|
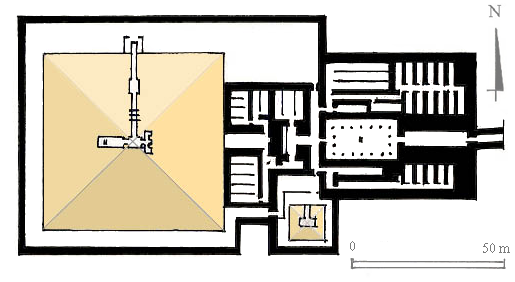
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas ( Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the '' Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Sekhemket and Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was constructed to provide access to the pyramid site. The causeway had elaborately decorated walls covered with a roof which had a slit in one section allowing light t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unas
Unas or Wenis, also spelled Unis ( egy, wnjs, hellenized form Oenas or Onnos), was a pharaoh, the ninth and last ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Unas reigned for 15 to 30 years in the mid- 24th century BC (circa 2345–2315 BC), succeeding Djedkare Isesi, who might have been his father. Little is known of Unas' activities during his reign, which was a time of economic decline. Egypt maintained trade relations with the Levantine coast and Nubia, and military action may have taken place in southern Canaan. The growth and decentralization of the administration in conjunction with the lessening of the king's power continued under Unas, ultimately contributing to the collapse of the Old Kingdom some 200 years later. Unas built a pyramid in Saqqara, the smallest of the royal pyramids completed during the Old Kingdom. The accompanying mortuary complex with its high and valley temples linked by a causeway was lavishly decorated with painted reliefs, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebra (Pharaoh)
Nebra or Raneb is the Horus name of the second early Egyptian king of the 2nd Dynasty. The exact length of his reign is unknown since the Turin canon is damaged and the year accounts are lost.Alan H. Gardiner: ''The royal canon of Turin''. Griffith Institute of Oxford, Oxford (UK) 1997, ; page 15 & Table I. Manetho suggests that Nebra's reign lasted 39 years, but Egyptologists question Manetho's view as a misinterpretation or exaggeration of information that was available to him. They credit Nebra with either a 10- or 14-year rule. Attestations Nebra's name appears on several stone vessels, mostly made of schist, alabaster and marble. Most of the bowls were found at Abydos, Giza and Saqqara. The inscriptions contain depictions of cultic buildings such as the ''Ka''-house, depictions of deities such as Bastet, Neith and Seth and also the mentionings of cultic feasts. All found objects present Nebra's name either together with that of his predecessor Hotepsekhemwy or wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom. It comprises the Seventh (although this is mostly considered spurious by Egyptologists), Eighth, Ninth, Tenth, and part of the Eleventh Dynasties. The concept of a "First Intermediate Period" was coined in 1926 by Egyptologists Georg Steindorff and Henri Frankfort. Very little monumental evidence survives from this period, especially from the beginning of the era. The First Intermediate Period was a dynamic time in which rule of Egypt was roughly equally divided between two competing power bases. One of the bases was at Heracleopolis in Lower Egypt, a city just south of the Faiyum region, and the other was at Thebes, in Upper Egypt. It is believed that during that time, temples were pillaged and violated, artwork was vandalized, and the statues of kings were broken or destroyed as a result of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Merenre
The pyramid of Pharaoh Merenre was constructed for Merenre Nemtyemsaf I during the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt at Saqqara to the south-west of the pyramid of Pepi I and a similar distance to the pyramid of Djedkare.Kinnaer, Jacques"The Pyramid of Merenre I".Accessed September 20, 2008. Its ancient name was "Merenre's beauty shines" or perhaps "The Perfection of Merenre Appears". Accessed September 20, 2008. Today it consists mostly of ruins;Winston, Alan Accessed September 20, 2008. it is hard to get to and is not open to the public. Accessed September 20, 2008. The pyramid was bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Pepi I
The pyramid of Pepi I (in ancient Egyptian Men-nefer-Pepi meaning Pepi's splendour is enduring) is the pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Pepi I of the Sixth Dynasty in the 24th or 23rd century BC. The complex gave its name to the capital city of Egypt, Memphis. As in the pyramids of his predecessors, Pepi I's substructure was filled with vertical columns of hieroglyphic texts, Pyramid Texts. It was in Pepi I's pyramid that these texts were initially discovered in 1880 by Gaston Maspero, though they originated in the pyramid of Unas. The corpus of Pepi I's texts is also the largest from the Old Kingdom, comprising 2,263 columns and lines of hieroglyphs. Pepi I sited his pyramid complex in South Saqqara an approximate north of Djedkare Isesi's pyramid. It is unclear why Pepi I relocated to South Saqqara. Perhaps Pepi I had moved the royal palace south and away from the city, or perhaps no viable sites were left in North and Central Saqqara after Teti built his p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaston Maspero
Sir Gaston Camille Charles Maspero (23 June 1846 – 30 June 1916) was a French Egyptologist known for popularizing the term "Sea Peoples" in an 1881 paper. Maspero's son, Henri Maspero, became a notable sinologist and scholar of East Asia. Early life Gaston Maspero was born in Paris in 1846 to Adela Evelina Maspero, born in Milan in 1822, daughter of a Milanese printer, and of an unnamed father, but identified by family tradition with Camillo Marsuzi de Aguirre, Italian revolutionary on the run. He was educated at the Lycee Louis-le-Grand, Jesuit boarding school and university at the ''École normale''. While at school he showed a special taste for history and became interested in Egypt following a visit to the Egyptian galleries of the Louvre at the age of fourteen. At university he excelled in Sanskrit as well as hieroglyphics. It was while Maspero was in final year at the ''École normale'' in 1867 that friends mentioned his skills at reading hieroglyphics to Egyptolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resistant hilltops. The nearly pure silica co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djedkare Isesi
Djedkare Isesi (known in Greek as Tancheres) was a pharaoh, the eighth and penultimate ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt in the late 25th century to mid- 24th century BC, during the Old Kingdom. Djedkare succeeded Menkauhor Kaiu and was in turn succeeded by Unas. His relationship to both of these pharaohs remain uncertain, although it is often conjectured that Unas was Djedkare's son, owing to the smooth transition between the two. Djedkare likely enjoyed a reign of more than 40 years, which heralded a new period in the history of the Old Kingdom. Breaking with a tradition followed by his predecessors since the time of Userkaf, Djedkare did not build a temple to the sun god Ra, possibly reflecting the rise of Osiris in the Egyptian pantheon. More significantly, Djedkare effected comprehensive reforms of the Egyptian state administration, the first undertaken since the inception of the system of ranking titles. He also reorganised the funerary cults of his forebears buri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
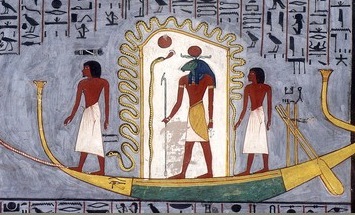
Solar Barque
Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet ( egy, mꜥnḏt) or the Boat of Millions of Years ( egy, wjꜣ-n-ḥḥw), and the vessel he used during the night was known as the Mesektet ( egy, msktt). Ra was said to travel through the sky on the barge, providing light to the world. Each twelfth of his journey formed one of the twelve Egyptian hours of the day, each overseen by a protective deity. Ra then rode the barque through the underworld, with each hour of the night considered a gate overseen by twelve more protective deities. Passing through all of these while fending off various destructive monsters, Ra reappeared each day on the eastern horizon. He was said to travel across the sky in the Mandjet Barque through the hours of the day, and then switch to the Mesektet Barque to descend into the underworld for the hours of the night. The progress of Ra upon the Mandje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teti
Teti, less commonly known as Othoes, sometimes also Tata, Atat, or Athath in outdated sources, was the first king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. He was buried at Saqqara. The exact length of his reign has been destroyed on the Turin King List but is believed to have been about 12 years. Biography Teti had several wives: * Iput, the daughter of Unas, the last king of the Fifth dynasty. Iput was the mother of Pepi I. *Khuit, who may have been the mother of Userkare (according to Jonosi and Callender)Miroslav Verner, The Pyramids,1994 *Khentkaus IV *Neith Teti is known to have had several children. He was the father of at least three sons and probably ten daughters. Of the sons, two are well attested, a third one is likely: * Pepi I * Tetiankhkem * Nebkauhor, with the name of Idu, "king’s eldest son of his body", buried in the mastaba of Vizier Akhethetep/Hemi, buried in a fallen Vizier’s tomb, within the funerary complex of his maternal grandfather According to N. Kanawati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortuary Temple
Mortuary temples (or funerary temples) were temples that were erected adjacent to, or in the vicinity of, royal tombs in Ancient Egypt. The temples were designed to commemorate the reign of the Pharaoh under whom they were constructed, as well as for use by the king's cult after death. Some refer to these temples as a cenotaph. These temples were also used to make sacrifices of food and animals. A mortuary temple is categorized as a monument. History Mortuary temples were built around pyramids in the Old Kingdom and Middle Kingdom. However, once the New Kingdom pharaohs began constructing tombs in the Valley of the Kings, they built their mortuary temples separately. These New Kingdom temples were called "mansions of millions of years" by the Egyptians. The mortuary temples were also used as a resting place for the boat of Amun at the time of the Beautiful Festival of the Valley, during which the cult statue of the deity visited the west bank of Thebes. It was a part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Period Of Ancient Egypt
The Late Period of ancient Egypt refers to the last flowering of native Egyptian rulers after the Third Intermediate Period in the 26th Saite Dynasty founded by Psamtik I, but includes the time of Achaemenid Persian rule over Egypt after the conquest by Cambyses II in 525 BC as well. The Late Period existed from 664 BC until 332 BC, following a period of foreign rule by the Nubian 25th Dynasty and beginning with a short period of Neo-Assyrian suzerainty, with Psamtik I initially ruling as their vassal. The period ended with the conquests of the Persian Empire by Alexander the Great and establishment of the Ptolemaic dynasty by his general Ptolemy I Soter, one of the Hellenistic diadochi from Macedon in northern Greece. With the Macedonian Greek conquest in the latter half of the 4th century BC, the age of Hellenistic Egypt began. History 26th Dynasty The Twenty-Sixth Dynasty, also known as the Saite Dynasty after its seat of power the city of Sais, reigned from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_032007_27_det.jpg)