|
Pseudo-convex Function
In convex analysis and the calculus of variations, both branches of mathematics, a pseudoconvex function is a function that behaves like a convex function with respect to finding its local minima, but need not actually be convex. Informally, a differentiable function is pseudoconvex if it is increasing in any direction where it has a positive directional derivative. The property must hold in all of the function domain, and not only for nearby points. Formal definition Consider a differentiable function f:X \subseteq \mathbb^ \rightarrow \mathbb, defined on a (nonempty) convex open set X of the finite-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^n. This function is said to be pseudoconvex if the following property holds: Equivalently: Here \nabla f is the gradient of f, defined by: \nabla f = \left(\frac,\dots,\frac\right). Note that the definition may also be stated in terms of the directional derivative of f, in the direction given by the vector v=y-x. This is because, as f is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Analysis
Convex analysis is the branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex functions and convex sets, often with applications in convex minimization, a subdomain of optimization theory. Convex sets A subset C \subseteq X of some vector space X is if it satisfies any of the following equivalent conditions: #If 0 \leq r \leq 1 is real and x, y \in C then r x + (1 - r) y \in C. #If 0 is a if holds for any real 0 is called if \operatorname f \neq \varnothing and f(x) > -\infty for x \in \operatorname f. Alternatively, this means that there exists some x in the domain of f at which f(x) \in \mathbb and f is also equal to -\infty. In words, a function is if its domain is not empty, it never takes on the value -\infty, and it also is not identically equal to +\infty. If f : \mathbb^n \to \infty, \infty/math> is a proper convex function then there exist some vector b \in \mathbb^n and some r \in \mathbb such that :f(x) \geq x \cdot b - r for every x where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiconvex Optimality
In mathematics, a quasiconvex function is a real-valued function defined on an interval or on a convex subset of a real vector space such that the inverse image of any set of the form (-\infty,a) is a convex set. For a function of a single variable, along any stretch of the curve the highest point is one of the endpoints. The negative of a quasiconvex function is said to be quasiconcave. All convex functions are also quasiconvex, but not all quasiconvex functions are convex, so quasiconvexity is a generalization of convexity. ''Univariate'' unimodal functions are quasiconvex or quasiconcave, however this is not necessarily the case for functions with multiple arguments. For example, the 2-dimensional Rosenbrock function is unimodal but not quasiconvex and functions with star-convex sublevel sets can be unimodal without being quasiconvex. Definition and properties A function f:S \to \mathbb defined on a convex subset S of a real vector space is quasiconvex if for all x, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
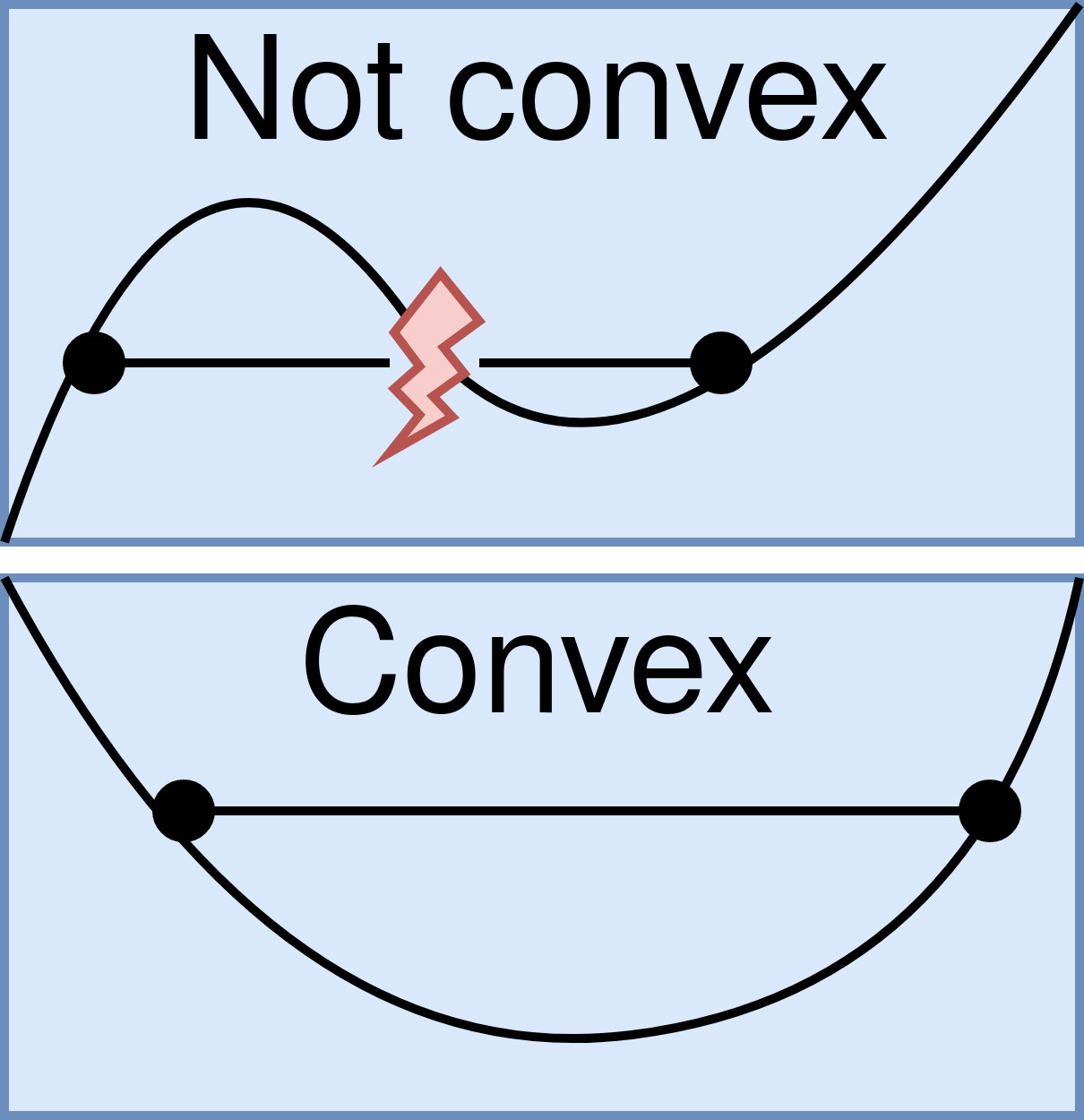
Convex Function
In mathematics, a real-valued function is called convex if the line segment between any two points on the graph of the function lies above the graph between the two points. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set. A twice-differentiable function of a single variable is convex if and only if its second derivative is nonnegative on its entire domain. Well-known examples of convex functions of a single variable include the quadratic function x^2 and the exponential function e^x. In simple terms, a convex function refers to a function whose graph is shaped like a cup \cup, while a concave function's graph is shaped like a cap \cap. Convex functions play an important role in many areas of mathematics. They are especially important in the study of optimization problems where they are distinguished by a number of convenient properties. For instance, a strictly convex function on an open set has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoconvexity
In mathematics, more precisely in the theory of functions of several complex variables, a pseudoconvex set is a special type of open set in the ''n''-dimensional complex space C''n''. Pseudoconvex sets are important, as they allow for classification of domains of holomorphy. Let :G\subset ^n be a domain, that is, an open connected subset. One says that G is ''pseudoconvex'' (or '' Hartogs pseudoconvex'') if there exists a continuous plurisubharmonic function \varphi on G such that the set :\ is a relatively compact subset of G for all real numbers x. In other words, a domain is pseudoconvex if G has a continuous plurisubharmonic exhaustion function. Every (geometrically) convex set is pseudoconvex. However, there are pseudoconvex domains which are not geometrically convex. When G has a C^2 (twice continuously differentiable) boundary, this notion is the same as Levi pseudoconvexity, which is easier to work with. More specifically, with a C^2 boundary, it can be sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIAM Review
Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) is a professional society dedicated to applied mathematics, computational science, and data science through research, publications, and community. SIAM is the world's largest scientific society devoted to applied mathematics, and roughly two-thirds of its membership resides within the United States. Founded in 1951, the organization began holding annual national meetings in 1954, and now hosts conferences, publishes books and scholarly journals, and engages in advocacy in issues of interest to its membership. Members include engineers, scientists, and mathematicians, both those employed in academia and those working in industry. The society supports educational institutions promoting applied mathematics. SIAM is one of the four member organizations of the Joint Policy Board for Mathematics. Membership Membership is open to both individuals and organizations. By the end of its first full year of operation, SIAM had 130 mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George B
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplex Algorithm
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm (or simplex method) is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The name of the algorithm is derived from the concept of a simplex and was suggested by T. S. Motzkin. Simplices are not actually used in the method, but one interpretation of it is that it operates on simplicial '' cones'', and these become proper simplices with an additional constraint. The simplicial cones in question are the corners (i.e., the neighborhoods of the vertices) of a geometric object called a polytope. The shape of this polytope is defined by the constraints applied to the objective function. History George Dantzig worked on planning methods for the US Army Air Force during World War II using a desk calculator. During 1946 his colleague challenged him to mechanize the planning process to distract him from taking another job. Dantzig formulated the problem as linear inequalities inspired by the work of Wassily Leontief, however, at tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Programming
Linear programming (LP), also called linear optimization, is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships. Linear programming is a special case of mathematical programming (also known as mathematical optimization). More formally, linear programming is a technique for the optimization of a linear objective function, subject to linear equality and linear inequality constraints. Its feasible region is a convex polytope, which is a set defined as the intersection of finitely many half spaces, each of which is defined by a linear inequality. Its objective function is a real-valued affine (linear) function defined on this polyhedron. A linear programming algorithm finds a point in the polytope where this function has the smallest (or largest) value if such a point exists. Linear programs are problems that can be expressed in canonical form as : \begin & \t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost" associated with the event. An optimization problem seeks to minimize a loss function. An objective function is either a loss function or its opposite (in specific domains, variously called a reward function, a profit function, a utility function, a fitness function, etc.), in which case it is to be maximized. The loss function could include terms from several levels of the hierarchy. In statistics, typically a loss function is used for parameter estimation, and the event in question is some function of the difference between estimated and true values for an instance of data. The concept, as old as Laplace, was reintroduced in statistics by Abraham Wald in the middle of the 20th century. In the context of economics, for example, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear-fractional Programming
In mathematical optimization, linear-fractional programming (LFP) is a generalization of linear programming (LP). Whereas the objective function in a linear program is a linear function, the objective function in a linear-fractional program is a ratio of two linear functions. A linear program can be regarded as a special case of a linear-fractional program in which the denominator is the constant function one. Relation to linear programming Both linear programming and linear-fractional programming represent optimization problems using linear equations and linear inequalities, which for each problem-instance define a feasible set. Fractional linear programs have a richer set of objective functions. Informally, linear programming computes a policy delivering the best outcome, such as maximum profit or lowest cost. In contrast, a linear-fractional programming is used to achieve the highest ''ratio'' of outcome to cost, the ratio representing the highest efficiency. For example, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdifferential
In mathematics, the subderivative, subgradient, and subdifferential generalize the derivative to convex functions which are not necessarily differentiable. Subderivatives arise in convex analysis, the study of convex functions, often in connection to convex optimization. Let f:I \to \mathbb be a real-valued convex function defined on an open interval of the real line. Such a function need not be differentiable at all points: For example, the absolute value function ''f''(''x'')=, ''x'', is nondifferentiable when ''x''=0. However, as seen in the graph on the right (where ''f(x)'' in blue has non-differentiable kinks similar to the absolute value function), for any ''x''0 in the domain of the function one can draw a line which goes through the point (''x''0, ''f''(''x''0)) and which is everywhere either touching or below the graph of ''f''. The slope of such a line is called a ''subderivative'' (because the line is under the graph of ''f''). Definition Rigorously, a ''subder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Vector
In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector (often a spatial vector) of length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex, or "hat", as in \hat (pronounced "v-hat"). The term ''direction vector'', commonly denoted as d, is used to describe a unit vector being used to represent spatial direction and relative direction. 2D spatial directions are numerically equivalent to points on the unit circle and spatial directions in 3D are equivalent to a point on the unit sphere. The normalized vector û of a non-zero vector u is the unit vector in the direction of u, i.e., :\mathbf = \frac where , u, is the norm (or length) of u. The term ''normalized vector'' is sometimes used as a synonym for ''unit vector''. Unit vectors are often chosen to form the basis of a vector space, and every vector in the space may be written as a linear combination of unit vectors. Orthogonal coordinates Cartesian coordinates Unit vectors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |