|
Pseudotyping
Pseudotyping is the process of producing viruses or viral vectors in combination with foreign viral envelope proteins. The result is a pseudotyped virus particle, also called a pseudovirus. With this method, the foreign viral envelope proteins can be used to alter host tropism or increase or decrease the stability of the virus particles. Pseudotyped particles do not carry the genetic material to produce additional viral envelope proteins, so the phenotypic changes cannot be passed on to progeny viral particles. In some cases, the inability to produce viral envelope proteins renders the pseudovirus replication incompetent. In this way, the properties of dangerous viruses can be studied in a lower risk setting. Pseudotyping allows one to control the expression of envelope proteins. A frequently used protein is the glycoprotein G (VSV-G) from the Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) which mediates entry via the LDL receptor. Envelope proteins incorporated into the pseudovirus allow th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies Lyssavirus
Rabies virus, scientific name ''Rabies lyssavirus'', is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in humans and animals. Rabies transmission can occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. ''Rabies lyssavirus'', like many rhabdoviruses, has an extremely wide host range. In the wild it has been found infecting many mammalian species, while in the laboratory it has been found that birds can be infected, as well as cell cultures from mammals, birds, reptiles and insects. Rabies is reported in more than 150 countries on all continents, with the exclusion of Antarctica. The main burden of disease is reported in Asia and Africa, but some cases have been reported also in Europe in the past 10 years, especially in returning travellers. ''Rabies lyssavirus'' has a cylindrical morphology and is a member of the ''Lyssavirus'' genus of the ''Rhabdoviridae'' family. These viruses are enveloped and have a single stranded RNA genome with negative-sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutralizing Antibody
A neutralizing antibody (NAb) is an antibody that defends a cell from a pathogen or infectious particle by neutralizing any effect it has biologically. Neutralization renders the particle no longer infectious or pathogenic. Neutralizing antibodies are part of the humoral response of the adaptive immune system against viruses, intracellular bacteria and microbial toxin. By binding specifically to surface structures (antigen) on an infectious particle, neutralizing antibodies prevent the particle from interacting with its host cells it might infect and destroy. Mechanism In order to enter cells, pathogens, such as circulating viral particles or extracellular bacteria, use molecules on their surfaces to interact with the cell surface receptors of their target cell which allows them to enter the cell and start their replication cycle. Neutralizing antibodies can inhibit infectivity by binding to the pathogen and blocking the molecules needed for cell entry. This can be due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evidence. Several methods can be used to detect antibodies and antigens, including ELISA, agglutination, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciferase
Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words '' luciferin'' and ''luciferase'', for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word ''lucifer'', meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (''lux)'' and "to bring or carry" (''ferre)''.Luciferases are widely used in biotechnology, for bioluminescence imaging microscopy and as reporter genes, for many of the same applications as fluorescent proteins. However, unlike fluorescent proteins, luciferases do not require an external light source, but do require addition of luciferin, the consumable substrate. Examples A variety of organisms regulate their light production using different luciferases in a variety of light-emitting reactions. The majority of studied luciferases have been found in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant Virus
A recombinant virus may occur naturally or be produced by recombining pieces of DNA using recombinant DNA technology. Synthetic recombination This may be used to produce viral vaccines or gene therapy vectors. Natural recombination The term is also used to refer to naturally occurring recombination between virus genomes in a cell infected by more than one virus strain. This occurs either by Homologous recombination of the nucleic acid strands or by reassortment of genomic segments. Both these and mutation within the virus have been suggested as ways in which influenza and other viruses evolve. An example of a recombinant virus is Western equine encephalitis virus (WEE), which is a recombinant virus between two other closely related yet distinct encephalitis viruses. In addition, reassortment is most important for pandemic influenza viruses. See also * Reassortment * Mutation In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
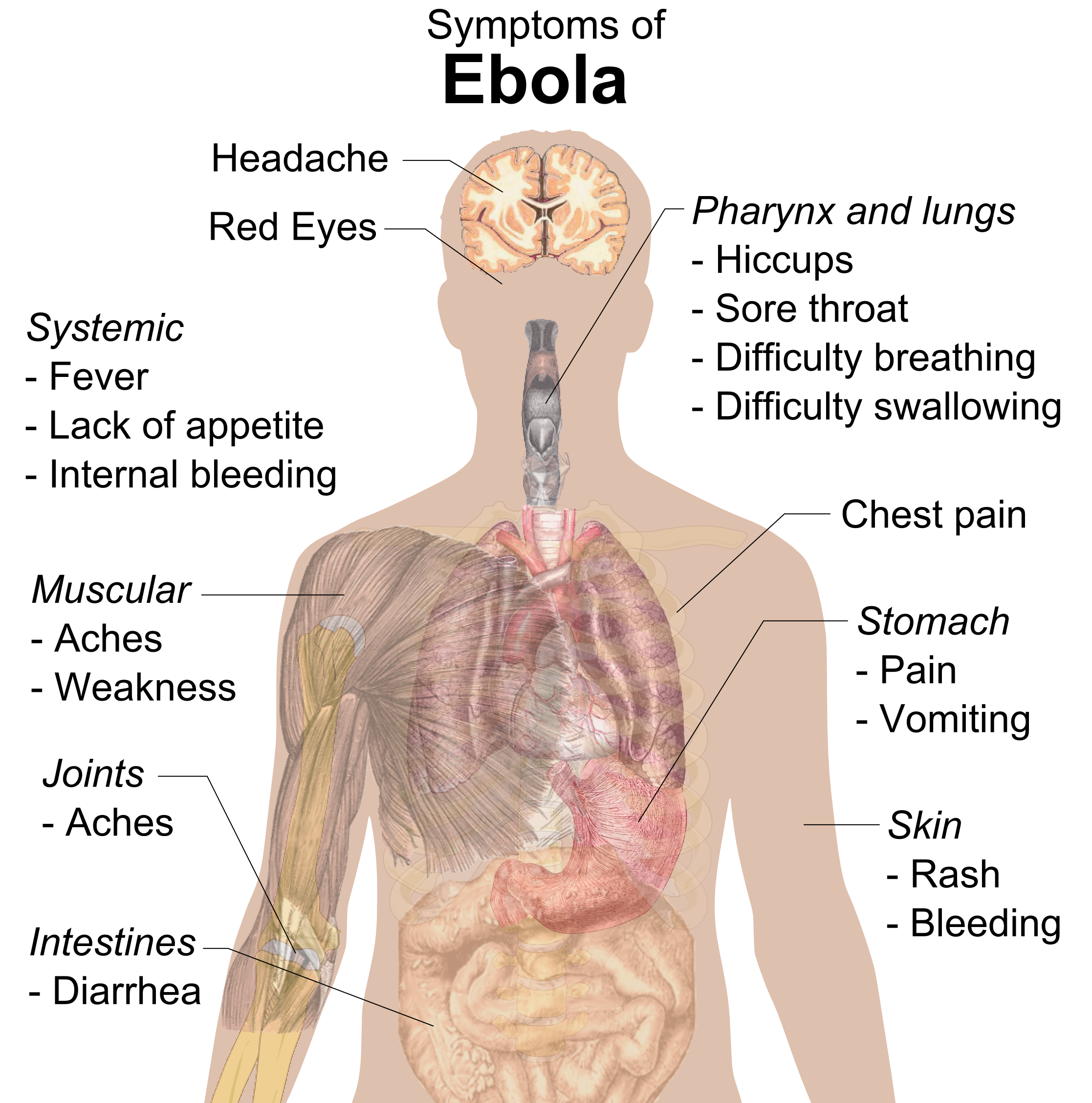
Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, Myalgia, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleeding, bleed both internal bleeding, internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to hypovolemic shock, shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Health Agency Of Canada
The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC; french: Agence de la santé publique du Canada, ASPC) is an agency of the Government of Canada that is responsible for public health, emergency preparedness and response, and infectious and chronic disease control and prevention. History The PHAC was formed because of a series of official inquiries about the SARS crisis in Canada which was particularly severe. For example, the province of Ontario inquiry and the National Advisory Committee on SARS and Public Health both recommended that a new organisation be formed. It was so instantiated, by Order in Council in 2004 under the Minister of State for Public Health (Canada) of the Martin government and subsequently by legislation that came into force on December 15, 2006 under the Harper government. It is part of the federal government's Health Portfolio (along with Health Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and other organizations). At the time of its creation in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RVSV-ZEBOV Vaccine
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus–Zaire Ebola virus (rVSV-ZEBOV), also known as Ebola Zaire vaccine live and sold under the brand name Ervebo, is an Ebola vaccine for adults that prevents Ebola caused by the Zaire ebolavirus. When used in ring vaccination, rVSV-ZEBOV has shown a high level of protection. Around half the people given the vaccine have mild to moderate adverse effects that include headache, fatigue, and muscle pain. rVSV-ZEBOV is a recombinant, replication-competent viral vector vaccine. It consists of rice-derived recombinant human serum albumin and live attenuated recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), which has been genetically engineered to express the main glycoprotein from the Zaire ebolavirus so as to provoke a neutralizing immune response to the Ebola virus. The vaccine was approved for medical use in the European Union and the United States in 2019. It was created by scientists at the National Microbiology Laboratory in Winnipeg, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, its closest known relatives, with which it forms a sister group, are the derived SAR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaire Ebolavirus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus '' Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus '' Ebolavirus'', family '' Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |