|
Pyruvate Synthase
In enzymology, a pyruvate synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. It is also called pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR). The relevant equilibrium catalysed by PFOR is: :pyruvate + CoA + oxidized ferredoxin \rightleftharpoons acetyl-CoA + CO2 + reduced ferredoxin The 3 substrates of this enzyme are pyruvate, CoA, and oxidized ferredoxin, whereas its 3 products are acetyl-CoA, CO2, and reduced ferredoxin. Function This enzyme participates in 4 metabolic pathways: pyruvate metabolism, propanoate metabolism, butanoate metabolism, and reductive carboxylate cycle ( fixation). Its major role is the extraction of reducing equivalents by the decarboxylation. In aerobic organisms, this conversion is catalysed by pyruvate dehydrogenase, also uses thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) but relies on lipoate as the electron acceptor. Unlike the aerobic enzyme complex PFOR transfers reducing equivalents to flavins or iron-sulflur clusters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
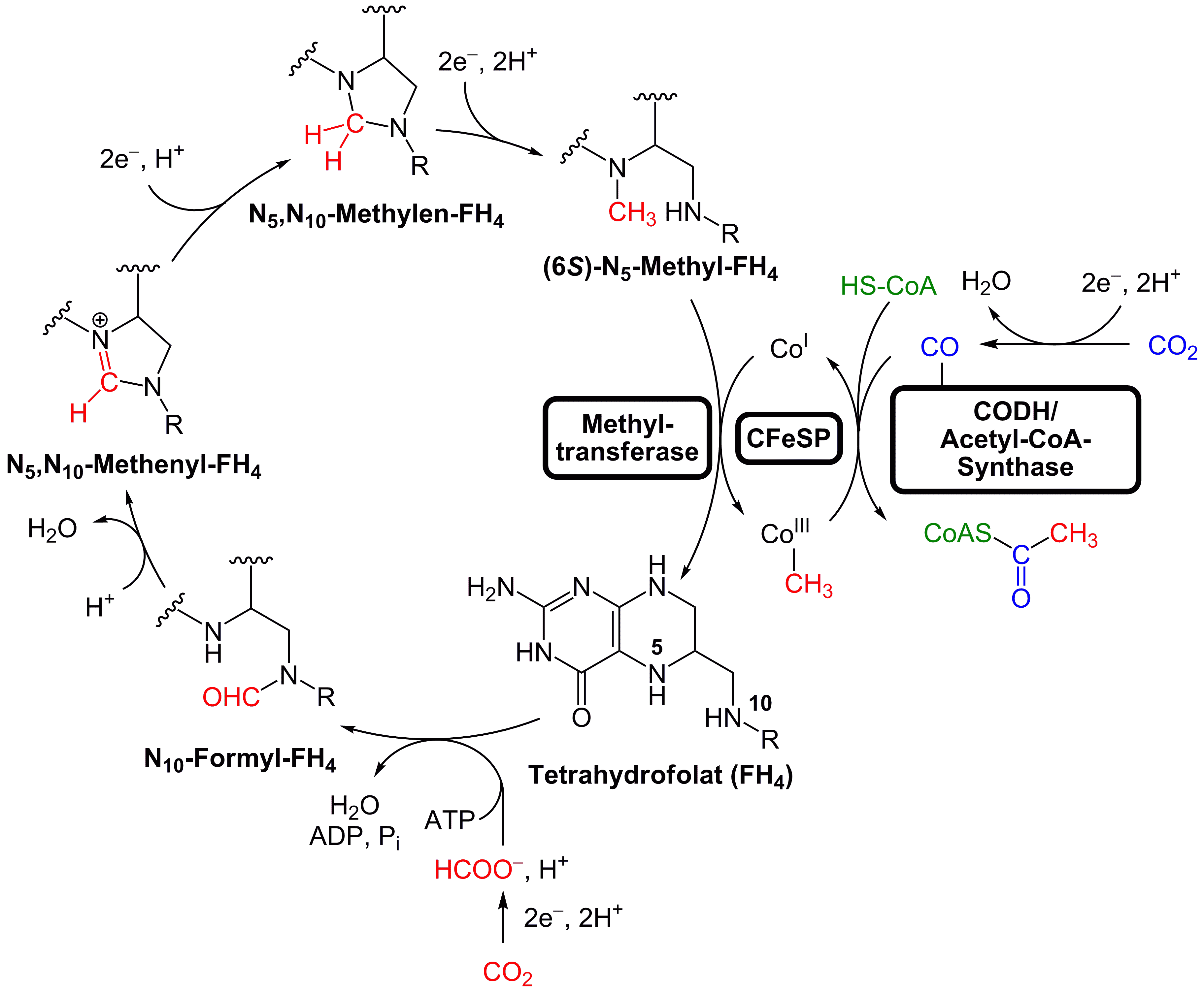
Wood–Ljungdahl Pathway
The Wood–Ljungdahl pathway is a set of biochemical reactions used by some bacteria. It is also known as the reductive acetyl-coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA) pathway. This pathway enables these organisms to use hydrogen as an electron donor, and carbon dioxide as an electron acceptor and as a building block for biosynthesis. In this pathway carbon dioxide is reduced to carbon monoxide and formic acid or directly into a formyl group, the formyl group is reduced to a methyl group and then combined with the carbon monoxide and Coenzyme A to produce acetyl-CoA. Two specific enzymes participate on the carbon monoxide side of the pathway: CO Dehydrogenase and acetyl-CoA synthase. The former catalyzes the reduction of the CO2 and the latter combines the resulting CO with a methyl group to give acetyl-CoA. Some anaerobic bacteria use the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway in reverse to break down acetate. For example, Sulfate reducing bacteria oxidize acetate completely to CO2 and H2 coupled w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
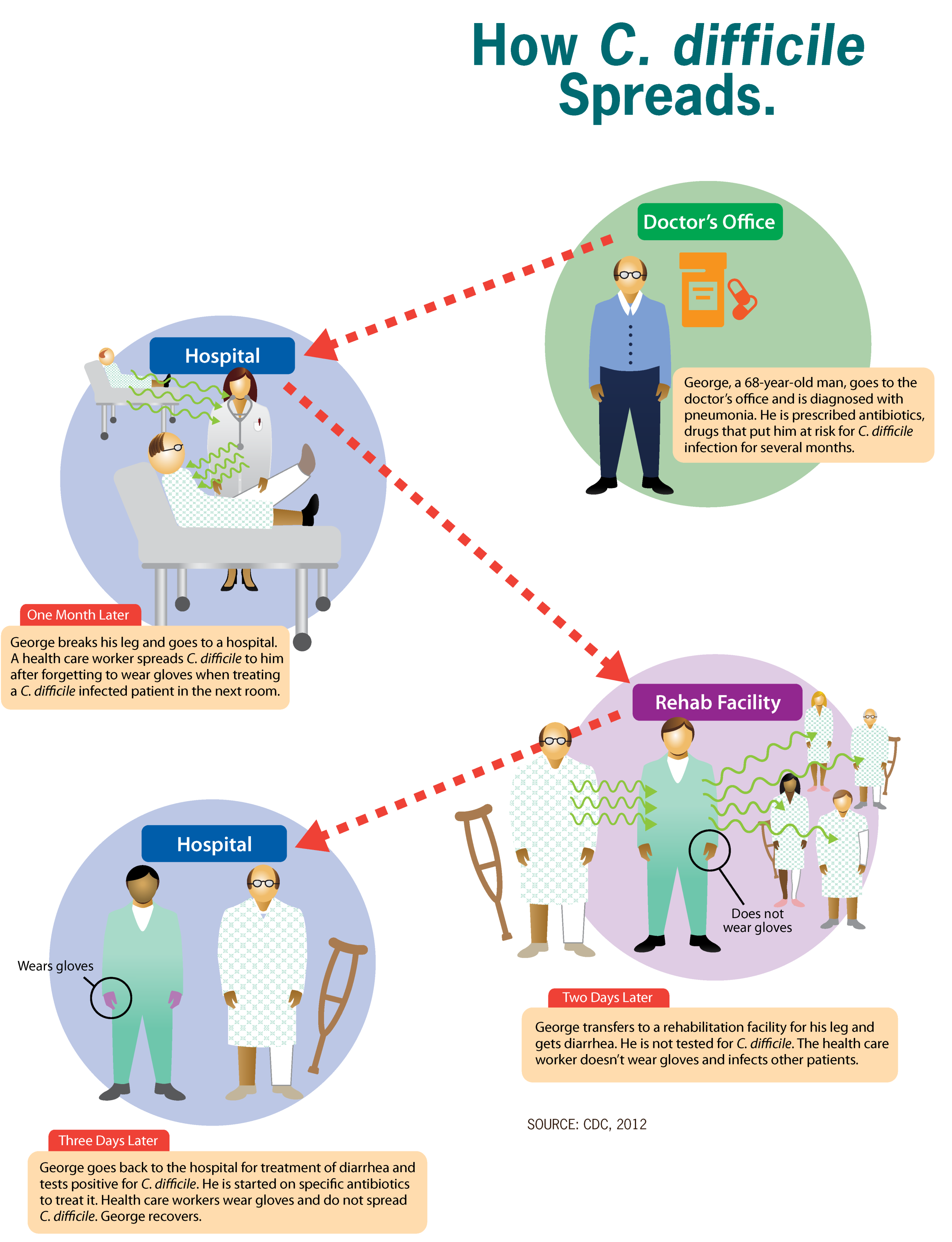
Clostridium Difficile Colitis
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection (CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics can contribute to detrimental changes in gut microbiota; specifically, they decrease short-chain fatty acid absorption which results in osmotic, or watery, diarrhea. Complications may include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, perforation of the colon, and sepsis. ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection is spread by bacterial spores found within feces. Surfaces may become contaminated with the spores with further spread occurring via the hands of healthcare workers. Risk factors for infection include antibiotic or proton pump inhibitor use, hospitalization, other health problems, and older age. Diagnosis is by stool culture or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tizoxanide
Tizoxanide, also known as desacetyl-nitazoxanide, is a thiazolide and an antiparasitic agent that occurs as a metabolite of nitazoxanide Nitazoxanide, sold under the brand name Alinia among others, is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and broad-spectrum antiviral medication that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections. It is ind ... in humans through hydrolysis. Tizoxanide may undergo further metabolism via conjugation into tizoxanide glucuronide. References Nitrothiazoles Salicylamides Human drug metabolites {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by '' Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tract in both immunocompetent (i.e., individuals with a normal functioning immune system) and immunocompromised (e.g., persons with HIV/AIDS or autoimmune disorders) individuals, resulting in watery diarrhea with or without an unexplained cough. In immunosuppressed individuals, the symptoms are particularly severe and can be fatal. It is primarily spread through the fecal-oral route, often through contaminated water; recent evidence suggests that it can also be transmitted via fomites contaminated with respiratory secretions. ''Cryptosporidium'' is commonly isolated in HIV-positive patients presenting with diarrhea. Despite not being identified until 1976, it is one of the most common waterborne diseases and is found worldwide. The inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
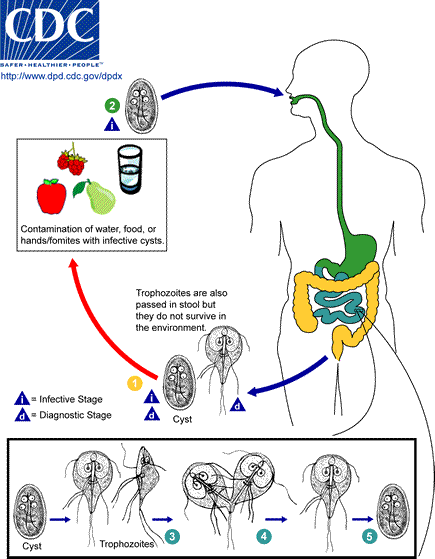
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''). Infected individuals who experience symptoms (about 10% have no symptoms) may have diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Less common symptoms include vomiting and blood in the stool. Symptoms usually begin 1 to 3 weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer. Giardiasis usually spreads when ''Giardia duodenalis'' cysts within feces contaminate food or water that is later consumed orally. The disease can also spread between people and through other animals. Cysts may survive for nearly three months in cold water. Giardiasis is diagnosed via stool tests. Prevention may be improved through proper hygiene practices. Asymptomatic cases often do not need treatment. When symptoms are present, treatment is typically provided with either tinidazole or metronidazole. Infection may cause a person to become lactose intolerant, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad-spectrum Antiparasitic
Antiparasitics are a class of medications which are indicated for the treatment of parasitic diseases, such as those caused by helminths, amoeba, ectoparasites, parasitic fungi, and protozoa, among others. Antiparasitics target the parasitic agents of the infections by destroying them or inhibiting their growth; they are usually effective against a limited number of parasites within a particular class. Antiparasitics are one of the antimicrobial drugs which include antibiotics that target bacteria, and antifungals that target fungi. They may be administered orally, intravenously or topically. Broad-Spectrum antiparasitics, analogous to broad-spectrum antibiotics for bacteria, are antiparasitic drugs with efficacy in treating a wide range of parasitic infections caused by parasites from different classes. Types Broad-spectrum * Nitazoxanide Antiprotozoals * Melarsoprol (for treatment of sleeping sickness caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'') * Eflornithine (for sleeping sickness) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitazoxanide
Nitazoxanide, sold under the brand name Alinia among others, is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and broad-spectrum antiviral medication that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections. It is indicated for the treatment of infection by ''Cryptosporidium parvum'' and ''Giardia lamblia'' in immunocompetent individuals and has been repurposed for the treatment of influenza. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to have ''in vitro'' antiparasitic activity and clinical treatment efficacy for infections caused by other protozoa and helminths; evidence suggested that it possesses efficacy in treating a number of viral infections as well. Chemically, nitazoxanide is the prototype member of the thiazolides, a class of drugs which are synthetic nitrothiazolyl- salicylamide derivatives with antiparasitic and antiviral activity. Tizoxanide, an active metabolite of nitazoxanide in humans, is also an antiparasitic drug of the thiazolide class. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
This article lists enzymes by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. * List of EC numbers (EC 5) * List of EC numbers (EC 6) :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase **Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase **L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase **HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * :EC 1.1.4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix. in Membranome database Reactions For e ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |