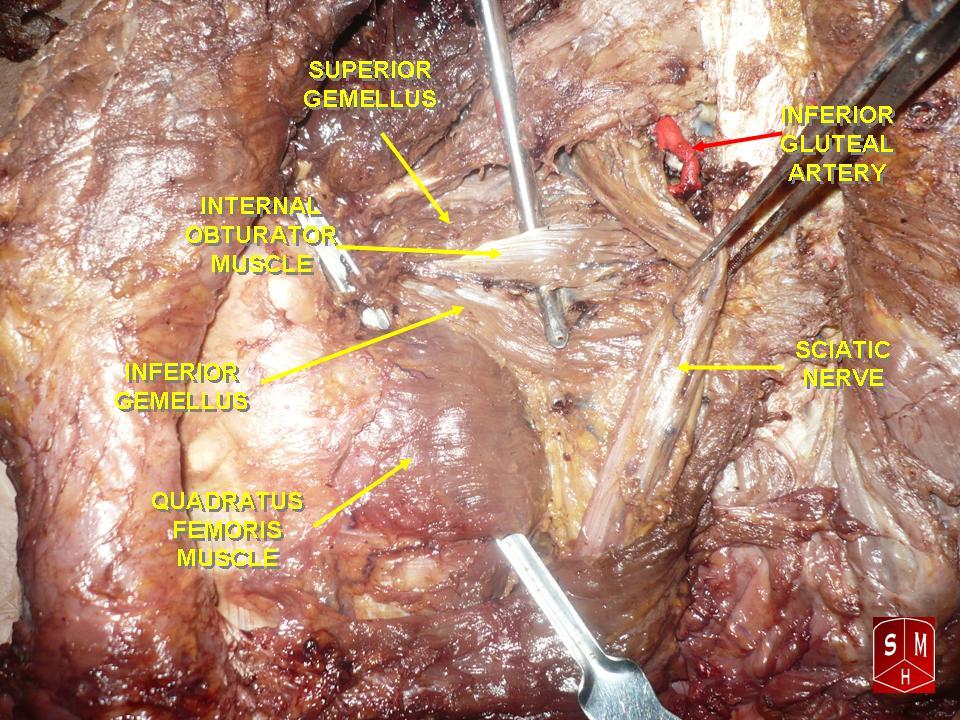
Quadratus Femoris
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. The quadratus femoris is used in Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head. Course It originates on the lateral border of the ischial tuberosity of the ischium of the pelvis. From there, it passes laterally to its insertion on the posterior side of the head of the femur: the quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest and along the quadrate line, the vertical line which runs downward to bisect the lesser trochanter on the medial side of the femur. Along its course, quadratus is aligned edge to edge with the inferior gemellus above and the adductor magnus below, so that its upper and lower borders run horizontal and parallel. At its origin, the upper margin of the adductor magnus is separated from it by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischial Tuberosity
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones, or as a pair the sitting bones, is a large posterior bony protuberance on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks the lateral boundary of the pelvic outlet. When sitting, the weight is frequently placed upon the ischial tuberosity. The gluteus maximus provides cover in the upright posture, but leaves it free in the seated position.Platzer (2004), p 236 The distance between a cyclist's ischial tuberosities is one of the factors in the choice of a bicycle saddle. Divisions The tuberosity is divided into two portions: a lower, rough, somewhat triangular part, and an upper, smooth, quadrilateral portion. * The ''lower portion'' is subdivided by a prominent longitudinal ridge, passing from base to apex, into two parts: ** The outer gives attachment to the adductor magnus ** The inner to the sacrotuberous ligament * The ''upper portion'' is subdiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertrochanteric Crest
The intertrochanteric crest is a prominent bony ridge upon the posterior surface of the femur at the junction of the neck and the shaft of the femur. It extends between the greater trochanter superiorly, and the lesser trochanter inferiorly. Anatomy The intertrochanteric crest is a prominent smooth bony ridge upon the posterior surface of the femur at the junction of the neck and the shaft of the femur; together with the intertrochanteric line on the anterior side of the head, the intertrochanteric crest marks the transition between the femoral neck and shaft. The intertrochanteric crest extends between the greater trochanter superiorly, and the lesser trochanter inferiorly; it passes obliquely inferomedially from the greater trochanter to the lesser trochanter. An elevation between the middle and proximal third of the crest is known as the quadrate tubercle. Relations The distal capsular attachment on the femur follows the shape of the irregular rim between the head and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip Muscles
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest, and lateral to the obturator foramen, with muscle tendons and soft tissues overlying the greater trochanter of the femur. In adults, the three pelvic bones ( ilium, ischium and pubis) have fused into one hip bone, which forms the superomedial/deep wall of the hip region. The hip joint, scientifically referred to as the acetabulofemoral joint (''art. coxae''), is the ball-and-socket joint between the pelvic acetabulum and the femoral head. Its primary function is to support the weight of the torso in both static (e.g. standing) and dynamic (e.g. walking or running) postures. The hip joints h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thieme Medical Publishers
Thieme Medical Publishers is a German academic publishing, medical and science publisher in the Thieme Publishing Group. It produces professional journals, textbooks, atlases, monographs and reference books in both German and English covering a variety of medical specialties, including neurosurgery, orthopaedics, endocrinology, urology, radiology, anatomy, chemistry, otolaryngology, ophthalmology, audiology and speech-language pathology, complementary medicine, complementary and alternative medicine. Thieme has more than 1,000 employees and maintains offices in seven cities worldwide, including New York City, Beijing, Delhi, Stuttgart, and three other cities in Germany. History Georg Thieme Verlag was founded in 1886 in Leipzig, Germany, by Georg Thieme when he was 26 years old. Thieme remains privately held and family-owned. The company received some early success in 1896 by publishing Wilhelm Röntgen's famous picture of his wife's hand in what is still one of Thieme's and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratus Femoris Muscle
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. The quadratus femoris is used in Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head. Course It originates on the lateral border of the ischial tuberosity of the ischium of the pelvis. From there, it passes laterally to its insertion on the posterior side of the head of the femur: the quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest and along the quadrate line, the vertical line which runs downward to bisect the lesser trochanter on the medial side of the femur. Along its course, quadratus is aligned edge to edge with the inferior gemellus above and the adductor magnus below, so that its upper and lower borders run horizontal and parallel. At its origin, the upper margin of the adductor magnus is separated from it b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischiofemoral Ligament
The ischiofemoral ligament (ischiocapsular ligament or ischiocapsular band) consists of a triangular band of strong fibers on the posterior side of the hip joint. It is one of the four ligaments that reinforce the hip joint. It attaches to the posterior surface of the acetabular rim and acetabular labrum, and extends around the circumference of the joint to insert on the anterior aspect of the femur. The ischiofemoral ligament limits the internal rotation and adduction of the hip when it is in a flexed position. Some deeper fibres of the ligament are continuous with the fibres of the zona orbicularis The zona orbicularis or annular ligament is a ligament on the neck of the femur formed by the circular fibers of the articular capsule of the hip joint In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hi ... of the capsule. This ligament is less well-defined than the other two capsular ligaments of the hip joint. Function Studies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendinitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tennis elbow, golfer's elbow), wrist, hip, knee ( jumper's knee, popliteus tendinopathy), or ankle ( Achilles tendinitis). Causes may include an injury or repetitive activities. Less common causes include infection, arthritis, gout, thyroid disease, diabetes and the use of quinolone antibiotic medicines. Groups at risk include people who do manual labor, musicians, and athletes. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms, examination, and occasionally medical imaging. A few weeks following an injury little inflammation remains, with the underlying problem related to weak or disrupted tendon fibrils. Treatment may include rest, NSAIDs, splinting, and physiotherapy. Less commonly steroid injections or surgery may be done. About 80% of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bursa (anatomy)
A synovial bursa, usually simply bursa (: bursae or bursas), is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body. Structure Based on location, there are three types of bursa: subcutaneous, submuscular and subtendinous. A subcutaneous bursa is located between the skin and an underlying bone. It allows skin to move smoothly over the bone. Examples include the prepatellar bursa located over the kneecap and the olecranon bursa at the tip of the elbow. A submuscular bursa is found between a muscle and an underlying bone, or between adjacent muscles. These prevent rubbing of the muscle during movements. A large submuscular bursa, the trochanteric bursa, is found at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Femoral Circumflex
The medial circumflex femoral artery (internal circumflex artery, medial femoral circumflex artery) is an artery in the upper thigh that arises from the profunda femoris artery''.'' It supplies arterial blood to several muscles in the region, as well as the femoral head and neck. Damage to the artery following a femoral neck fracture may lead to avascular necrosis (ischemic) of the femoral neck/head. Structure Origin The medial femoral circumflex artery arises from the posteromedial aspect of the profunda femoris artery''.'' The medial femoral circumflex artery may occasionally arise directly from the femoral artery. Course and relations It winds around the medial side of the femur to pass along the posterior aspect of the femur. It first passes between the pectineus and the iliopsoas muscles, then between the obturator externus and the adductor brevis muscles. Branches At the upper border of the adductor brevis it gives off two branches: * The '' ascending branch'' * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Magnus
The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh. It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium) is called the pubofemoral portion, adductor portion, or adductor minimus, and the portion arising from the tuberosity of the ischium is called the ischiocondylar portion, extensor portion, or "hamstring portion". Due to its common embryonic origin, innervation, and action the ischiocondylar portion (or hamstring portion) is often considered part of the hamstring group of muscles. The ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus is considered a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh while the pubofemoral portion of the adductor magnus is considered a muscle of the medial compartment. Structure Pubofemoral (adductor) portion Those fibers which arise from the ramus of the pubis are short, horizontal in direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Magnus Muscle
The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh. It consists of two parts. The portion which arises from the ischiopubic ramus (a small part of the inferior ramus of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium) is called the pubofemoral portion, adductor portion, or adductor minimus, and the portion arising from the tuberosity of the ischium is called the ischiocondylar portion, extensor portion, or "hamstring portion". Due to its common embryonic origin, innervation, and action the ischiocondylar portion (or hamstring portion) is often considered part of the hamstring group of muscles. The ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus is considered a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh while the pubofemoral portion of the adductor magnus is considered a muscle of the medial compartment. Structure Pubofemoral (adductor) portion Those fibers which arise from the ramus of the pubis are short, horizontal in directio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |