|
Pulse Generator
A pulse generator is either an electronic circuit ''or'' a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. Pulse generators are used primarily for working with digital circuits; related function generators are used primarily for analog circuits. Bench pulse generators Simple bench pulse generators usually allow control of the pulse repetition rate (frequency), pulse width, delay with respect to an internal or external trigger and the high- and low-voltage levels of the pulses. More sophisticated pulse generators may allow control over the rise time and fall time of the pulses. Pulse generators are available for generating output pulses having widths (duration) ranging from minutes to under 1 picosecond. Pulse generators are generally voltage sources, with true current pulse generators being available only from a few suppliers. Pulse generators may use digital techniques, analog techniques, or a combination of both techniques to form the output puls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Generators
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck (carotid artery), wrist (radial artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee (popliteal artery), near the ankle joint (posterior tibial artery), and on foot (dorsalis pedis artery). Pulse (or the count of arterial pulse per minute) is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart (usually the ring finger) is used to nullify the effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet, such as letters or digits. An example is a text document, which consists of a string of alphanumeric characters. The most common form of digital data in modern information systems is ''binary data'', which is represented by a string of binary digits (bits) each of which can have one of two values, either 0 or 1. Digital data can be contrasted with ''analog data'', which is represented by a value from a continuous range of real numbers. Analog data is transmitted by an analog signal, which not only takes on continuous values but can vary continuously with time, a continuous real-valued function of time. An example is the air pressure variation in a sound wave. The word ''digital'' comes from the same source as the words digit and ''digitus'' (the Latin word for ''finge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
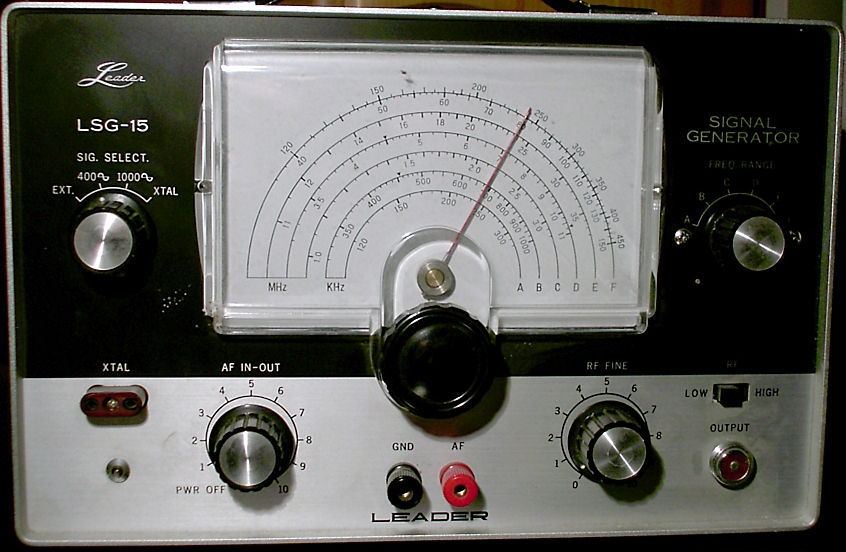
Signal Generator
A signal generator is one of a class of electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well. There are many different types of signal generators with different purposes and applications and at varying levels of expense. These types include function generators, RF and microwave signal generators, pitch generators, arbitrary waveform generators, digital pattern generators, and frequency generators. In general, no device is suitable for all possible applications. A signal generator may be as simple as an oscillator with calibrated frequency and amplitude. More general-purpose signal generators allow control of all the characteristics of a signal. Modern general-purpose signal generators will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Automatic Cascode Exchange
Rapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep stream gradient, gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. Rapids are hydrology, hydrological features between a ''run'' (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a ''waterfall#Types, cascade''. Rapids are characterized by the river becoming shallower with some Rock (geology), rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white color, forming what is called "whitewater". Rapids occur where the stream bed, bed material is highly resistant to the erosive power of the stream in comparison with the bed downstream of the rapids. Very young streams flowing across solid rock may be rapids for much of their length. Rapids cause water aeration of the stream or river, resulting in better water quality. Rapids are categorized in International Scale of River Difficulty, classes, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step Recovery Diode
In electronics, a step recovery diode (SRD, snap-off diode or charge-storage diode or memory varactor) is a semiconductor junction diode with the ability to generate extremely short pulses. It has a variety of uses in microwave (MHz to GHz range) electronics as pulse generator or parametric amplifier. When diodes switch from forward conduction to reverse cut-off, a reverse current flows briefly as stored charge is removed. It is the abruptness with which this reverse current ceases which characterises the step recovery diode. Historical note The first published paper on the SRD is : the authors start the brief survey stating that "the recovery characteristics of certain types of pn-junction diodes exhibit a discontinuity which may be used to advantage for the generation of harmonics or for the production of millimicrosecond pulses". They also refer that they first observed this phenomenon in February, 1959 Operating the SRD Physical principles The main phenomenon use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Delay Generator
A digital delay generator (also known as digital-to-time converter) is a piece of electronic test equipment that provides precise delays for triggering, syncing, delaying, and gating events. These generators are used in many experiments, controls, and processes where electronic timing of a single event or multiple events to a standard timing reference is needed. The digital delay generator may initiate a sequence of events or be triggered by an event. What differentiates it from ordinary electronic timing is the synchronicity of its outputs to each other and the initiating event. A time-to-digital converter does the inverse function. Equipment The digital delay generator is similar to a pulse generator in function, but the timing resolution is much finer, and the delay and width jitter much less. Some manufacturers, calling their units "digital delay and pulse generators", have added independent amplitude polarity and level control to each of their outputs in addition to delay a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Adjusting
The Amplitude adjusting (also referred to as Amplitude control) enables the power control of electric loads, which are operated with AC voltage. A representative application is the heating control of industrial high temperature furnaces. Functionality Contrary to the conventional phase angle or full wave control, during amplitude control only the Amplitude of the sinusoidal supply current is changed. The level of the amplitude only depends on the consumed power. The sinus oscillation does not change. Because current and voltage are in phase, only real power is taken from the mains for amplitude control. So the current consumption from the mains is considerably lower than the current consumption in case of phase-angle operation. Advantages The continuous current flow causes a mild operation of the used heater elements and consequently significant longer lifetimes are realized. Depending on the ambient conditions the lifetime can be twice as long. Especially the surface d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Wave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions between minimum and maximum are instantaneous. The square wave is a special case of a pulse wave which allows arbitrary durations at minimum and maximum amplitudes. The ratio of the high period to the total period of a pulse wave is called the duty cycle. A true square wave has a 50% duty cycle (equal high and low periods). Square waves are often encountered in electronics and signal processing, particularly digital electronics and digital signal processing. Its stochastic counterpart is a two-state trajectory. Origin and uses Square waves are universally encountered in digital switching circuits and are naturally generated by binary (two-level) logic devices. Square waves are typically generated by metal–oxide–semiconductor fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
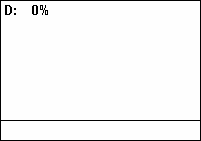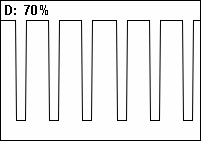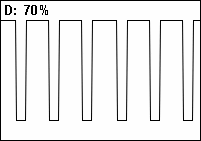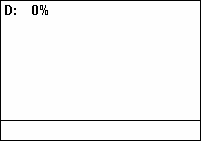
Duty Cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as: :D = \frac \times 100\% Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as: :D = \frac where D is the duty cycle, PW is the pulse width (pulse active time), and T is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period. Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron. The duty factor for periodic signal expresses the same notion, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Circuit
Analogue electronics ( en-US, analog electronics) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the el, word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional". Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Source
A voltage source is a two-terminal device which can maintain a fixed voltage. An ideal voltage source can maintain the fixed voltage independent of the load resistance or the output current. However, a real-world voltage source cannot supply unlimited current. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. Real-world sources of electrical energy, such as batteries and generators, can be modeled for analysis purposes as a combination of an ideal voltage source and additional combinations of impedance elements. Ideal voltage sources An ideal voltage source is a two-terminal device that maintains a fixed voltage drop across its terminals. It is often used as a mathematical abstraction that simplifies the analysis of real electric circuits. If the voltage across an ideal voltage source can be specified independently of any other variable in a circuit, it is called an independent voltage source. Conversely, if the voltage across an ideal voltage source is determined b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electrical circuit and to be referred to as ''electronic'', rather than ''electrical'', generally at least one active component must be present. The combination of components and wires allows various simple and complex operations to be performed: signals can be amplified, computations can be performed, and data can be moved from one place to another. Circuits can be constructed of discrete components connected by individual pieces of wire, but today it is much more common to create interconnections by photolithographic techniques on a laminated substrate (a printed circuit board or PCB) and solder the components to these interconnections to create a finished circuit. In an integrated circuit or IC, the components and interconnections are formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |